A study of 8,000 years of genetics from Spain and Portugal yields a surprisingly complex picture of the inhabitants’ ancestry.

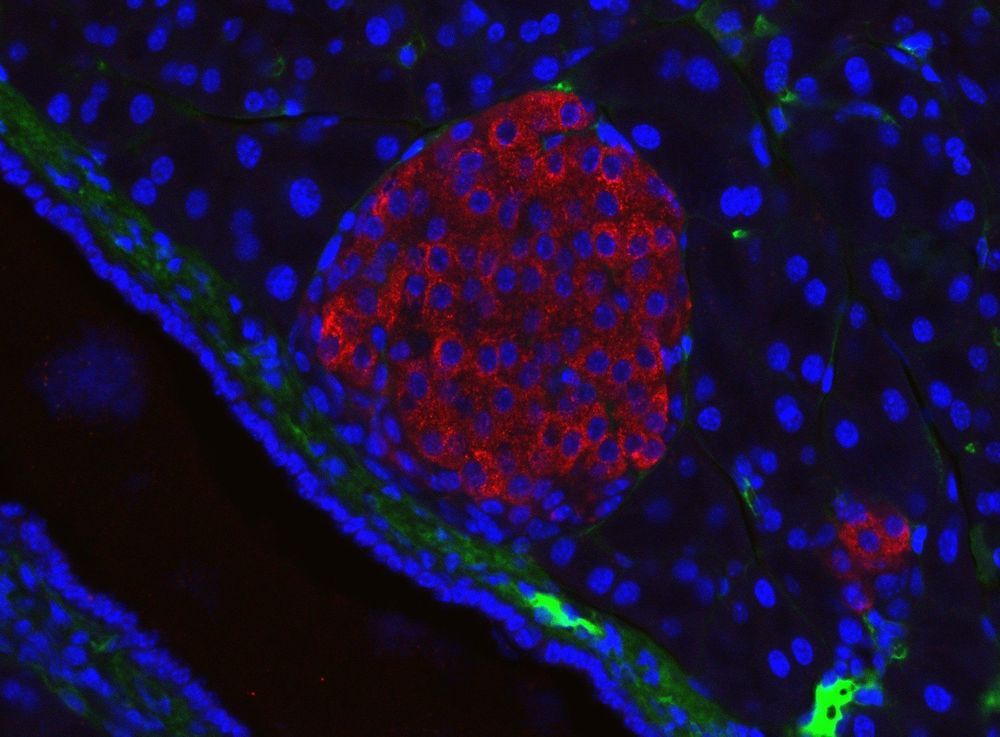
Two known gene mutations induce pathways that enhance pancreatic cancer’s ability to invade tissues and evade the immune system. Researchers report the molecular details of this process, providing insights into druggable targets for immunotherapies.
Mutations in the genes KRAS and TP53 are closely linked to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, by far the most common type of pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic cancers are often already malignant when diagnosed, making its five-year survival rate extremely low—less than ten percent. So, understanding how it evolves at the molecular level could help anti-cancer drug development.
Hisataka Sabe of Hokkaido University and colleagues in Japan conducted tests in human cancer cells and in mouse models of the disease to investigate the roles of KRAS and TP53 gene mutations in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. The study was published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).

