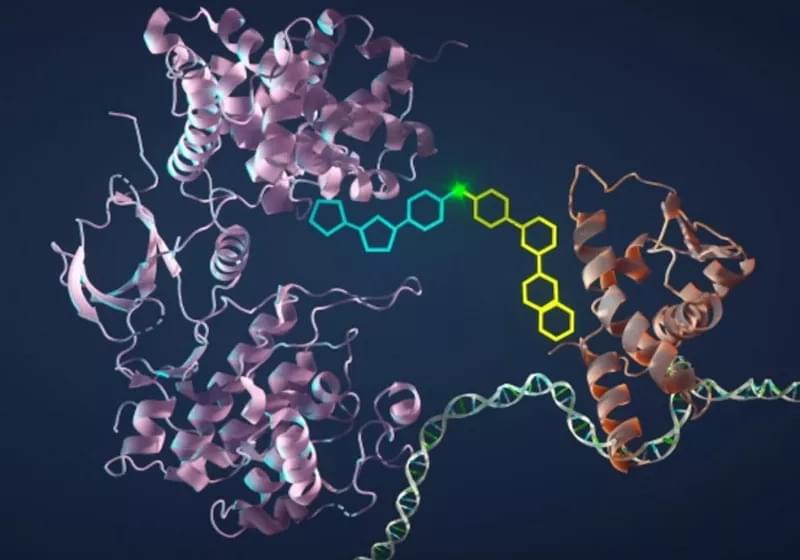
The researchers’ recently published study describes a way to re-activate apoptosis in mutated cells, which would amount to forcing cancer to self-destruct through a bioengineered, bonding molecule.
Gerald Crabtree, one of the study’s authors and a professor of development biology, said he had the idea while hiking through Kings Mountain, California, during the pandemic period. The new compound would have to bind two proteins which already exist in the cancerous cells, turning apoptosis back on and making the cancer kill itself.
“We essentially want to have the same kind of specificity that can eliminate 60 billion cells with no bystanders,” Crabtree said, so that no cell gets destroyed if it isn’t the proper target of this new killing mechanism. The two proteins in question are known as BCL6, an oncogene which suppresses apoptosis-promoting genes in the B-cell lymphoma, and CDK9, an enzyme that catalyzes gene activation instead.