Scientists in Austria have developed wafer-thin tattoo electrodes for recording brain activity, which are also “dry” and therefore do not require a gel medium to function.

It can be a gastrointestinal disease causing only diarrhea and abdominal pain. It can cause symptoms that may be confused with a cold or the flu. It can cause pinkeye, a runny nose, loss of taste and smell, muscle aches, fatigue, diarrhea, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, whole-body rashes, and areas of swelling and redness in just a few spots.
In a more severe disease, doctors have also reported people having heart rhythm problems, heart failure, kidney damage, confusion, headaches, seizures, Guillain-Barre syndrome, and fainting spells, along with new sugar control problems.
It’s not just a fever and coughing, leading to shortness of breath, like everyone thought at first.
Mathematicians were shocked when a graduate student worked through a decades-old problem in just a few days. University of Texas at Austin mathematician Lisa Piccirillo learned about the Conway knot—a knot with 11 crossings, so named for the late mathematician John Horton Conway—from a colleague’s talk during a conference. Within a week, she’d solved the longstanding problem of whether or not the special knot was slice. (It’s not.)

Maximizing the protection of life on Earth requires knowledge of the global patterns of biodiversity at multiple dimensions, from genetic diversity within species, to species and ecosystem diversity. Yet, the lack of genetic sequences with geographic information at global scale has so far hindered our ability to map genetic diversity, an important, but hard to detect, biodiversity dimension.
In a new study, researchers from the Universities of Copenhagen and Adelaide have collected and georeferenced a massive amount of genetic data for terrestrial mammals and evaluated long-standing theories that could explain the global distribution of genetic diversity. They found that regions of the world rich in deep evolutionary history, such as Northern Andes, the Eastern Arc Mountains, Amazonia, the Brazilian Atlantic forest, the central America jungles, sub-Saharan Africa and south-eastern Asia are also strongholds of genetic diversity. They also show that the relatively stable climate in these regions during the past 21’000 years contributes significantly to this intraspecific richness.
“Genetic diversity within species is a critical component of biodiversity, playing two important roles at the same time. It reflects species evolutionary history and defines their capacity to adapt under future environmental change. However, and despite the predictions of major biodiversity theories, the actual global distribution of genetic diversity remained, so far, a mystery. Recent collective efforts to populate public databases with genetic sequences and their localities allowed us to evaluate these theories and generate the first global maps of genetic diversity in terrestrial mammal assemblages”, says Spyros Theodoridis, Postdoctoral Researcher at the Center for Macroecology, Evolution and Climate, GLOBE Institute, and lead author of the study.



Zhou Yi was terrible at math. He risked never getting into college. Then a company called Squirrel AI came to his middle school in Hangzhou, China, promising personalized tutoring. He had tried tutoring services before, but this one was different: instead of a human teacher, an AI algorithm would curate his lessons. The 13-year-old decided to give it a try. By the end of the semester, his test scores had risen from 50% to 62.5%. Two years later, he scored an 85% on his final middle school exam.
“I used to think math was terrifying,” he says. “But through tutoring, I realized it really isn’t that hard. It helped me take the first step down a different path.”

Molecular dynamics is at the point of simulating bulk matter – but don’t expect it to predict the future.
The TV series Devs took as its premise the idea that a quantum computer of sufficient power could simulate the world so completely that it could project events accurately back into the distant past (the Crucifixion or prehistory) and predict the future. At face value somewhat absurd, the scenario supplied a framework on which to hang questions about determinism and free will (and less happily, the Many Worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics).
Quite what quantum computers will do for molecular simulations remains to be seen, but the excitement about them shouldn’t eclipse the staggering advances still being made in classical simulation. Full ab initio quantum-chemical calculations are very computationally expensive even with the inevitable approximations they entail, so it has been challenging to bring this degree of precision to traditional molecular dynamics, where molecular interactions are still typically described by classical potentials. Even simulating pure water, where accurate modelling of hydrogen bonding and the ionic disassociation of molecules involves quantum effects, has been tough.
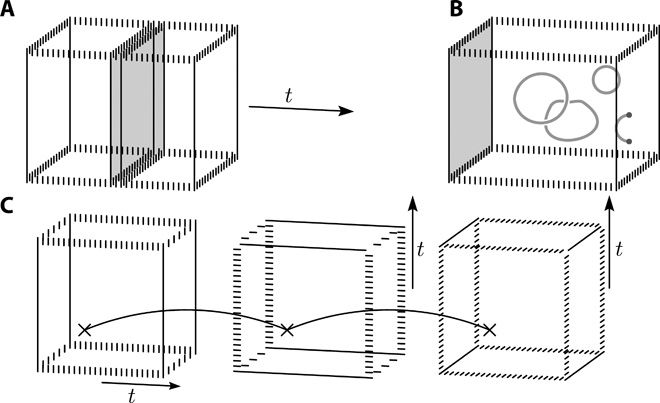
Fault-tolerant logic gates will consume a large proportion of the resources of a two-dimensional quantum computing architecture. Here we show how to perform a fault-tolerant non-Clifford gate with the surface code; a quantum error-correcting code now under intensive development. This alleviates the need for distillation or higher-dimensional components to complete a universal gate set. The operation uses both local transversal gates and code deformations over a time that scales with the size of the qubit array. An important component of the gate is a just-in-time decoder. These decoding algorithms allow us to draw upon the advantages of three-dimensional models using only a two-dimensional array of live qubits. Our gate is completed using parity checks of weight no greater than four. We therefore expect it to be amenable with near-future technology. As the gate circumvents the need for magic-state distillation, it may reduce the resource overhead of surface-code quantum computation considerably.
A scalable quantum computer is expected to solve difficult problems that are intractable with classical technology. Scaling such a machine to a useful size will necessarily require fault-tolerant components that protect quantum information as the data is processed (1–4). If we are to see the realization of a quantum computer, its design must respect the constraints of the quantum architecture that can be prepared in the laboratory. In many cases, for instance, superconducting qubits (5–7), this restricts us to two-dimensional architectures.
Leading candidate models for fault-tolerant quantum computation are based on the surface code (3, 8) due to its high threshold (9) and multitude of ways of performing Clifford gates (10). Universal quantum computation is possible if this gate set is supplemented by a non-Clifford gate. Among the most feasible approaches to realize a non-Clifford gate is by the use of magic-state distillation (11). However, this is somewhat prohibitive as a large fraction of the resources of a quantum computer will be expended by these protocols (12, 13).

High-quality data is the fuel that powers AI algorithms. Without a continual flow of labeled data, bottlenecks can occur and the algorithm will slowly get worse and add risk to the system.
It’s why labeled data is so critical for companies like Zoox, Cruise and Waymo, which use it to train machine learning models to develop and deploy autonomous vehicles. That need is what led to the creation of Scale AI, a startup that uses software and people to process and label image, lidar and map data for companies building machine learning algorithms. Companies working on autonomous vehicle technology make up a large swath of Scale’s customer base, although its platform is also used by Airbnb, Pinterest and OpenAI, among others.
The COVID-19 pandemic has slowed, or even halted, that flow of data as AV companies suspended testing on public roads — the means of collecting billions of images. Scale is hoping to turn the tap back on, and for free.