And wherever humans go, they’ll be taking satellite constellations with them to moon and Mars.


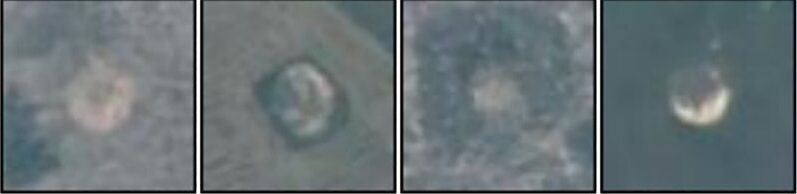
Researchers have used artificial intelligence to detect Vietnam War-era bomb craters in Cambodia from satellite images—with the hope that it can help find unexploded bombs.
The new method increased true bomb crater detection by more than 160 percent over standard methods.
The model, combined with declassified U.S. military records, suggests that 44 to 50 percent of the bombs in the area studied may remain unexploded.
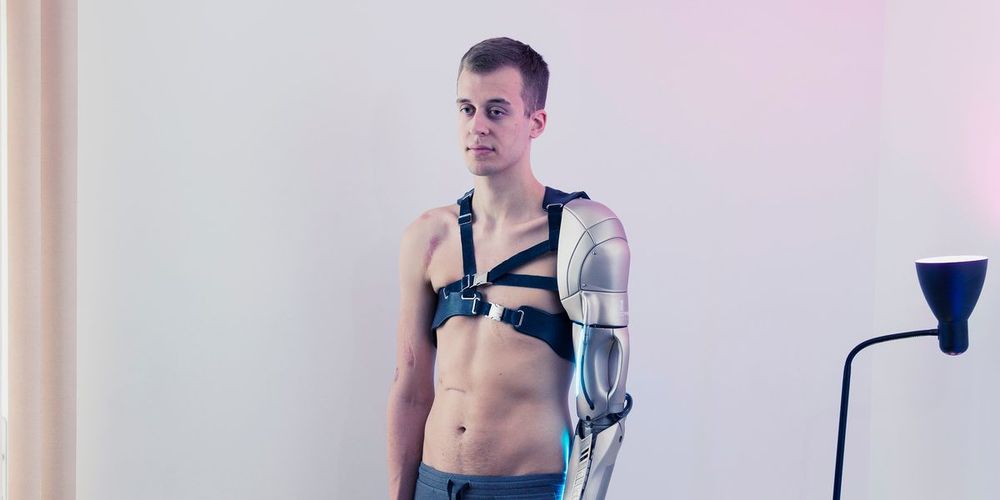

