Jun 22, 2021
Russia Wants To Send A Nuclear-Powered Spacecraft To Jupiter This Decade
Posted by Montie Adkins in categories: nuclear energy, satellites
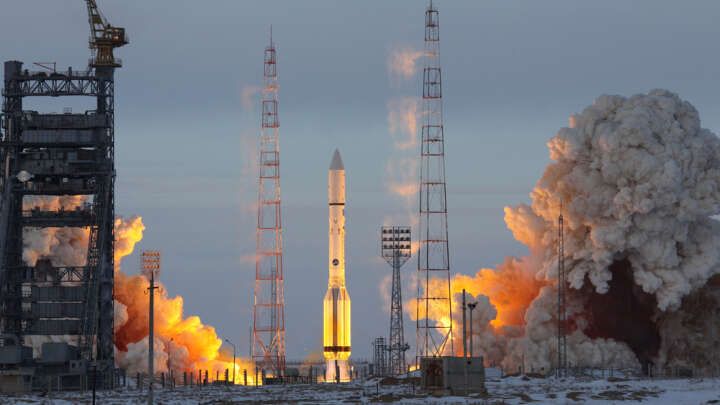
Russia is planning to send a nuclear-powered spacecraft to the grand gas giant of the Solar System, Jupiter, in 2030.
Roscosmos, Russia’s federal space agency, announced the plan for the mammoth 50-month journey last week. The journey will take it on a mini tour of the Solar System, taking pit stops around the Moon and Venus, dropping off spacecraft along its way, before heading on to Jupiter.
More specifically, a “space tug” with a nuclear-based transport and energy module dubbed Zeus will head towards the Moon where a spacecraft will separate from it. It will then pass by Venus to perform a gravity assist maneuver and drop off another spacecraft, before venturing towards Jupiter and one of its satellites.