May 11, 2016
Scientists take a major leap toward a ‘perfect’ quantum metamaterial
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: electronics, nanotechnology, particle physics, quantum physics
Scientists have devised a way to build a “quantum metamaterial” — an engineered material with exotic properties not found in nature — using ultracold atoms trapped in an artificial crystal composed of light. The theoretical work represents a step toward manipulating atoms to transmit information, perform complex simulations or function as powerful sensors.
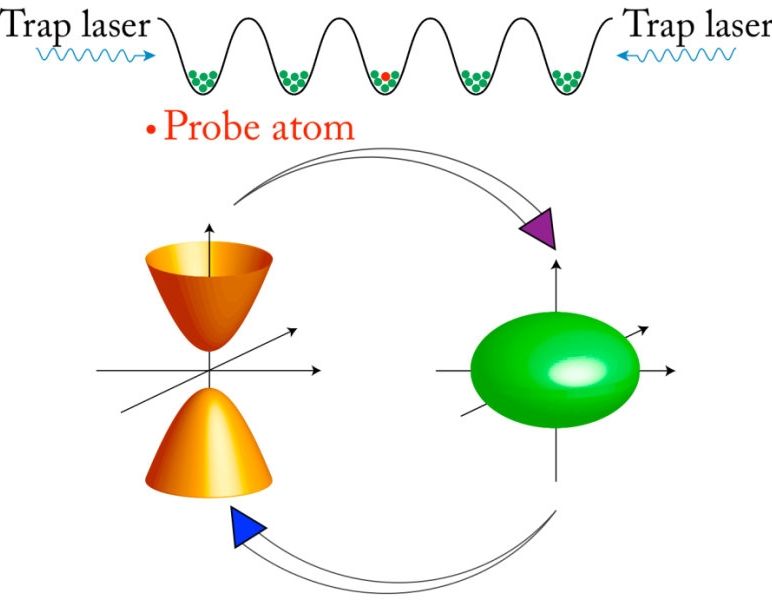
The research team, led by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley, proposes the use of an accordion-like atomic framework, or “lattice” structure, made with laser light to trap atoms in regularly spaced nanoscale pockets. Such a light-based structure, which has patterned features that in some ways resemble those of a crystal, is essentially a “perfect” structure — free of the typical defects found in natural materials.
Researchers believe they can pinpoint the placement of a so-called “probe” atom in this crystal of light, and actively tune its behavior with another type of laser light (near-infrared light) to make the atom cough up some of its energy on demand in the form of a particle of light, or photon.