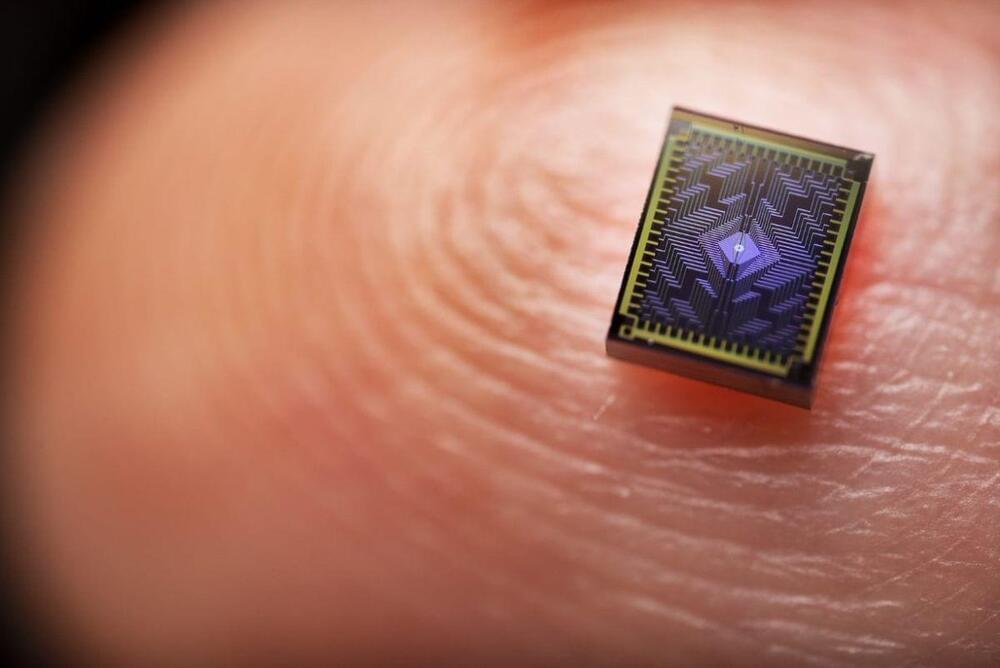
Intel announced the next step on its road to quantum with the release of its latest quantum chip, a 12-qubit, silicon-based chip the company is calling “Tunnel Falls”. No, no, it’s okay, you can keep those greenbacks in your wallet: Intel isn’t in the commercialization phase yet. Instead, Tunnel Falls is meant to be a research test chip: it’s still a stepping stone towards the actual Quantum Processing Units of the future. Hopefully, those will be more like Intel’s own Tunnel Falls than Iran’s Amazon-based “quantum computing” technology.
“Tunnel Falls is Intel’s most advanced silicon spin qubit chip to date and draws upon the company’s decades of transistor design and manufacturing expertise. The release of the new chip is the next step in Intel’s long-term strategy to build a full-stack commercial quantum computing system. While there are still fundamental questions and challenges that must be solved along the path to a fault-tolerant quantum computer, the academic community can now explore this technology and accelerate research development.” says Jim Clarke, Intel’s director of Quantum Hardware.
While it may be underwhelming to know that Tunnel Falls is just a research test chip, it’s also an often overlooked necessity for any new technology. Before any work can be done within the quantum computers of the future, the algorithms, the learning and the how-to have to be started today. One issue with that is the difficulty in producing quantum computing hardware; there’s a reason such a small number of big companies — from Intel to Microsoft, IBM, IonQ, and Google — are actively developing quantum computing hardware.