Recent technological advances have enabled the development of increasingly sophisticated sensors, which can help to advance the sensing capabilities of robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, and other smart systems. Many of these sensors, however, rely on individual cameras, thus the accuracy of the measurements they collect is limited by the cameras’ field of view (FOV).
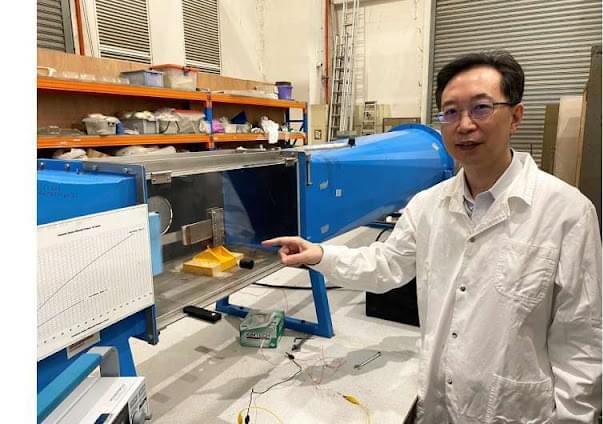
Researchers at Beihang University in China recently developed a new multi-camera differential binocular vision sensor with a wider FOV that could collect more accurate measurements. This sensor, introduced in a paper published in Optics & Laser Technology, could be integrated into a wide range of devices and smart robotic systems.
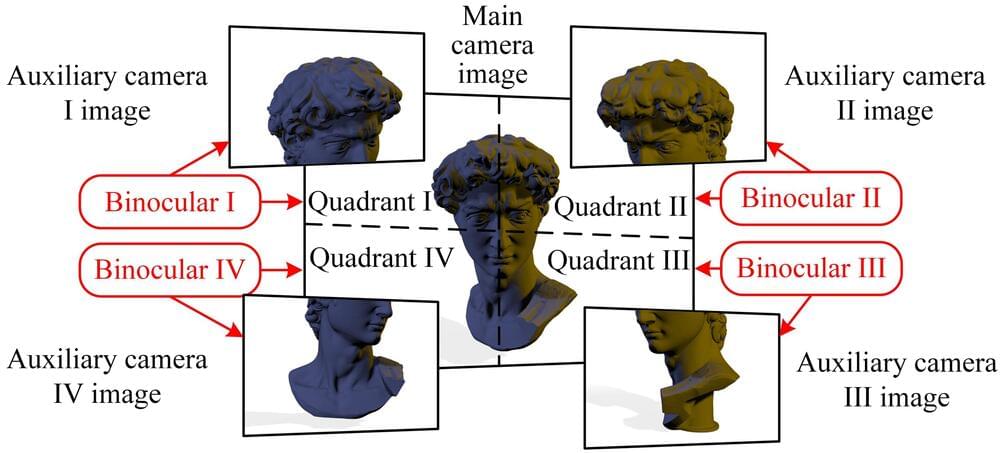
“Aiming at the high-precision requirements of environment perception for unmanned aerial vehicle detection, robot navigation, and autonomous driving, inspired by the multi-camera module of mobile phones, we introduced a visual perception mode based on the principle of high-precision binocular vision measurement,” Fuqiang Zhou, co-author of the paper, told Tech Xplore. “This principle involves a central high-resolution camera and peripheral auxiliary cameras that work together.”