Australian scientists have developed a new cryogenic computer system called Gooseberry which has potential for scaling up quantum computers from dozens to thousands of qubits.
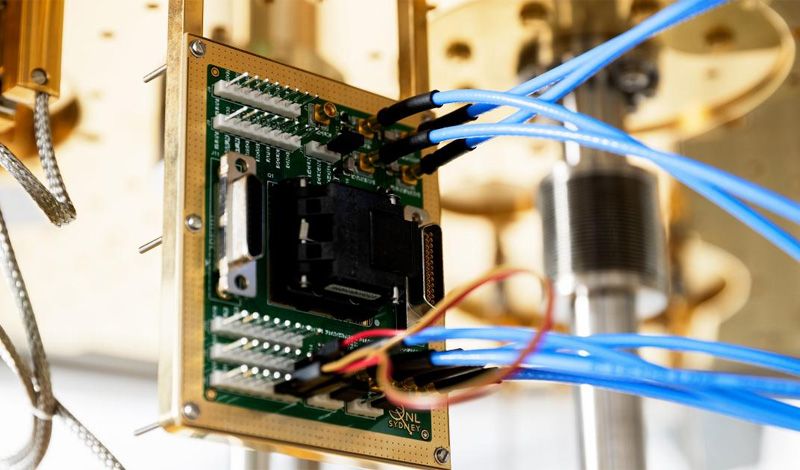



