This video explains the details of eukaryotes, replication in eukaryotes and differences between prokaryotic DNA replication and eukaryotic DNA replication.
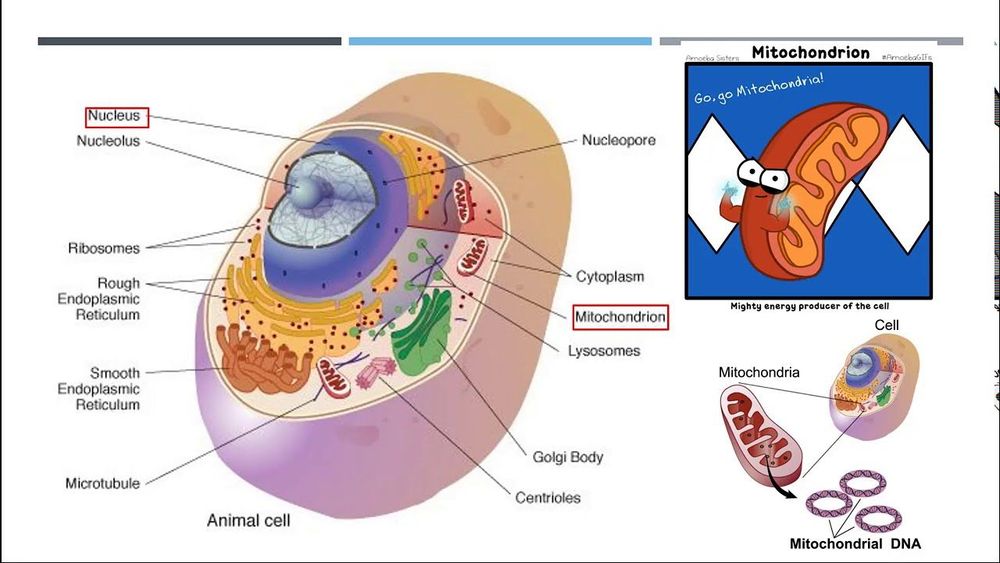
This video explains the details of eukaryotes, replication in eukaryotes and differences between prokaryotic DNA replication and eukaryotic DNA replication.
Malak Trabelsi Loeb
13-08-2020

Covid-19 did not only cause a health crisis around the world; It led to severe economic, social, and political challenges in various countries.
In response to the World Health Organization recommendations, governments imposed various precautionary measures in the course of managing its risks. Measures varied from mere social distancing to total lockdown and isolation in quarantine centers.
Continue reading “The Legal Industry and COVID-19 Challenges” »
The emergence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes severe respiratory tract infections in humans (COVID-19), has become a global health concern. Currently, several vaccine candidates against SARS-CoV-2 are in clinical trials but approval of these vaccines is likely to take a long time before they are available for public use. In a previous report, the importance of passive immunity and how immunoglobulin (Ig)G collected from recovered coronavirus patients could help in the protection against COVID-19 and boost the immune system of new patients was reported. Passive immunity by immunoglobulin transfer is a concept employed by most mammals and bovine IgG has a role to play in human therapy. IgG is one of the major components of the immunological activity found in cow’s milk and colostrum. Heterologous transfer of passive immunity associated with the consumption of bovine immune milk by humans has been investigated for decades for its immunological activity against infections. This short review focuses on passive immunity and how microfiltered raw immune milk or colostrum collected from cows vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 could provide short-term protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans and could be used as an option until a vaccine becomes commercially available.
Currently, different academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies worldwide have started programs to develop and test vaccine candidates against SARS-CoV-2 in clinical trials. An S-glycoprotein-based vaccine is a promising approach that has attracted the attention of scientists, since S-glycoprotein can be directly recognized by the host’s immune system. For the first coronavirus (SARS-CoV-1), which was identified in Guangdong province, China, in November 2002, different vaccines were developed and tested in animal models. Some of these vaccines prevented animal infection after challenge with SARS-CoV-1. Kapadia et al. showed that neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-1 could be detected in sera from mice immunized with S-glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-1 (10, 11).
