A team of astronomers led by researchers from the University of Birmingham, University College London and Queen’s University Belfast have discovered one of the most dramatic ‘switches on’ of a black hole ever seen. They will present their findings on Tuesday 4 July at the 2023 National Astronomy Meeting in Cardiff. The work will also be published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
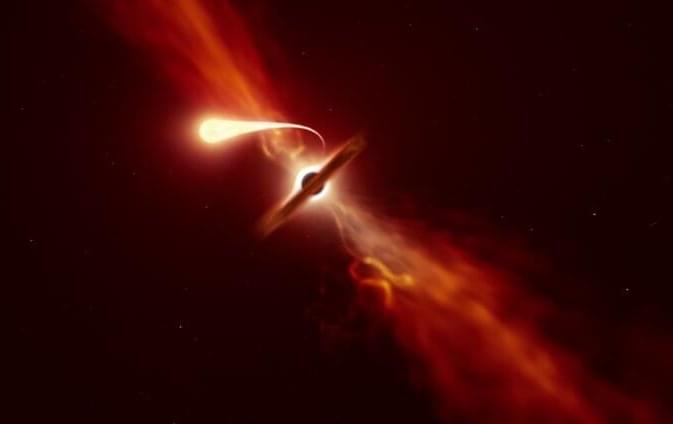
J221951-484240, known as J221951, is one of the most luminous transients—astrophysical objects that change their brightness over a short period of time—ever recorded. It was discovered by Dr. Samantha Oates, an astronomer at the University of Birmingham, and her team, in September 2019 while searching for the electromagnetic light from a gravitational wave event. The team were using the Ultra-Violet and Optical Telescope on board the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory to look for a kilonova, the sign of a neutron star merging with another neutron star or a black hole. A kilonova typically appears blue, then fades and turns more red in color over a timescale of days. What they found instead something even more unusual: J221951. The transient appeared blue, but didn’t change color or fade rapidly as a kilonova would.
Multiple telescopes were used to follow-up J221951 and determine its nature, including NASA’s Swift/UVOT and Hubble Space Telescope, the South African Large Telescope, and ESO facilities such as the Very Large Telescope and the GROND instrument on the MPG/ESO 2.2-meter telescope at the La Silla Observatory.