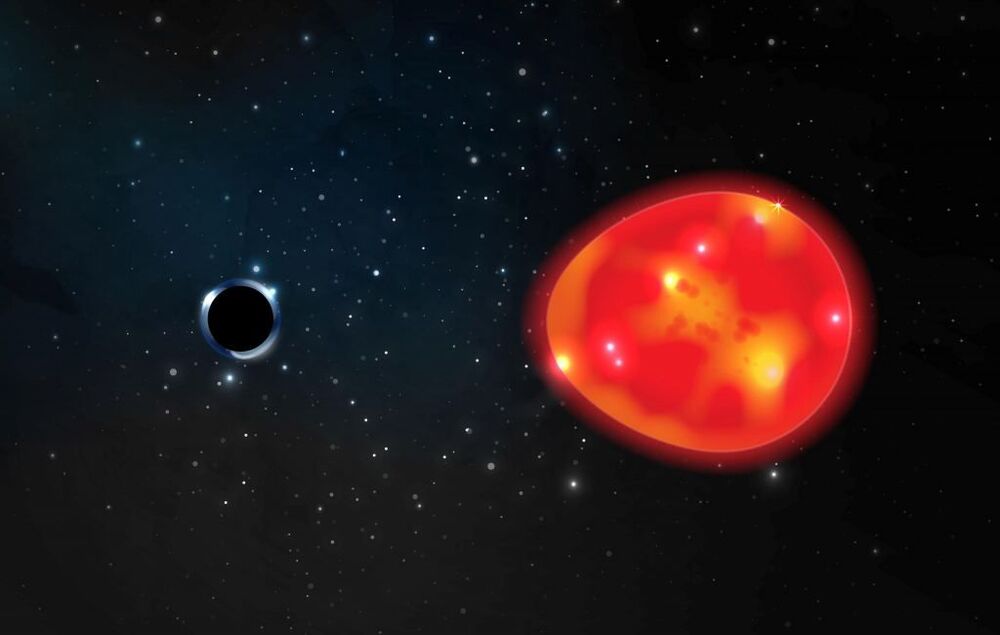
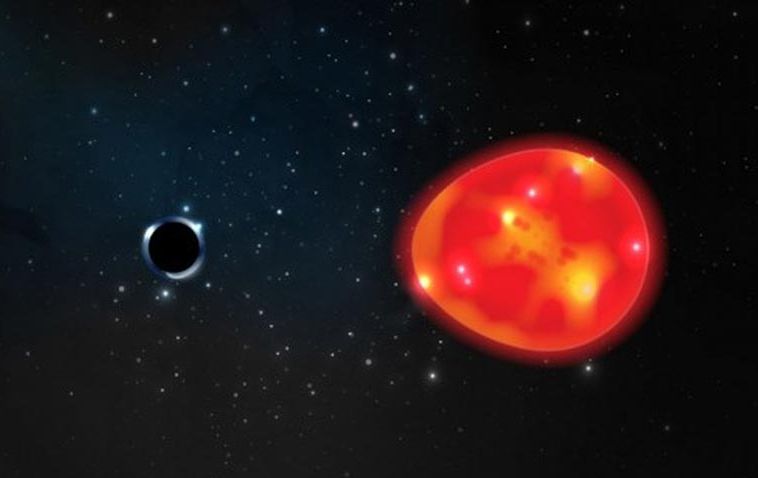
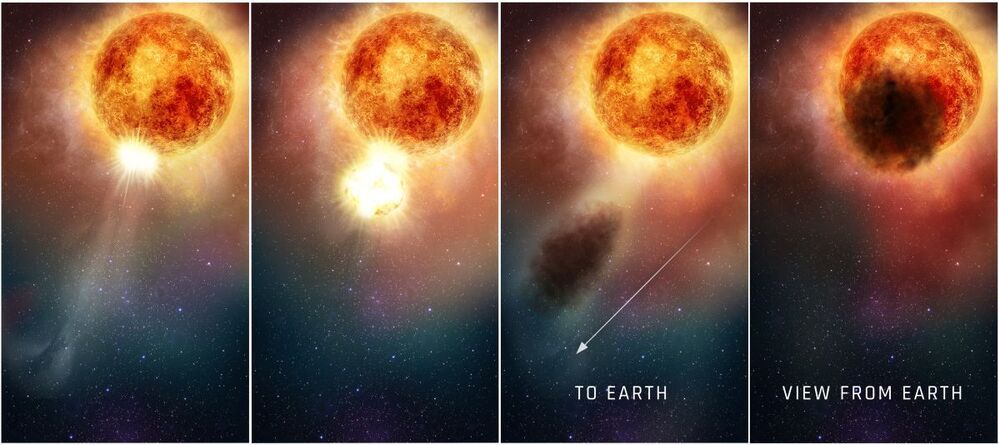
A red giant star may have a black hole companion that is only three solar masses in size.
In theory, a black hole is easy to make. Simply take a lump of matter, squeeze it into a sphere with a radius smaller than the Schwarzschild radius, and poof! You have a black hole. In practice, things aren’t so easy. When you squeeze matter, it pushes back, so it takes a star’s worth of weight to squeeze hard enough. Because of this, it’s generally thought that even the smallest black holes must be at least 5 solar masses in size. But a recent study shows the lower bound might be even smaller.
The work focuses red giant star known as V723 Monoceros. This star has a periodic wobble, meaning it’s locked in orbit with a companion object. The companion is too small and dark to see directly, so it must be either a neutron star or black hole. Upon closer inspection, it turns out the star is not just wobbling in orbit with its companion, it’s being gravitationally deformed by its companion, an effect known as tidal disruption.
Continue reading “Smallest, Closest Black Hole Ever Discovered is Only 1,500 Light-Years Away” »