Apr 12, 2020
Low plasma citrulline levels are associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with severe sepsis
Posted by Brent Ellman in category: biotech/medical
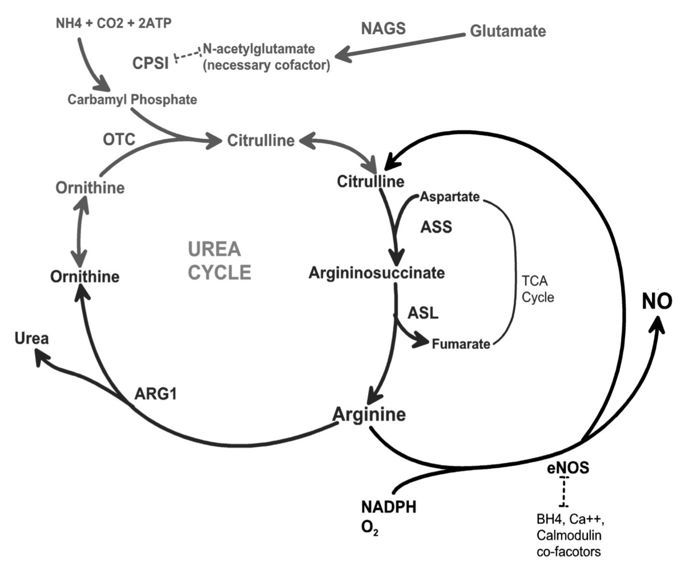
The role of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is not well understood. Inducible NOS is upregulated during physiologic stress; however, if NOS substrate is insufficient then NOS can uncouple and switch from NO generation to production of damaging peroxynitrites. We hypothesized that NOS substrate levels are low in patients with severe sepsis and that low levels of the NOS substrate citrulline would be associated with end organ damage including ARDS in severe sepsis.
Plasma citrulline, arginine and ornithine levels and nitrate/nitrite were measured at baseline in 135 patients with severe sepsis. ARDS was diagnosed by consensus definitions.
Plasma citrulline levels were below normal in all patients (median 9.2 uM, IQR 5.2 — 14.4) and were significantly lower in ARDS compared to the no ARDS group (6.0 (3.3 — 10.4) vs. 10.1 (6.2 — 16.6), P = 0.002). The rate of ARDS was 50% in the lowest citrulline quartile compared to 15% in the highest citrulline quartile (P = 0.002). In multivariable analyses, citrulline levels were associated with ARDS even after adjustment for covariates including severity of illness.