May 25, 2016
Engineers take first step toward flexible, wearable, tricorder-like device
Posted by Bruno Henrique de Souza in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, computing, electronics, engineering, mobile phones, wearables
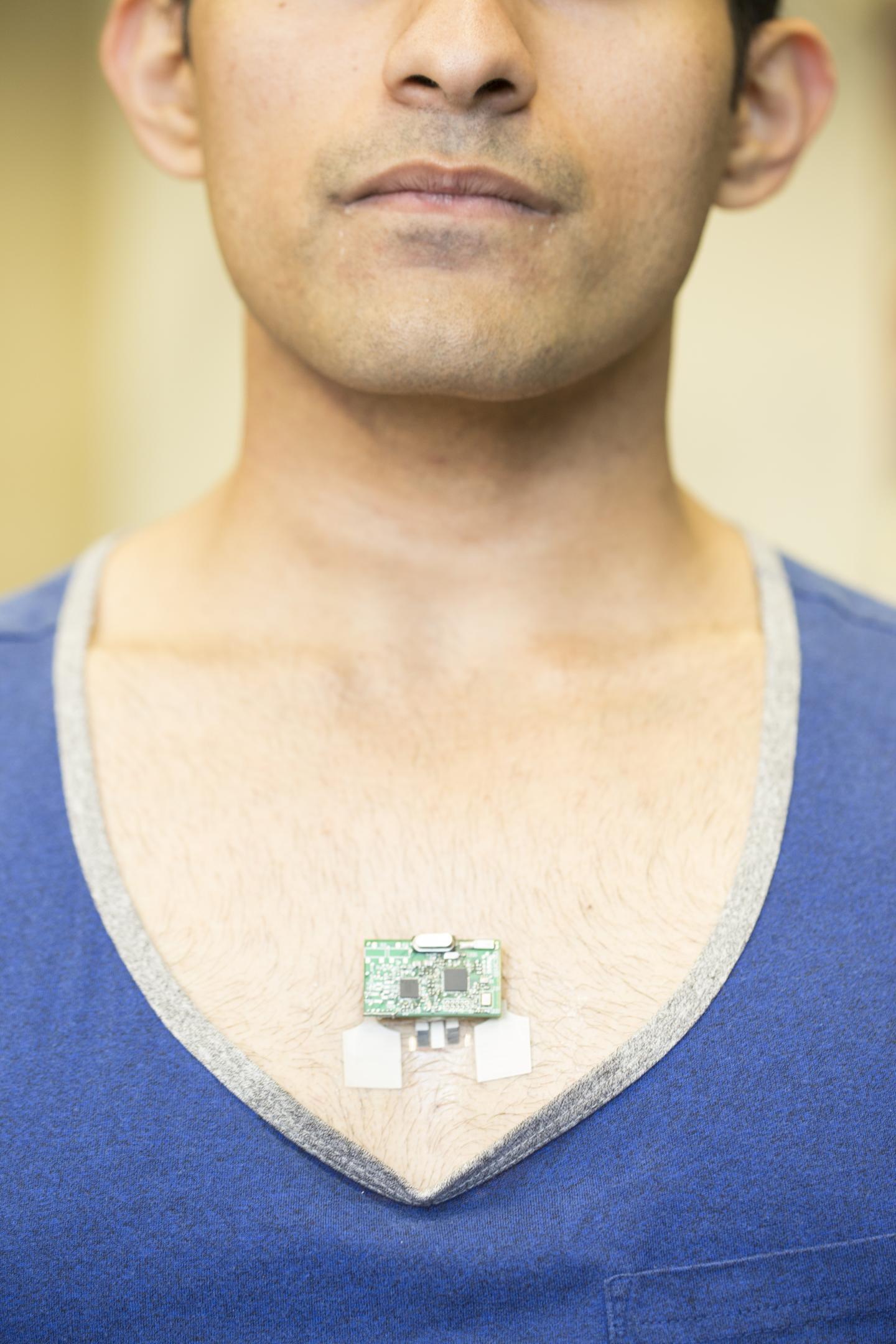
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed the first flexible wearable device capable of monitoring both biochemical and electric signals in the human body. The Chem-Phys patch records electrocardiogram (EKG) heart signals and tracks levels of lactate, a biochemical that is a marker of physical effort, in real time. The device can be worn on the chest and communicates wirelessly with a smartphone, smart watch or laptop. It could have a wide range of applications, from athletes monitoring their workouts to physicians monitoring patients with heart disease.
Nanoengineers and electrical engineers at the UC San Diego Center for Wearable Sensors worked together to build the device, which includes a flexible suite of sensors and a small electronic board. The device also can transmit the data from biochemical and electrical signals via Bluetooth.
Nanoengineering professor Joseph Wang and electrical engineering professor Patrick Mercier at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering led the project, with Wang’s team working on the patch’s sensors and chemistry, while Mercier’s team worked on the electronics and data transmission. They describe the Chem-Phys patch in the May 23 issue of Nature Communications.