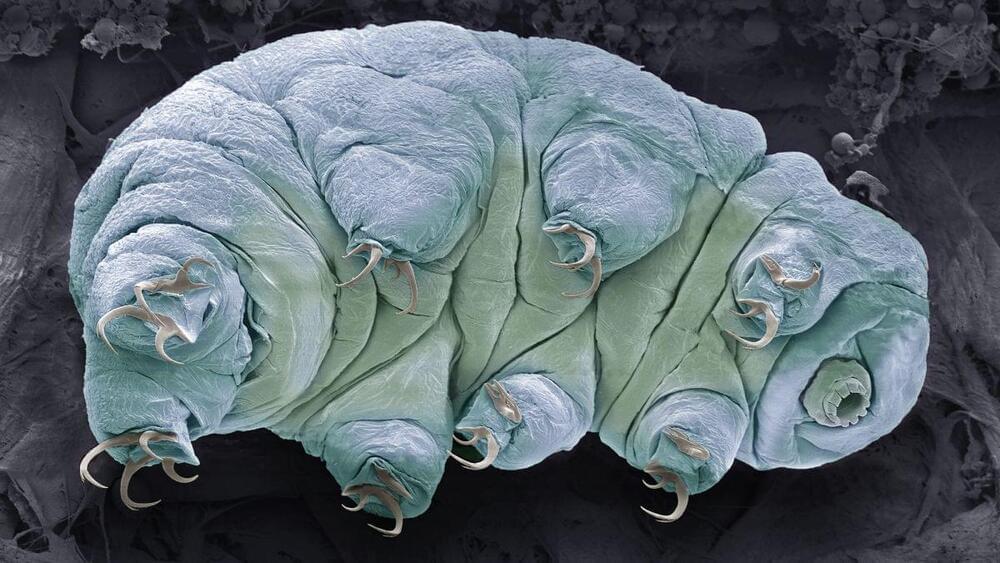
Some experts are skeptical that the frozen moss piglet really entered a quantum state.
A new pre-print study claims to have quantum entangled a tardigrade with two superconductor qubits, though experts are skeptical.
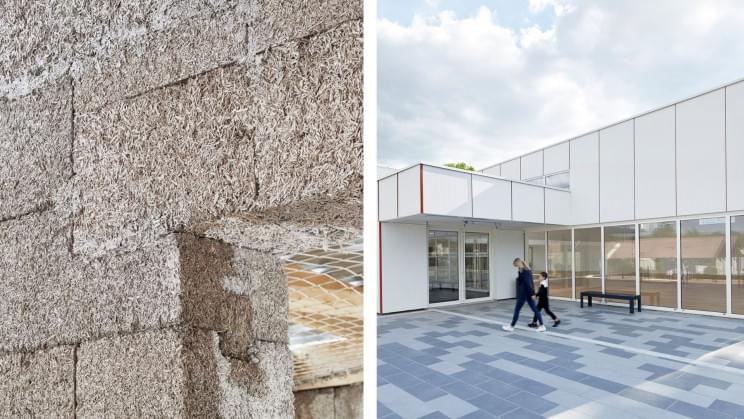

