Apr 15, 2017
Affordable deep space missions using asteroids
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: government, mathematics, physics, space
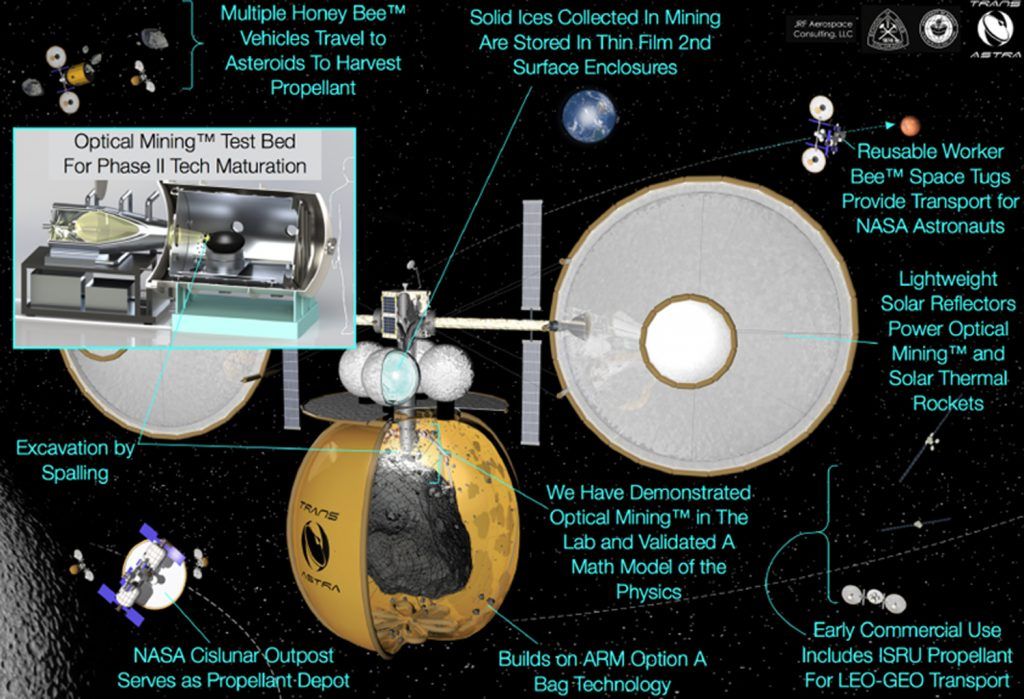
Phase 1 work demonstrated Optical Mining in the laboratory and performed mission and systems analysis of the application of Optical Mining to human exploration missions. Their mission analysis showed that the most accessible Near Earth Objects (NEOs) can be used to provide NASA with mission consumables for human exploration in deep space with the potential of saving up to $10 billion per year or $150 billion over the 15 year operational life cycle of a human exploration program. This savings alone would be enough to transform NASA’s vision of human exploration from being unaffordable to being affordable within budgets that Congress can approve. Phase 1 technical work included a full scale (8 kW) Optical Mining demonstration using a high fidelity CI-type asteroid simulant in vacuum using sunlight from a 10 meter diameter solar concentrator without mechanical contact or downforce. This work confirmed our physics based mathematical model of the excavation and volatile extraction process and scalability of results from 36 prior, small scale (≈ 1 cm diameter) demonstrations and tests.
Phase 2 work will complete mission and system analysis of the application of Optical Mining to an exciting program of human exploration and we will mature the technology of Optical Mining to the point at which NASA can baseline this approach for an affordable program of human exploration. Our mission studies will address the production via Optical Mining missions to extract and retrieve resources, consumable processing, storage, and application of consumables to human exploration mission in cislunar, NEO and Martian space. The mission studies will be tightly coupled with our laboratory work. Laboratory work will include the development and integration of a 30 kW Optical Mining test apparatus in our laboratory and integration with our high quality vacuum chamber for a test program involving Optical Mining.