A new CRISPR-Cas toolkit, dubbed “pAblo·pCasso,” is set to transform the landscape of bacterial genome editing, offering unprecedented precision and flexibility in genetic engineering. The new technology, developed by researchers at The Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Biosustainability (DTU Biosustain), expands the range of genome sites available for base-editing and dramatically accelerates the development of bacteria for a wide range of bioproduction applications.
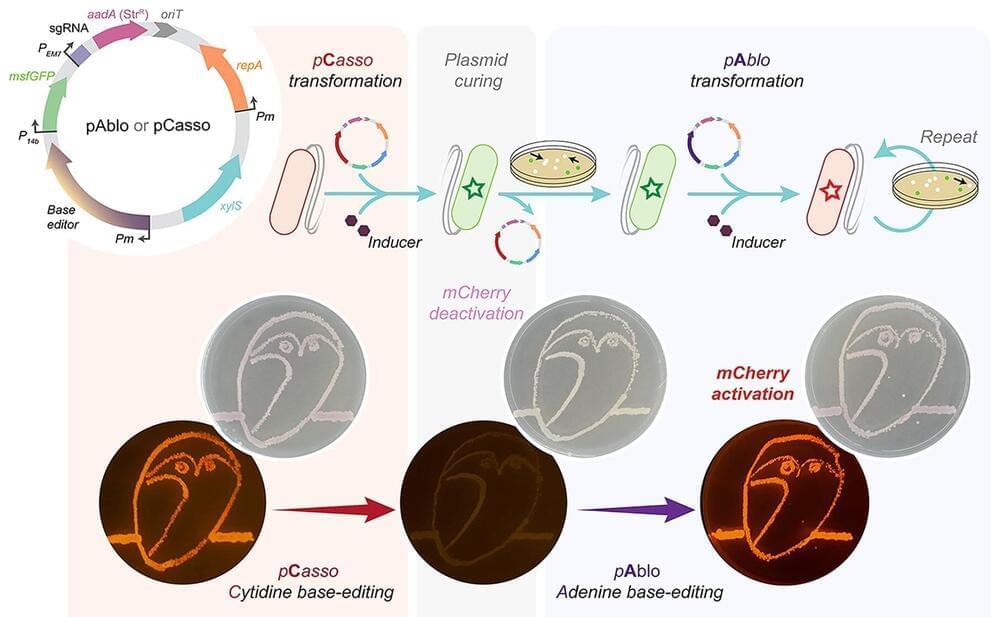
PAblo·pCasso sets a new standard in CRISPR-Cas technologies. A key innovation is to enable precise and reversible DNA edits within Gram-negative bacteria, a feat not achievable with previous CRISPR systems. The toolkit utilizes specialized fusion enzymes, modified Cas9 coupled with editor modules CBE or ABE, which act like molecular pencils to alter specific DNA nucleotides, thus accurately controlling gene function.
The development of pAblo·pCasso involved overcoming significant challenges. Traditional CRISPR-Cas systems were limited by their need for specific DNA sequences (PAM sequences) near the target site and were less effective in making precise, single-nucleotide changes. pAblo·pCasso transcends these limitations by incorporating advanced Cas-fusion variants that do not require specific PAM sequences, thereby expanding the range of possible genomic editing sites.