The proposed mechanism of action described in the claim that 5G millimeter waves can generate SARS-CoV-2 in human cells violates fundamental principles of biology. Scientific evidence does not support a causal relationship between 5G and COVID-19. Many of the regions with the highest COVID-19 infection rates, such as Brazil, do not have 5G coverage, providing further evidence that 5G is not associated with the pandemic.
FULL CLAIM: 5G generates coronavirus in human skin cells
Scientists from 4 different Swiss universities describe how adhesion molecules activate autoaggressive immune cells and drive their infiltration in the nervous system in a model of multiple sclerosis.
Click to read the paper published in Frontiers in Immunology: https://fro.ntiers.in/tp1U
In experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS), myelin-specific T cells are activated in the periphery and differentiate in T helper (Th) 1 and Th17 effector cells, which cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to reach the central nervous system (CNS), where they induce neuroinflammation. Here, we explored the role of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and ICAM-2 in the activation of naïve myelin-specific T cells and in the subsequent migration of differentiated encephalitogenic Th1 and Th17 cells across the BBB in vitro and in vivo. While on antigen-presenting cells ICAM-1, but not ICAM-2 was required for the activation of naïve CD4+ T cells, endothelial ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 mediated both Th1 and Th17 cell migration across the BBB. ICAM-1/-2-deficient mice developed ameliorated typical and atypical EAE transferred by encephalitogenic Th1 and Th17 cells, respectively. Our study underscores important yet cell-specific contributions for ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 in EAE pathogenesis.
The UK, US and Canada say state-backed hackers tried to steal coronavirus vaccine research.
COSTA MESA, Calif. – Health experts say around half of American adults are overweight or obese. While excessive body weight is linked to a number of serious health conditions, including diabetes and heart disease, a new study reveals it can also reduce blood flow to the brain. Researchers warn this can put overweight individuals at great risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
The study examines brain blood flow in 17,721 adults between 18 and 94. To do this, researchers use a brain imaging technique known as single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).
SPECT is a technique in which doctors inject a radioactive tracer into a patient’s blood and then use a special camera to look at the flow of blood. Participants were then split into five categories: underweight, normal weight, overweight, obese, and morbidly obese — to examine blood flow in each of their brains. The brain scan data reveals lower blood flow across virtually all brain regions as body weight increases.
While satellite imaging lets researchers observe the outer life of plankton populations, the complex genetics in microscopic marine life have made looking inward more challenging. According to a new study published in Nature Methods, researchers from the University of East Anglia were able to deliver and express foreign DNA in 13 species that have never before transformed. They were also able to evaluate the potential cause of non-transformation in 17 other species; in turn, laying the foundation for an expanded understanding of genomes discovered in plankton.
The sheer variety of plankton potential — from antibacterial compounds to antiviral and antifungal solutions — makes this a worthwhile endeavor. If scientists can create reliable methods to modify phytoplankton, it should be possible to reduce their toxic impact, better control their bloom cycle and even increase the photosynthetic output — all critical in the fight to keep our oceans blue and our terra firma green.
As noted by Science Magainze, the international research team used a variety of methods to modify plankton DNA. For some species, shooting tiny gold or tungsten particles covered with DNA through cell walls produced the best result. For others, jolts of electricity made cell walls “leaky” and allowed new DNA to seep through. Specific protist successes included modification of a fish-killing toxic plankton species, and one that infects both mollusks and amphibians. While these discoveries don’t present a complete understanding of the genetics in microscopic marine life, they provide a key testing protocol: By modifying genetic structure and then observing how plankton react, teams could uncover ways to boost antibiotic resistance or lower infectious impact. According to lead UK study author Thomas Mock, “These insights will improve our understanding about their role in the oceans, and they are invaluable for biotechnological applications such as building factories for biofuel or the production of bioactive compounds.”
What is CTAP?
FDA has created a special emergency program for possible coronavirus therapies, the Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program (CTAP)
.
Continue reading “Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program (CTAP)” »
