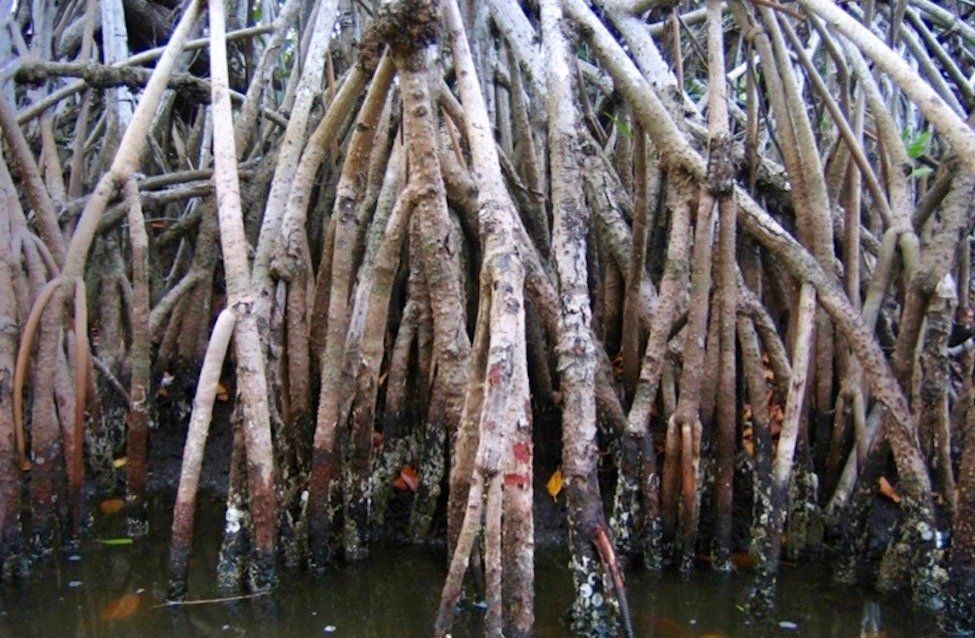
With threats of sea level rise, storm surge and other natural disasters, researchers from Florida Atlantic University’s College of Engineering and Computer Science are turning to nature to protect humans from nature. They are developing innovative ways to guard coastlines and prevent scouring and erosion from waves and storms using bioinspired materials that mimic mangrove trees found along shores, rivers and estuaries in the tropics and subtropics. Growing from a tangle of roots that twist their way out of the mud, mangrove trees naturally protect shorelines, shelter coastal ecosystem habitats and provide important water filtration. In many cases, these roots trap sediments flowing down rivers and off the land, helping to stabilize the coastline.
Certain mangrove root systems even have the ability to dissipate tidal energy through unique hydrological flows and divert the energy of water in different directions reducing risk of coastal damage. Yet, to date, few studies have examined the fluid dynamics such as flow structure and drag force on mangrove roots.
For a study, published in the American Physical Society’s journal, Physical Review Fluids, researchers singled out the red mangrove tree (Rhizophora mangle) from more than 80 different species of mangroves, because of its robust network of roots that can withstand extreme environmental conditions. The red mangrove provided the researchers with an ideal model for bioinspired shoreline applications.
Read more