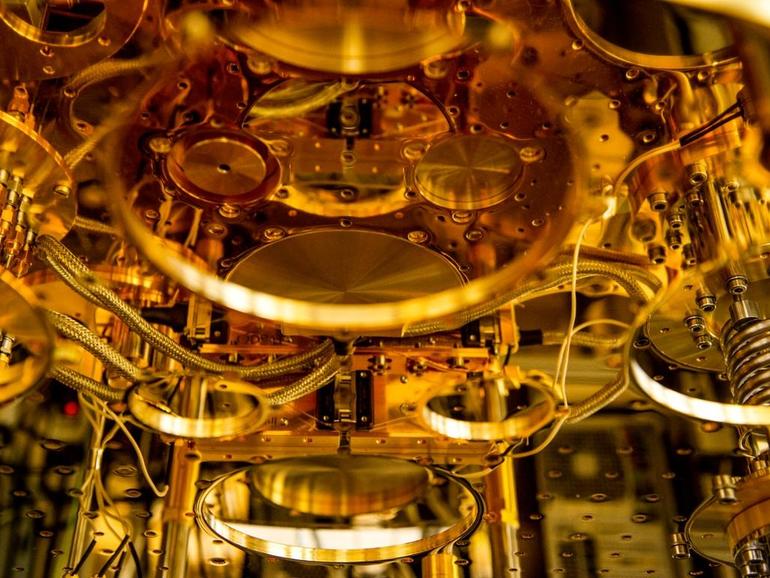

Circa 2013 o.o
Quantum entanglement, one of the odder aspects of quantum theory, links the properties of particles even when they are separated by large distances. When a property of one of a pair of entangled particles is measured, the other “immediately” settles down into a state compatible with that measurement. So how fast is “immediately”? According to research by Prof. Juan Yin and colleagues at the University of Science and Technology of China in Shanghai, the lower limit to the speed associated with entanglement dynamics – or “spooky action at a distance” – is at least 10000 times faster than light.
Despite playing a vital role in the development of quantum theory, Einstein felt philosophically at odds with its description of how the universe works. His famous quote that “God does not play dice” hints at his level of discomfort with the role of probability in quantum theory. He believed there exists another level of reality in which all of physics would be deterministic, and that quantum mechanics would turn out to be a description that emerges from the workings of that level – rather like a traffic jam emerges from the independent motions of a large number of cars.
In 1935 Einstein and his coworkers discovered quantum entanglement lurking in the equations of quantum mechanics, and realized its utter strangeness. This lead to the EPR paradox introduced by Einstein, Poldolsky and Rosen. The EPR paradox stated that the only ways of explaining the effects of quantum entanglement were to assume the universe is nonlocal, or that the true basis of physics is hidden (otherwise known as a hidden-variable theory). Nonlocality in this case means that events occurring to entangled objects are linked even when the events cannot communicate through spacetime, spacetime having the speed of light as a limiting velocity. Nonlocality is also known as spooky action at a distance (Einstein’s phrase).
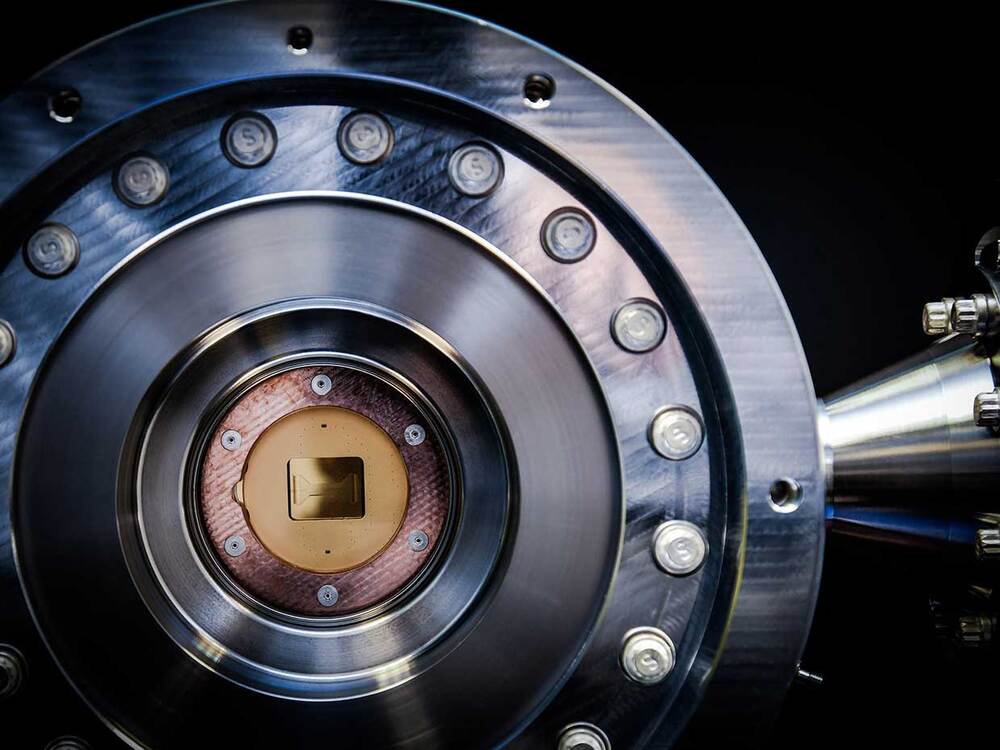

O., o circa 2020.
Last week, Honeywell’s Quantum Solutions division released its first commercial quantum computer: a system based on trapped ions comprising 10 qubits. The H1, as it’s called, is actually the same ion trap chip the company debuted as a prototype, but with four additional ions. The company revealed a roadmap that it says will rapidly lead to much more powerful quantum computers. Separately, a competitor in ion-trap quantum computing, Maryland-based startup IonQ, unveiled a 32-qubit ion computer last month.



Quantum Encryption, Privacy Preservation, And Blockchains — Dr. Vipul Goyal, NTT Ltd. Cryptography & Information Security Labs
Dr Vipul Goyal is a senior scientist at NTT Research (a division of Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation, a telecommunications company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan.) and an Associate Professor in the Computer Science Department at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), where he is part of the Crypto group, the theory group, a core faculty at CyLab (CMU security and privacy institute) and the faculty advisor of CMU Blockchain Group.
Previously, Dr. Goyal was a researcher in the Cryptography and Complexity group at Microsoft Research, India.
Dr. Goyal received his PhD from the University of California, Los Angeles.
Dr. Goyal is broadly interested in all areas of cryptography with a particular focus on the foundations of cryptography. Currently his research topics include secure multi-party computation, non-malleable cryptography, and foundations of blockchains.