Quantum computing requires meticulously prepared hardware and big budgets, but cloud-based solutions could make the technology available to broader business audiences Several tech giants are racing to achieve “quantum supremacy”, but reliability and consistency in quantum output is no simple trick Covid-19 has prompted some researchers to look at how quantum computing could mitigate future pandemics with scientific precision and speed Quantum computing (QC) has been theorized for decades and has evolved rapidly over the last few years. An escalation in spend and development has seen powerhouses IBM, Microsoft, and Google race for ‘quantum supremacy’ — whereby quantum reliably and consistently outperforms existing computers. But do quantum computers remain a sort of elitist vision of the future or are we on course for more financially and infrastructurally viable applications across industries?
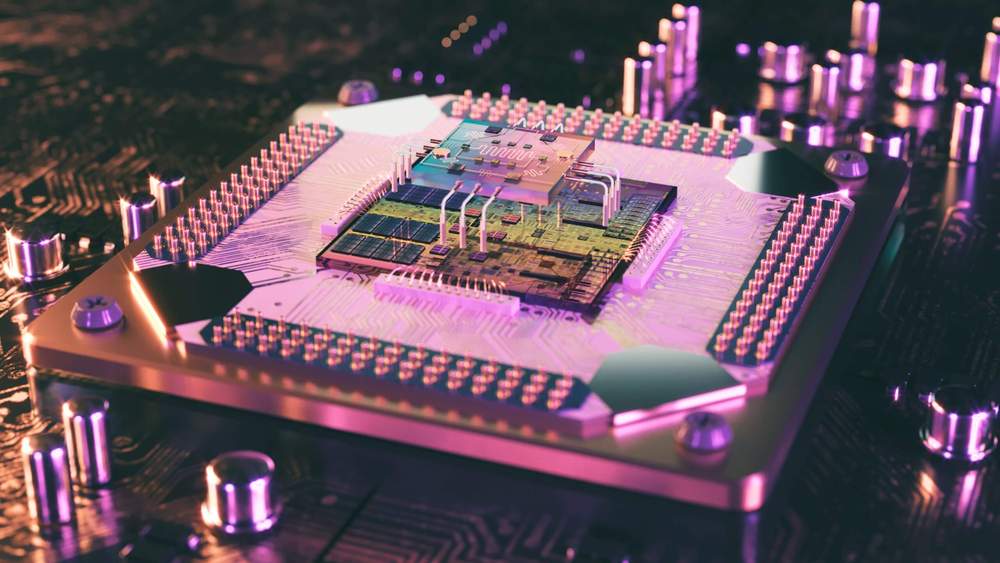
Getting to grips with qubits How much do you know? Ordinary computers (even supercomputers) deploy bits, and these bits comprise of traditional binary code. Computer processes – like code – are made up of countless combinations of 0’s and 1’s. Quantum computers, however, are broken down into qubits. Qubits are capable of ‘superpositions’: effectively adopting both 1 and 0 simultaneously, or any space on the spectrum between these two formerly binary points. The key to a powerful, robust, and reliable quantum computer is more qubits. Every qubit added exponentially increases the processing capacity of the machine.
Qubits and the impact of the superposition give quantum computers the ability to process large datasets within seconds, doing what it would take humans decades to do. They can decode and deconstruct, hypothesize and validate, tackling problems of absurd complexity and dizzying magnitude — and can do so across many different industries.
Wherein lies the issue then? Quantum computing for everybody! We’re still a way off – the general consensus being, it’s 5 years, at least, before this next big wave of computing is seen widely across industries and use cases, unless your business is bustling with the budgets of tech giants like Google, IBM, and the like. But expense isn’t the only challenge.
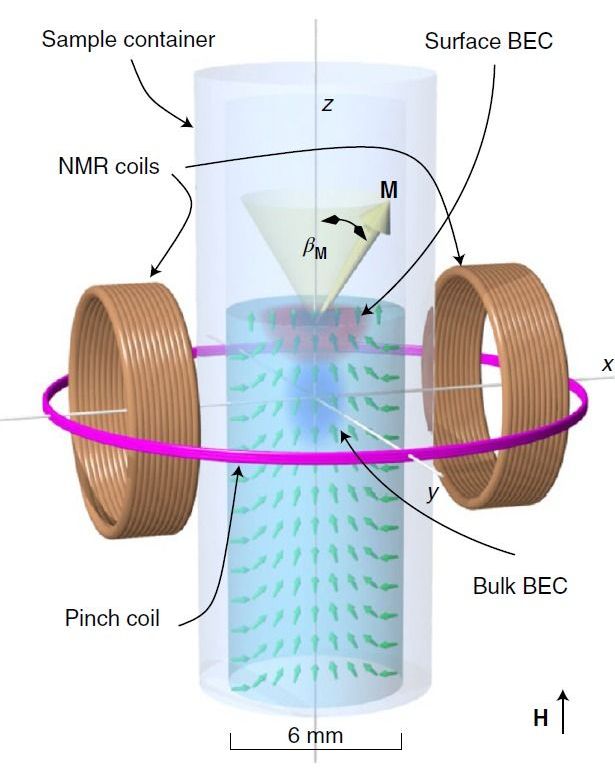
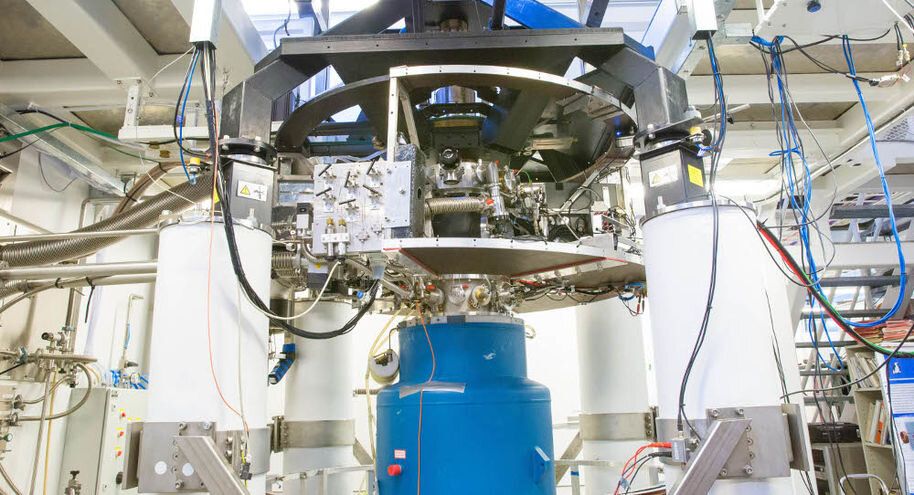
Frail and demanding — the quantum hardware Quantum computers are interminably intricate machines. It doesn’t take much at all to knock a qubit out of the delicate state of superposition. They’re powerful, but not reliable. The slightest interference or frailty leads to high error rates in quantum processing, slowing the opportunity for more widespread use, and rendering ‘quantum supremacy’ a touch on the dubious side.
Quantum computing (QC) has been theorized for decades and has evolved rapidly over the last few years. An escalation in spend and development has seen powerhouses IBM, Microsoft, and Google race for ‘quantum supremacy’ — whereby quantum reliably and consistently outperforms existing computers. But do quantum computers remain a sort of elitist vision of the future or are we on course for more financially and infrastructurally viable applications across industries?