(repeat) Are you ready to defer all your personal decision-making to machines? Polls show that most Americans are uneasy about the unchecked growth of artificial intelligence. The possible misuse of genetic engineering also makes us anxious. We all have a stake in the responsible development of science and technology, but fortunately, science fiction films can help.
The movies Ex Machina and Jurassic Park suggest where A.I. and unfettered gene-tinkering could lead. But even less popular sci-fi movies can help us imagine unsettling scenarios regarding over-population, smart drugs, and human cloning.
And not all tales are grim. The 1951 film, The Man in the White Suit, weaves a humorous story of materials science run amok.
On Wednesday, we wrote about a database of mutations that could give people superhuman characteristics or medical benefits.
The database, which reads like a real-life skill tree from a video game, is housed on the website of famed Harvard geneticist George Church. Now Church has opened up, telling Futurism why he assembled the list and how he hopes others will use it as gene-hacking technology develops.
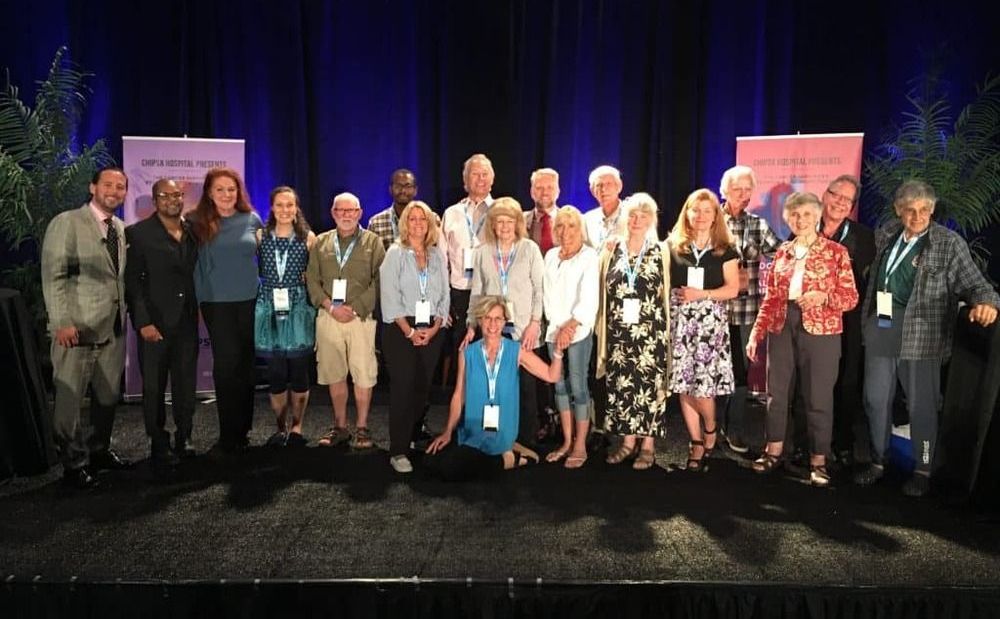

It’s not everyday that you see some of the worlds leading cancer scientists attending a scientific forum put on by a hospital from Mexico. But CHIPSA hospital isn’t your average hospital and the scientists showed presenting their research, much of which they are working on with CHIPSA.
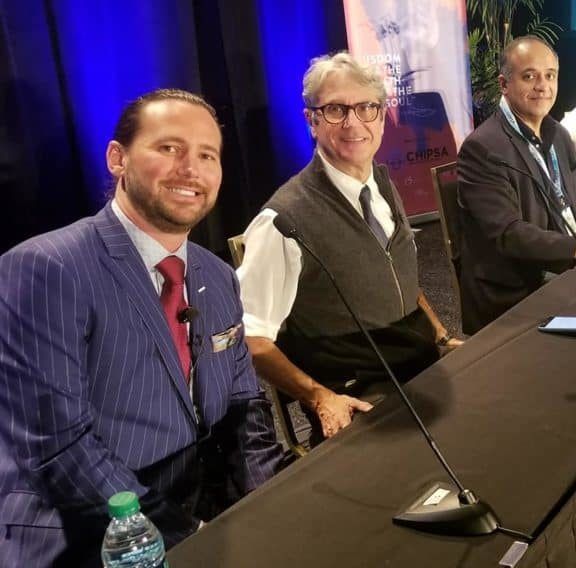

Take for instance Dr. Franco Marincola. The fa med former chief of immunogenetics for the NIH, editor of 9 peer reviewed publications and co-author of the textbook mosts oncologists use for immunotherapy reference. Dr. Marincola joined the CHIPSA Scientific advisory board in June and speaks highly of their work and passion for translational science.
Or Dr. Vijay Mahant, who did his post doctorate at MD Anderson in 1985 and invented the prostate cancer test that is widely used today. He also co-founded auto-genomics a leading liquid biopsy company that is studying diagnosing cancer through the blood.

