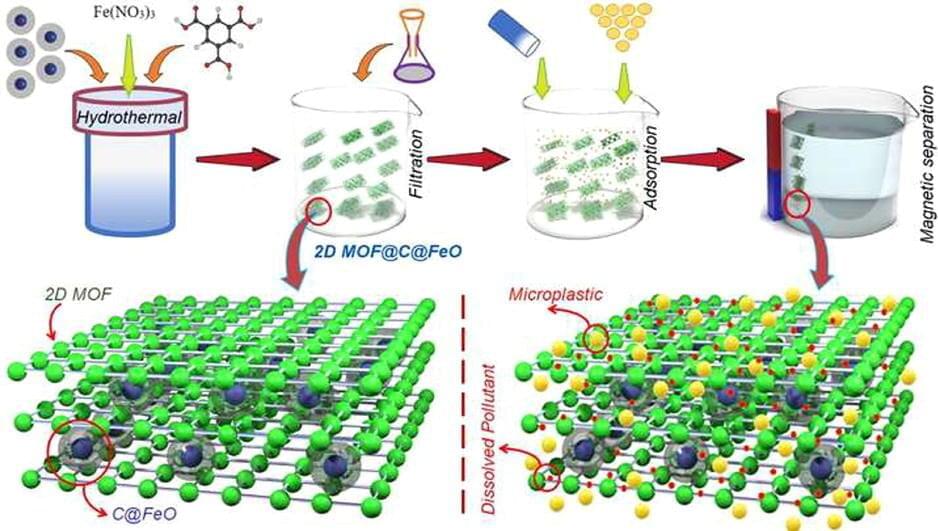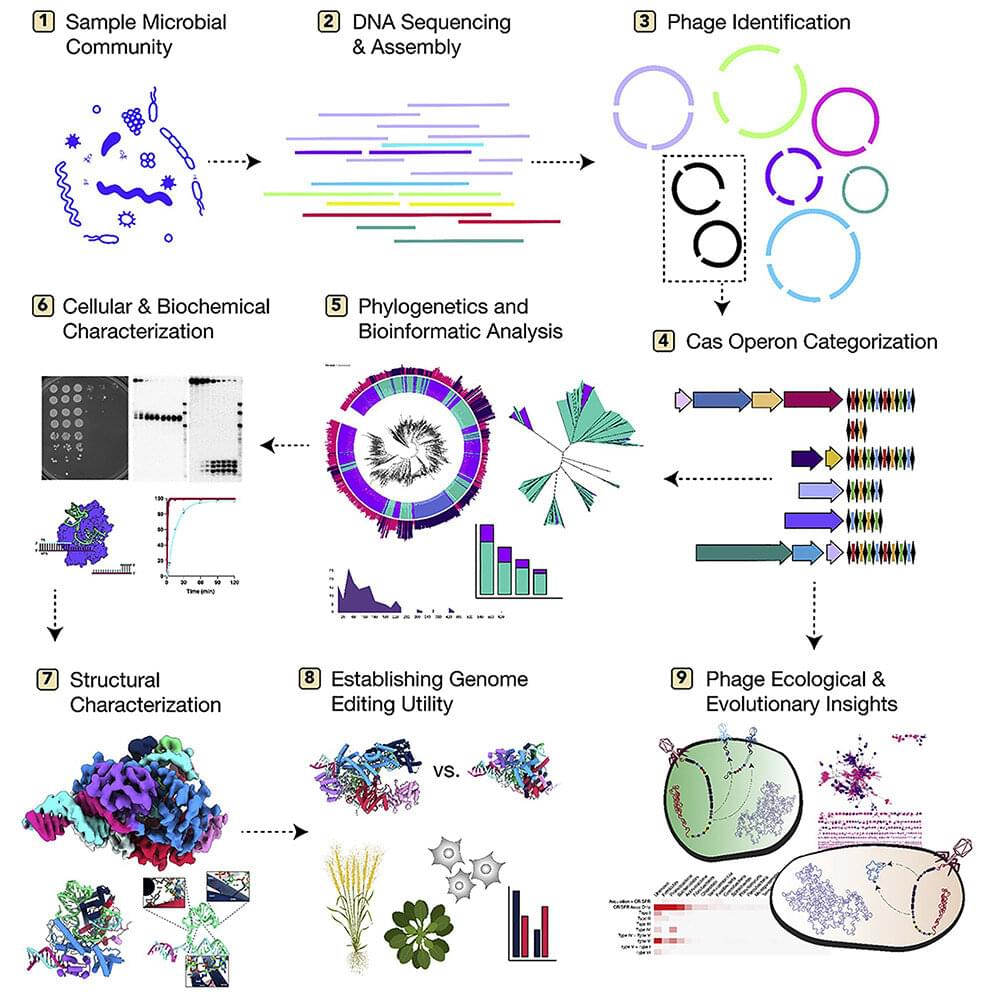
A team of researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, and University of California, Los Angeles, working with a colleague from Vilnius University, has found evidence of thousands of phages with DNA strands that should allow them to conduct gene editing on other viruses or bacteria. Their paper has been published in the open-access journal Cell.
In 2012, some of the researchers on this same team discovered that CRISPR-Cas9 could be programmed using RNA to edit targeted DNA strands from other organisms (and won a Nobel prize for it). Their work emerged from findings that many types of bacteria use CRISPR-Cas systems to defend against viral attacks. Using such systems, bacteria can cut and remove strands of DNA from viruses and store them in their own genomes to combat the same viral strain should it attack again.
Since that time, researchers have found that some viruses have similar machinery, but it was deemed to be rare. In this new effort, the researchers sought to determine actual prevalence.