Jan 28, 2017
The Ethics of Organoids: Scientists Weigh in on New Mini-Organs
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: biotech/medical, ethics, neuroscience
Growing organs in the lab is an enduring sci-fi trope, but as stem cell technology brings it ever closer to reality, scientists are beginning to contemplate the ethics governing disembodied human tissue.
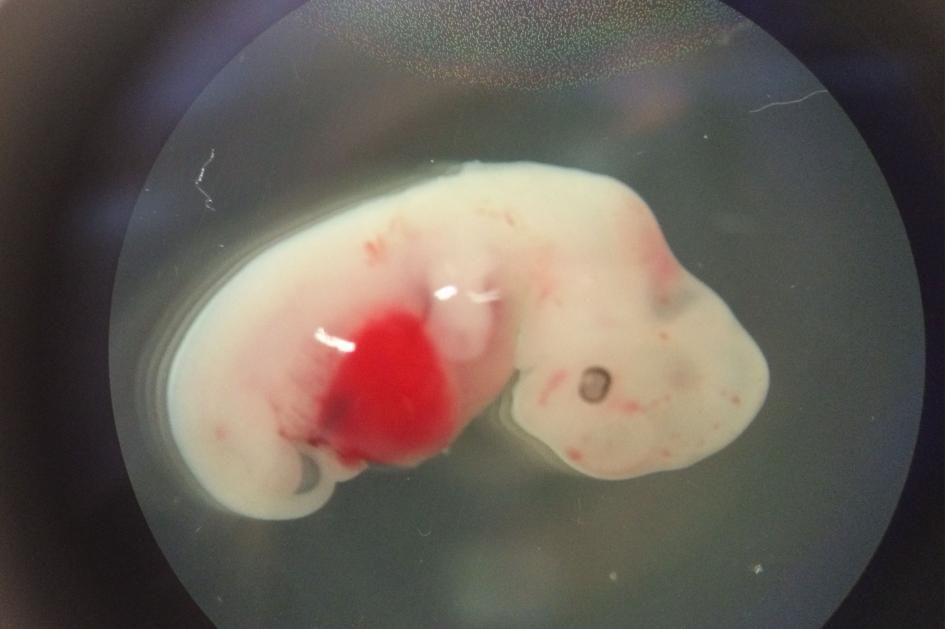
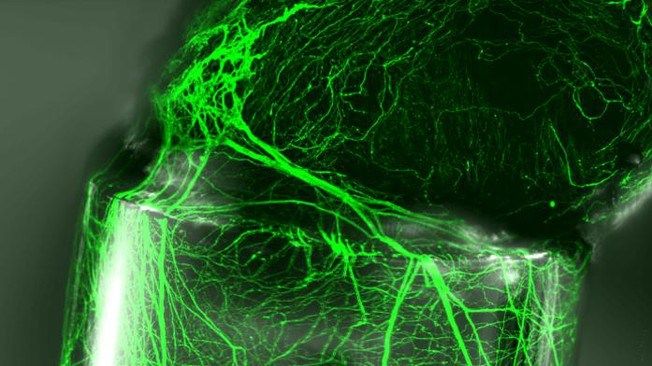
So-called organoids have now been created from gut, kidney, pancreas, liver and even brain tissue. Growing these mini-organs has been made possible by advances in stem cell technology and the development of 3D support matrices that allow cells to develop just like they would in vivo.
Unlike simple tissue cultures, they exhibit important structural and functional properties of organs, and many believe they could dramatically accelerate research into human development and disease.
Continue reading “The Ethics of Organoids: Scientists Weigh in on New Mini-Organs” »