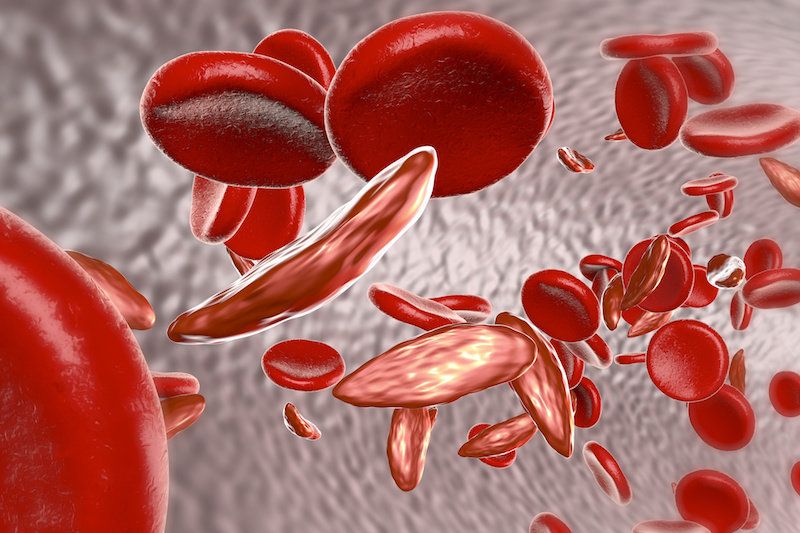
In a paper published in the July 31 issue of Science Translational Medicine, researchers at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center used CRISPR-Cas9 to edit long-lived blood stem cells to reverse the clinical symptoms observed with several blood disorders, including sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia.
It’s the first time that scientists have specifically edited the genetic makeup of a specialized subset of adult blood stem cells that are the source of all cells in the blood and immune system.
The proof-of-principle study suggests that efficient modification of targeted stem cells could reduce the costs of gene-editing treatments for blood disorders and other diseases while decreasing the risks of unwanted effects that can occur with a less discriminating approach.

FAIRY-SIZED astronauts will become humanity’s weapon of choice when it comes to exploring the universe.
That’s the shock claim made by one expert, who reckons by the end of the century we’ll be creating tiny people with wings to travel to new worlds for us.
Dr Ian Pearson, a “futurologist” – someone who specialises in predicting future tech trends – says we’ll soon be able to genetically engineer folk of all shapes and sizes.
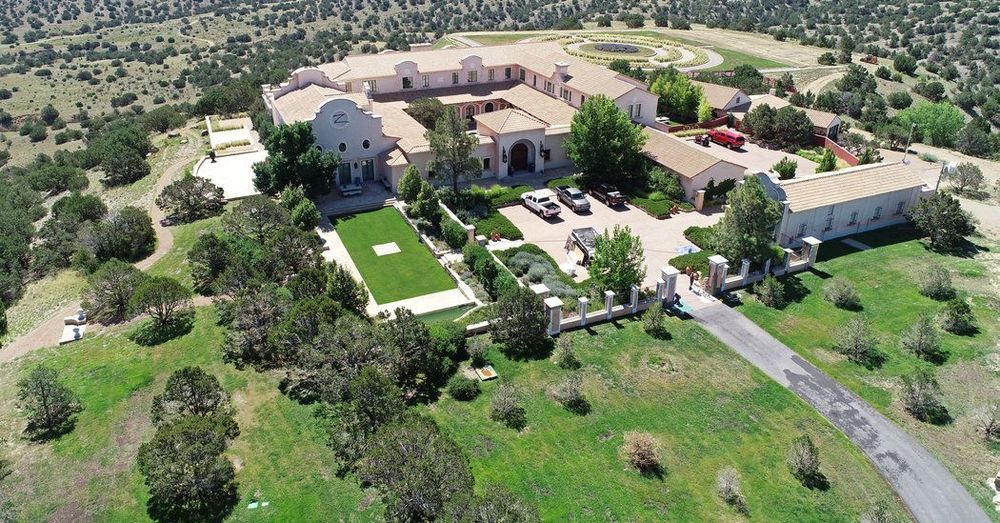

Mr. Epstein’s vision reflected his longstanding fascination with what has become known as transhumanism: the science of improving the human population through technologies like genetic engineering and artificial intelligence. Critics have likened transhumanism to a modern-day version of eugenics, the discredited field of improving the human race through controlled breeding.
Mr. Epstein, the accused sex trafficker, was fascinated by eugenics. He told scientists and others of his vision of using his New Mexico ranch to impregnate women.

Working with mouse and human tissue, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers report new evidence that a protein pumped out of some—but not all—populations of “helper” cells in the brain, called astrocytes, plays a specific role in directing the formation of connections among neurons needed for learning and forming new memories.
Using mice genetically engineered and bred with fewer such connections, the researchers conducted proof-of-concept experiments that show they could deliver corrective proteins via nanoparticles to replace the missing protein needed for “road repairs” on the defective neural highway.
Since such connective networks are lost or damaged by neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s or certain types of intellectual disability, such as Norrie disease, the researchers say their findings advance efforts to regrow and repair the networks and potentially restore normal brain function.