In 2018, a discovery in materials science sent shock waves throughout the community. A team showed that stacking two layers of graphene at a precise magic angle turned it into a superconductor, says Ritesh Agarwal of the University of Pennsylvania. This sparked the field of twistronics, revealing that twisting layered materials could unlock extraordinary material properties.
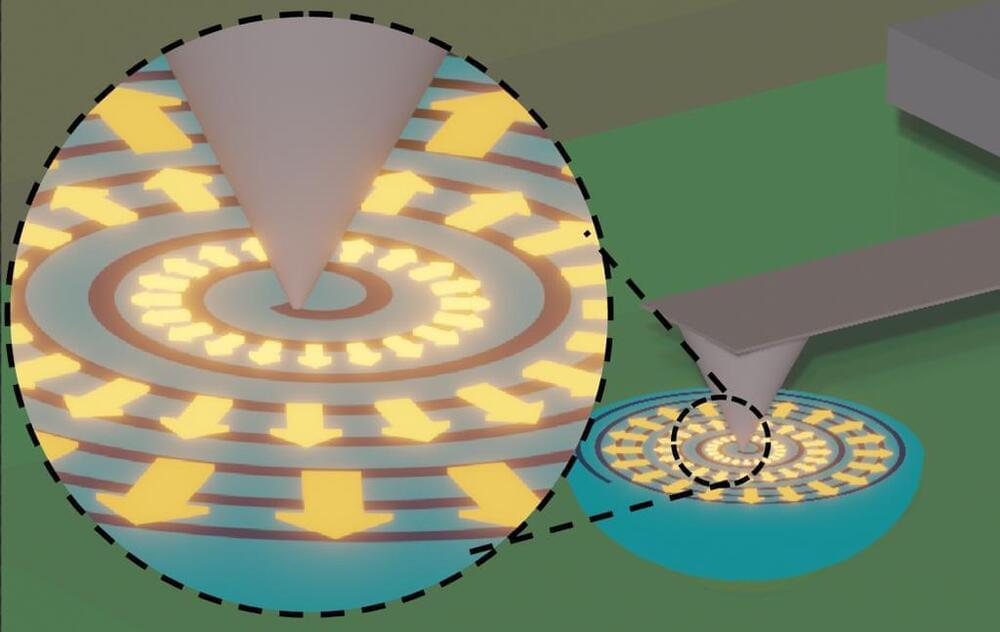
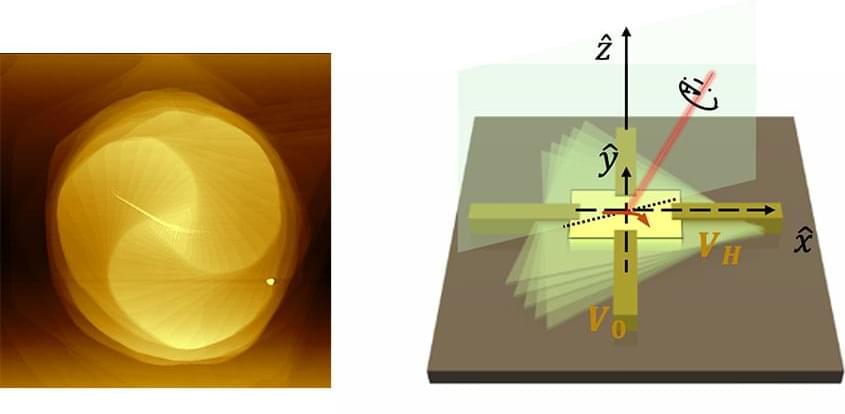
Building on this concept, Agarwal, Penn theoretical physicist Eugene Mele, and collaborators have taken twistronics into new territory. In a study published in Nature (“Opto-twistronic Hall effect in a three-dimensional spiral lattice”), they investigated spirally stacked tungsten disulfide (WS 2) crystals and discovered that, by twisting these layers, light could be used to manipulate electrons. The result is analogous to the Coriolis force, which curves the paths of objects in a rotating frame, like how wind and ocean currents behave on Earth.
“What we discovered is that by simply twisting the material, we could control how electrons move,” says Agarwal, Srinivasa Ramanujan Distinguished Scholar in the School of Engineering and Applied Science. This phenomenon was particularly evident when the team shined circularly polarized light on WS 2 spirals, causing electrons to deflect in different directions based on the material’s internal twist.