Over the last five years, London-based photographer David Vintiner and art director Gemma Fletcher have been documenting the subculture of transhumanists across Europe, Russia and the United States. Their photobook I Want To Believe, due out this spring, explores these enthusiasts’ achievements and motivations.
Dispatches from the transhumanist movement.
By Bill D’Zio, Originally posted on www.westeastspace.com March 28, 2020
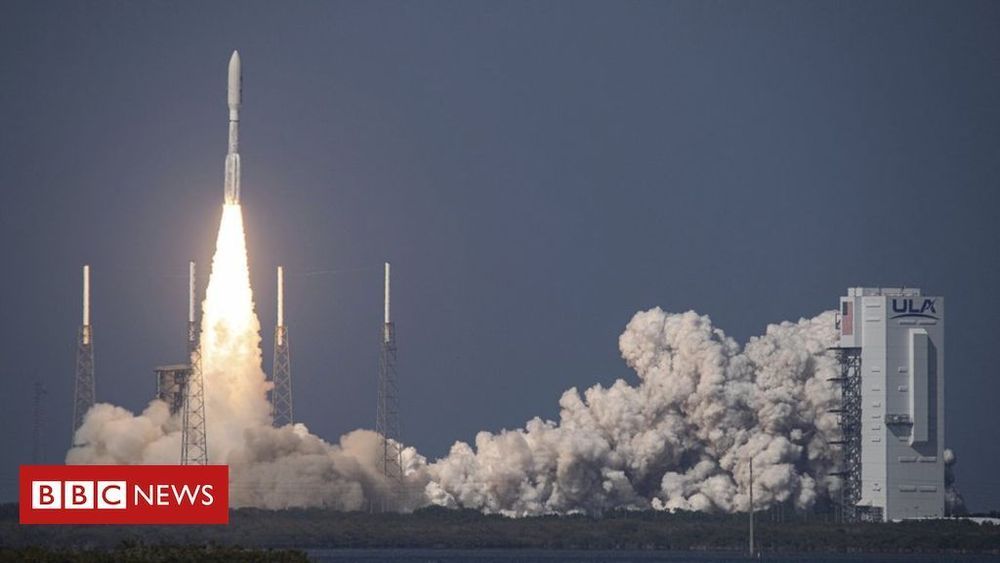
NASA may have sidelined the Lunar Gateway for a return mission to the Moon, but it is not stopping the momentum. NASA has awarded several contracts for the Lunar Gateway including the most recent one to SpaceX. This demonstrates the growing capabilities of New Space companies to capture contracts and complete missions.
“This contract award is another critical piece of our plan to return to the Moon sustainably. The Gateway is the cornerstone of the long-term Artemis architecture and this deep space commercial cargo capability integrates yet another American industry partner into our plans for human exploration at the Moon in preparation for a future mission to Mars.”
NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine in a press release statement about the award to SpaceX.
NASA Awarded SpaceX the first Artemis Gateway Logistics Services (GLS) contract. The award for resupply services to the Gateway will require delivery of goods to a Near Rectilinear Halo Orbit (NRHO). Not sure what a NRHO orbit is? A NRHO is a highly elliptical orbit that takes about 7 days for each orbit. Want some more details, just click here: Near Rectilinear Halo Orbit (NRHO). There are a few options for NRHO orbits, but NASA is leaning towards the L2 9:2 lunar synodic resonant southerly Near-Rectilinear Halo Orbit (NRHO) which would be the likely location of the lunar Gateway. A simplification of the orbit is shown below.


If the U.S. is going to do more work in cold weather climates to deter malign activity from Russia and China, one Air Force general says it will need more equipment to operate full-time in the South Pole.
Pacific Air Forces commander Gen. Charles Q. Brown said Tuesday he’d like to see a boost in “some of the capability we have, but don’t have a lot of.”
“Icebreakers, for example. LC-130s? There’s not a lot of those,” Brown said during a speech at the Mitchell Institute for Aerospace Studies in Arlington, Virginia.



:0000
This article follows on from several others on this theme that I wrote some time ago, for details of which see footnote.
The idea of the earth as a superorganism re-emerged in modern times with the work of the independent scientist James Lovelock and his Gaia hypothesis. This was developed further by the spiritually oriented writer Peter Russell in The Awakening Earth.
When Lovelock published the first edition, where he described the Earth as a kind of self-regulating, living organism, he was attacked by biologists who said that this could not have emerged through a process of natural selection, thus contradicting Darwinian theory, the dominant biological paradigm. Even worse, “one critic referred to it scathingly as a fairy story about a Greek goddess”. These are statements typical of modern materialist, Enlightenment science for, as Lovelock says, “the idea of Mother Earth or, as the Greeks called her, Gaia, has been widely held throughout history and has been the basis of a belief that coexists with the great religions”.

An interesting opinion:
The US Government Comparative Toxicogenomics database shows that Fluoride can inhibit Human immunity to viruses and pneumonia. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE), 2’-5’-Oligoadenylate Synthetase 1 (OAS1) and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 (ICAM1) are included as susceptible epigenetic targets of the poison.
Read 3 answers by scientists with 1 recommendation from their colleagues to the question asked by Geoff Pain on Feb 4, 2020.