It’s a sports hall.
A French architecture and landscaping company from the town of Croissy-Beaubourg has completed the country’s first hempcrete public building: Pierre Chevet sports hall.
The 4,000-square foot (380 square meters) building includes an exercise hall and changing rooms. What is Hempcrete? A mixture of hemp with lime and water, the sports hall that’s made of Hempcrete is a carbon-negative building.
Hempcrete weights an eight of regular concrete hempcrete has thermal and acoustic properties, as well as being fire-resistant. Hemp can grow up to 13 feet (4 m) and can be cultivated in 90 to 120 days. It is lighter and less expensive than wood and can grow 100 times faster than an oak tree.
According to researcher Darshil Shah the Centre for Natural Material Innovation at Cambridge, hemp can capture carbon twice as effectively as a forest of trees.
Full Story:
Here are some of the most amazing advancements in fabric technology and smart fabrics.
Chain mail-based fabric for smart exoskeletons
Hauberks, or chain mail shirts, were used in the Middle Ages, but they’ve certainly gone out of style, right?
Wrong. They’ve only transformed into something else. In 2021, engineers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and the Nanyang Technological University (NTU) in Singapore created a chain mail-like material that goes from soft to stiff on command, bearing a load of 50 times its own weight when rigid.
The new zinc batteries are made up of electrodes that are screen-printed onto both sides of a sheet of hydrogel-reinforced cellulose paper. A layer of gold thin foil is coated on the electrodes to increase the conductivity of the battery. The battery is about 0.4mm thick, which is roughly the thickness of two strands of human hair.
Impressively, once the battery has reached the end of its lifespan, it can be buried in soil, where it will break down completely within a month.
The NTU researchers, who outlined their findings in the journal Advanced Science 0, demonstrated how a 1.5 in x 1.5 in (4 cm x 4 cm) square printed paper battery could power a small electric fan for up to 45 minutes. The researchers emphasized the fact that bending the battery did not interrupt the supply of power to the fan.
Scientists aboard the International Space Station (ISS) have used magnetism as a gravity replacement in a biomanufacturing device that can make human cartilage tissue out of individual cells. The researchers say this isn’t just the first time a complex material has been assembled—it also represents an entire new field using magnets to “levitate” materials in zero-gravity environments.
🤯 Let’s go deeper. Click here to read more stories like this, solve life’s mind-blowing mysteries, and get unlimited access to Popular Mechanics.
The HB1 has a 30m range from the ground but is potentially unlimited if the tether can be supplied from the roof. The robot can be equipped with different attachments such as a brush, robot arm, airless spray, concrete surveying equipment.
To ensure that the robot itself doesn’t fall, it had to undergo extensive electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing to make sure that fans, which essentially attach it to the surface, are functioning correctly.
The WMG SME team tested the robot by placing it in the EMC chamber and assessing how it responds to noise. It made sure it didn’t emit any unwanted noise into the atmosphere itself. Using amplifiers to simulate noise and analyzers, the researchers were able to detect any unwanted interference and emissions with the robot and record results.
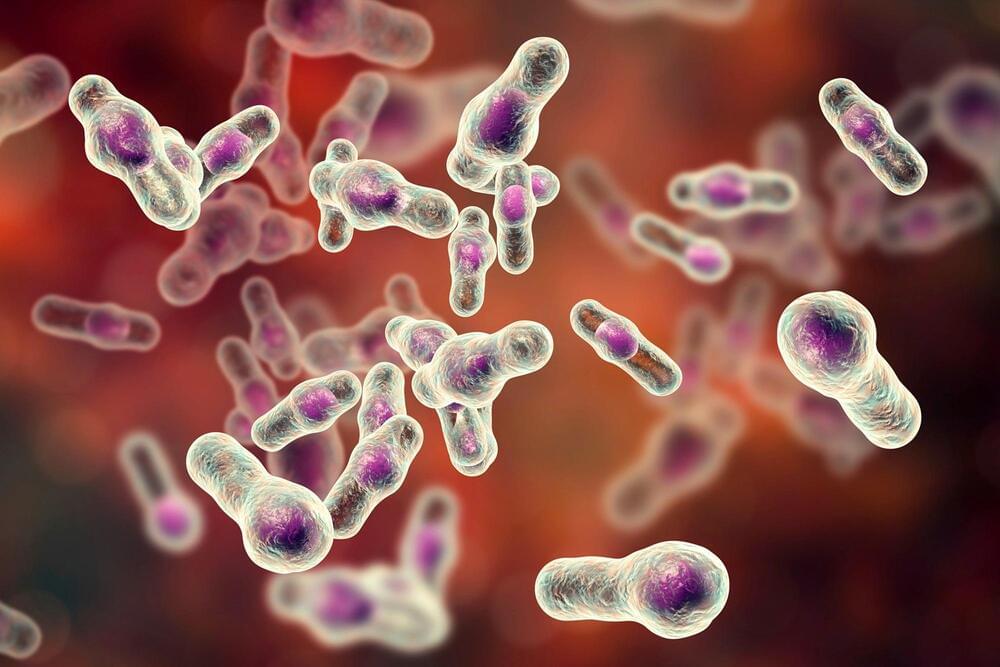
Findings suggest way to help patients heal from dangerous C. difficile.
New research from the University of Virginia School of Medicine sheds light on why a fecal transplant can benefit patients with dangerous recurrent C. difficile infections – and suggests a way to improve patient outcomes.
C. difficile infection causes life-threatening diarrhea, and it often takes hold in patients in hospitals and nursing homes as a result of long-term antibiotic use. Doctors have known that fecal transplants – literally transplanting fecal material from a healthy person into the sick – can improve C. difficile outcomes, but they haven’t fully understood why. The new UVA research offers important answers.

Nature’s strongest material now has some stiff competition. For the first time, researchers have hard evidence that human-made hexagonal diamonds are stiffer than the common cubic diamonds found in nature and often used in jewelry.
Named for their six-sided crystal structure, hexagonal diamonds have been found at some meteorite impact sites, and others have been made briefly in labs, but these were either too small or had too short of an existence to be measured.
Now scientists at Washington State University’s Institute for Shock Physics created hexagonal diamonds large enough to measure their stiffness using sound waves. Their findings are detailed in a recent paper in Physical Review B.
Visit our sponsor, Brilliant: https://brilliant.org/IsaacArthur/
In order to forge a bright future, we’ll need materials stronger, lighter, and better than ever before. Advances in material science are the gateway to tomorrow’s technologies.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Isaac_A_Arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: https://discord.gg/53GAShE
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud:
Episode’s Audio-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/upcoming-advan…al-science.
Episode’s Narration-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/upcoming-advan…ation-only.
Credits:
Upcoming Advances in Material Science.
Science & Futurism with Isaac Arthur.
Episode 320; December 9, 2021
Produced, Written, and Narrated by Isaac Arthur.
Editors:
Sig’unnr.
Yamagashi.
Cover Art:

This design can either double the performance of chips or reduce power use by 85%.
In May of 2021, we brought you a breakthrough in semiconductor materials that saw the creation of a chip that could push back the “end” of Moore’s Law and further widen the capability gap between China and U.S.-adjacent efforts in the field of 1-nanometer chips.
The breakthrough was accomplished in a joint effort, involving the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), National Taiwan University (NTU), and the Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC), which is the world’s largest contract manufacturer of advanced chips. At the core of the breakthrough was a process that employs semi-metal bismuth to allow for the manufacture of semiconductors below the 1-nanometer (nm) level.
Now, IBM and Samsung claim they have also made a breakthrough in semiconductor design, revealing a new concept for stacking transistors vertically on a chip, according to a press release acquired by IE. It’s called Vertical Transport Field Effect Transistors (VTFET) and it sees transistors lie perpendicular to one another while current flows vertically.
This is a drastic change from today’s models where transistors lie flat on the surface of the silicon, and then electric current flows from side to side. By doing this, IBM and Samsung hope to extend Moore’s Law beyond the nanosheet threshold and waste less energy.
Full Story: