Jan 29, 2016
Biotechnology, synthetic biology keys to humans colonizing other planets
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: alien life, biotech/medical, food, genetics, particle physics, space travel, sustainability
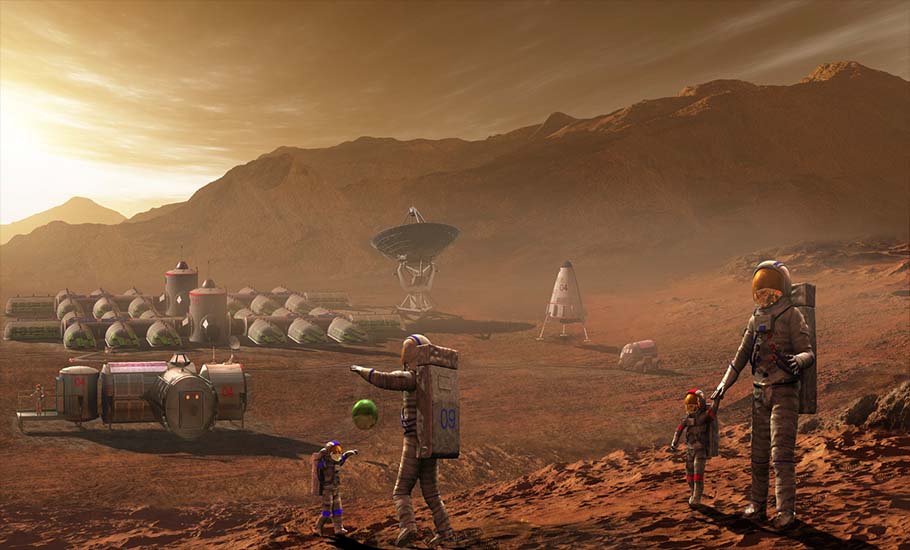
Over the last 12,000 years or so, human civilization has noticeably reshaped the Earth’s surface. But changes on our own planet will likely pale in comparison when humans settle on other celestial bodies. While many of the changes on Earth over the centuries have been related to food production, by way of agriculture, changes on other worlds will result, not only from the need for on-site production of food, but also for all other consumables, including air.
As vital as synthetic biology will be to the early piloted missions to Mars and voyages of exploration, it will become indispensable to establish a long-term human presence off-Earth, namely colonization. That’s because we’ve evolved over billions of years to thrive specifically in the environments provides by our home planet.
Our physiology is well-suited to Earth’s gravity and its oxygen-rich atmosphere. We also depend on Earth’s magnetic field to shield us from intense space radiation in the form of charged particles. In comparison, Mars currently has no magnetic field to trap particle radiation and an atmosphere that is so thin that any shielding against other types of space radiation is negligible compared with the protection that Earth’s atmosphere affords. At the Martian surface, atmospheric pressure never gets above 7 millibars. That’s like Earth at an altitude of about 27,000 m (89,000 ft), which is almost the edge of space. And it’s not like the moon is a better option for us since it has no atmosphere at all.