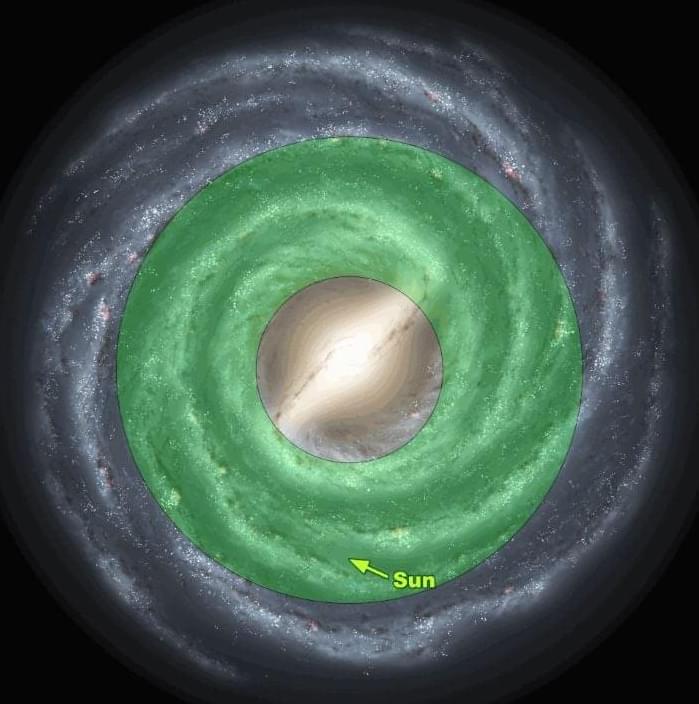
What can the galactic habitable zone (GHZ), galactic regions where complex life is hypothesized to be able to evolve, teach scientists about finding the correct stars that could have habitable planets?
This is what a recent study accepted for publication in Astronomy & Astrophysics hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated a connection between the migration of stars, commonly called stellar migration, and what this could mean for finding habitable planets within our galaxy. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand the astrophysical parameters for finding habitable worlds beyond Earth and even life as we know it. The findings are published on the arXiv preprint server.
For the study, the researchers used a series of computer models to simulate how stellar migration could influence the location and parameters of the GHZ. The models included scenarios both with and without stellar migration to ascertain the statistical probabilities for terrestrial (rocky) planets forming around stars throughout the galaxy. The researchers also used a chemical evolution model to ascertain the formation and evolution of our galaxy, specifically regarding its thickness.