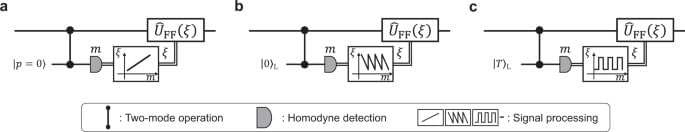
We have implemented a nonlinear quadrature measurement of \(\hat{p}+\gamma {\hat{x}}^{2}\) using the nonlinear electro-optical feedforward and non-Gaussian ancillary states. The nonlinear feedforward makes the tailored measurement classically nonlinear, while the ancillary state pushes the measurement into highly non-classical regime and determines the excess noise of the measurement. By using a non-Gaussian ancilla we have observed 10% reduction of the added noise relative to the use of vacuum ancillary state, which is consistent with the amount of nonlinear squeezing in the ancilla. Higher reduction of the noise can be realized in the near future by a better approximation of the CPS using a superposition of higher photon number states38,42. We can now create broadband squeezed state of light beyond 1 THz8,9 and can make a broadband amplitude measurement on it with 5G technology beyond 40 GHz10, as well as a broadband photon-number measurement beyond 10 GHz11. Furthermore, the nonlinear feedforward presented here can be compatible with these technologies if an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) is developed based on the FPGA board presented here. By using such technologies we can efficiently create non-Gaussian ancillary states with large nonlinear squeezing by heralding schemes36,43 even when the success rate is very low. It is because we can repeat heralding beyond 10 GHz and can compensate for the very low success rate.
When supplied with such high-quality ancillary state, this nonlinear measurement can be directly used in the implementation of the deterministic non-Gaussian operations required in the universal quantum computation. Our experiment is a key milestone for this development as it versatilely encompasses all the necessary elements for universal manipulation of the cluster states. Furthermore, this method is extendable to multiple ancillary states case in implementation of the higher-order quantum non-Gaussianity44 and multi-mode quantum non-Gaussianity45.
Our experiment demonstrates an active, flexible, and fast nonlinear feedforward technique applicable to traveling quantum states localized in time. If the nonlinear feedforward system is combined with the cluster states13,14 and GKP states19, all operations required for large-scale fault-tolerant universal quantum computation can be implemented in the same manner. As such, we have demonstrated a key technology needed for optical quantum computing, bringing it closer to reality.