Jun 17, 2024
MXenes for energy storage: Chemical imaging more than just surface deep
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: chemistry, energy, nanotechnology
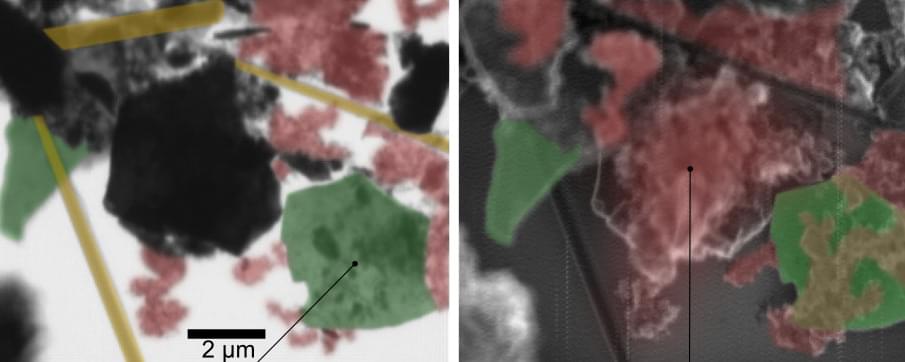
A new method in spectromicroscopy significantly improves the study of chemical reactions at the nanoscale, both on surfaces and inside layered materials. Scanning X-ray microscopy (SXM) at MAXYMUS beamline of BESSY II enables the investigation of chemical species adsorbed on the top layer (surface) or intercalated within the MXene electrode (bulk) with high chemical sensitivity. The method was developed by a HZB team led by Dr. Tristan Petit. The scientists demonstrated among others first SXM on MXene flakes, a material used as electrode in lithium-ion batteries.
Since their discovery in 2011, MXenes have gathered significant scientific interest due to their versatile tunable properties and diverse applications, from energy storage to electromagnetic shielding. Researchers have been working to decipher the complex chemistry of MXenes at the nanoscale.
The team of Dr. Tristan Petit now made a significant progress in MXene characterization, as described in their recent publication (Small Methods, “Nanoscale surface and bulk electronic properties of Ti 3 C 2 Tx MXene unraveled by multimodal X-ray spectromicroscopy”). They utilized SXM to investigate the chemical bonding of Ti 3 C 2 Tx MXenes, with Tx denoting the terminations (Tx=O, OH, F, Cl), with high spatial and spectral resolution. The novelty in this work is to combine simultaneously two detection modes, transmission and electron yield, enabling different probing depths.