Page 10318
Jan 12, 2017
Craig Venter — How Genome Sequencing Can Fight Aging
Posted by Montie Adkins in categories: biotech/medical, life extension
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G6m2tmKlJWQ
A genome sequenced every 15 minutes.
Filmed November 2016.
Continue reading “Craig Venter — How Genome Sequencing Can Fight Aging” »
Jan 12, 2017
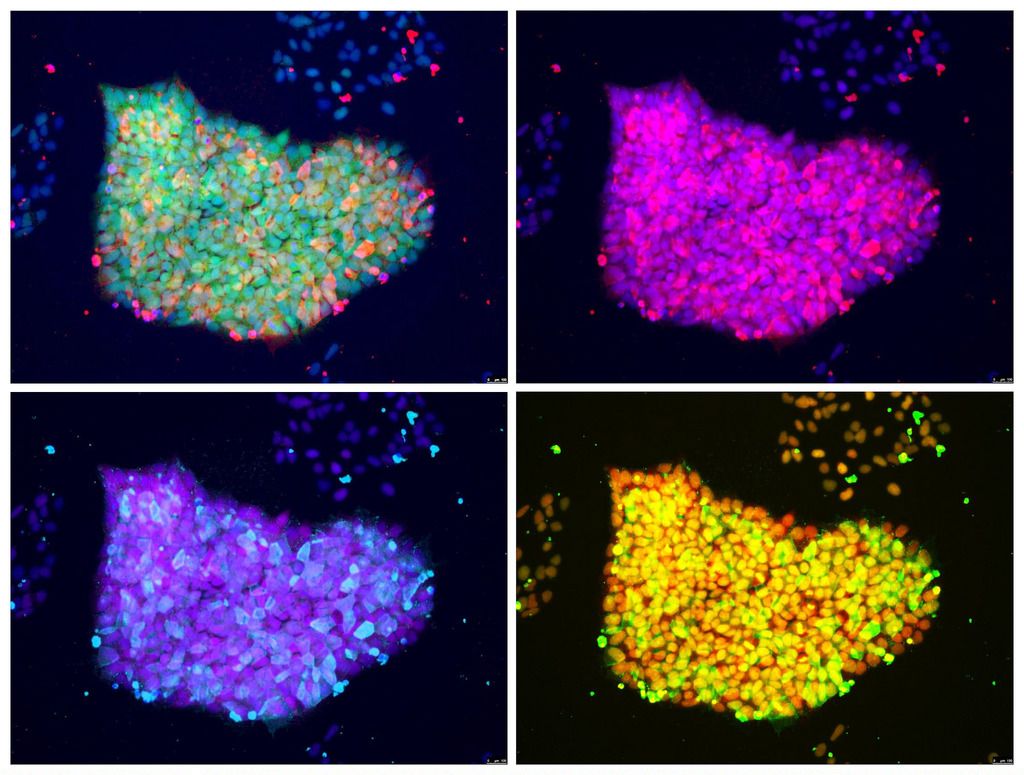
Donor Age Shows Up In Induced Stem Cells
Posted by Steve Hill in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
Epigenetic changes are not all reset with iPS thankfully science has recently demonstrated a technique for reversing that too. The future is looking bright for stem cell quality improvements.
Reprogramming stem cells back to a functionally younger state is not a pefect process and epigenetic changes and mutations remain in place tainting the cells and reducing their quality.
Scientists working in the stem cell field will no doubt be finding ways to work around this and indeed recent work at SALK could reset epigenetic changes in these cells so solutions are within reach in the next few years.
Continue reading “Donor Age Shows Up In Induced Stem Cells” »
Jan 12, 2017
New Robot Can Operate on Eyes With More Accuracy Than a Human Surgeon
Posted by Shane Hinshaw in categories: biotech/medical, robotics/AI
In Brief
- This two-armed, teleoperated robot can precisely move in a 10 mm space, giving it the ability to operate on eyes more accurately and with less potential for error than human surgeons.
- Axsis is just one of a growing number of robot surgeons that are changing how doctors treat patients.
Jan 12, 2017
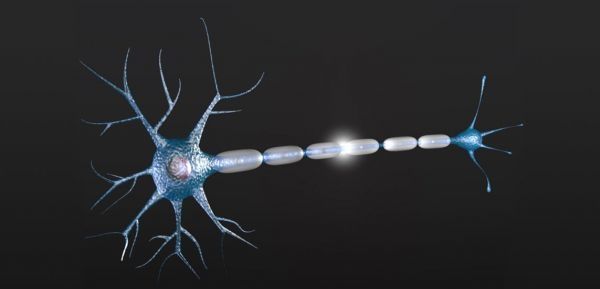
Reprogramming Stem Cells Could Soon Lead Us to a World Without Paralysis
Posted by Shane Hinshaw in categories: biotech/medical, genetics, neuroscience
Motor neurons are vital cells that facilitate muscle contraction and also affect sensation. In diseases like ALS and spinal muscular atrophy, motor cells are plagued with mutations that cause degrees of paralysis and pain in patients. In a study detailed in Cell Stem Cell, scientists developed a mechanism to directly reprogram stem cells into motor neurons.
Cell reprogramming is a novel exploration in medical studies that could treat numerous diseases by growing the body’s own stem cells into healthy cells. The mechanism of reprogramming, however, has just begun to be understood.
The researchers elucidated a new pathway for cell reprogramming by analyzing gene transcription in mice. As established by previous studies, reprogramming is brought about by a series of transcriptions, AKA, how the genes control the expression of other genes.
Continue reading “Reprogramming Stem Cells Could Soon Lead Us to a World Without Paralysis” »
Jan 12, 2017
Healing Human Flesh: NASA’s New High-Tech Gauze Could Accelerate Wound Recovery
Posted by Shane Hinshaw in categories: biotech/medical, futurism

In Brief
- NASA’s Technology Transfer Program may have given us the future of wound care with its electroactive polymer which speeds up healing time.
- NASA continues to fuel scientific progress across many disciplines, continued investment in the sciences will lead to more unexpected technology with untold applications.
Jan 12, 2017
New model could help scientists design materials for artificial photosynthesis
Posted by Shane Hinshaw in categories: solar power, sustainability
Plants and other photosynthetic organisms use a wide variety of pigments to absorb different wavelengths of light. MIT researchers have now developed a theoretical model to predict the spectrum of light absorbed by aggregates of these pigments, based on their structure.
The new model could help guide scientists in designing new types of solar cells made of organic materials that efficiently capture light and funnel the light-induced excitation, according to the researchers.
“Understanding the sensitive interplay between the self-assembled pigment superstructure and its electronic, optical, and transport properties is highly desirable for the synthesis of new materials and the design and operation of organic-based devices,” says Aurelia Chenu, an MIT postdoc and the lead author of the study, which appeared in Physical Review Letters on Jan. 3.
Continue reading “New model could help scientists design materials for artificial photosynthesis” »
Jan 12, 2017
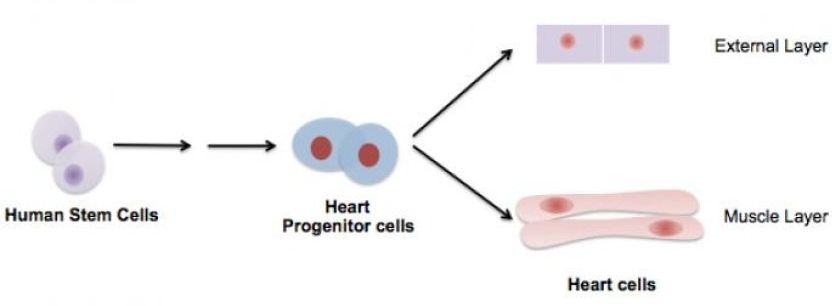
Stem cells used to regenerate the external layer of a human heart
Posted by Shane Hinshaw in categories: biotech/medical, engineering
A process using human stem cells can generate the cells that cover the external surface of a human heart — epicardium cells — according to a multidisciplinary team of researchers.
“In 2012, we discovered that if we treated human stem cells with chemicals that sequentially activate and inhibit Wnt signaling pathway, they become myocardium muscle cells,” said Xiaojun Lance Lian, assistant professor of biomedical engineering and biology, who is leading the study at Penn State. Myocardium, the middle of the heart’s three layers, is the thick, muscular part that contracts to drive blood through the body.
The Wnt signaling pathway is a group of signal transduction pathways made of proteins that pass signals into a cell using cell-surface receptors.
Continue reading “Stem cells used to regenerate the external layer of a human heart” »
Jan 12, 2017
New Stem Cell Treatment Can Restore Sight to the Blind
Posted by Shane Hinshaw in category: biotech/medical
In Brief
- Researchers were able to prevent immune system rejection of stem cells, blocking the usual immune responses that trigger rejection of the stem cells by the recipient’s body.
- Using this technique, they were able to restore vision in mice as far out as nine months following the injection of these cells.
Jan 12, 2017
Immune System, part 2: Crash Course A&P #46
Posted by Steve Hill in category: biotech/medical

Part 2 of the immune system explained in this easy going pop culture style series.
In the penultimate episode of Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology, Hank explains your adaptive immune system. The adaptive immune system’s humoral response guards extracellular terrain against pathogens. Hank also explains B cells, antibodies, and how vaccines work.
Continue reading “Immune System, part 2: Crash Course A&P #46” »