Korolev crater on Mars—the largest ice skating rink in the solar system, basically—has never looked more enthralling than it does in this impressive new visualization.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
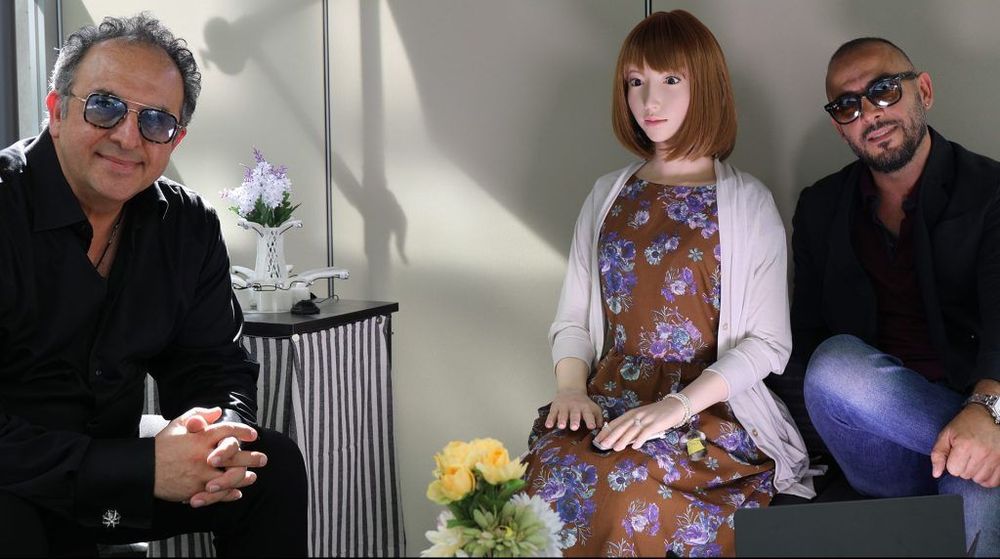


Hollywood Is Banking That a Robot Named Erica Can Be the Next Movie Star
She can’t get sick or be late to the set, and her hair and makeup needs are minimal: Her name is Erica, and Hollywood is hoping that a sophisticated robot can be its next big star. The synthetic actor has been cast in “b,” a $70 million science-fiction movie which producer Sam Khoze describes as “a James Bond meets Mission Impossible story with heart.”
Scribe Tarek Zohdy (“1st Born”), says, the story is about scientists who create an AI robot named Erica who quickly realize the danger of this top-secret program that is trying to perfect a human through a non-human form.
Variety caught up with the filmmakers Zohdy and Khoze to discuss “b” the $70 million film that plans to finish shooting next year, after a director and human star have been brought on.
Researchers observe branched flow of light for the first time
A team of researchers from the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology has observed branched flow of light for the very first time. The findings are published in Nature and are featured on the cover of the July 2, 2020 issue.
The study was carried out by Ph.D. student Anatoly (Tolik) Patsyk, in collaboration with Miguel A. Bandres, who was a postdoctoral fellow at Technion when the project started and is now an Assistant Professor at CREOL, College of Optics and Photonics, University of Central Florida. The research was led by Technion President Professor Uri Sivan and Distinguished Professor Mordechai (Moti) Segev of the Technion’s Physics and Electrical Engineering Faculties, the Solid State Institute, and the Russell Berrie Nanotechnology Institute.
When waves travel through landscapes that contain disturbances, they naturally scatter, often in all directions. Scattering of light is a natural phenomenon, found in many places in nature. For example, scattering of light is the reason for the blue color of the sky. As it turns out, when the length over which disturbances vary is much larger than the wavelength, the wave scatters in an unusual fashion: it forms channels (branches) of enhanced intensity that continue to divide, or branch out, as the wave propagates. This phenomenon is known as branched flow. It was first observed in 2001 with electrons, and had been suggested to be ubiquitous and occur also for all waves in nature, for example sound waves and even ocean waves. Now, Technion researchers are bringing branched flow to the domain of light: they have made an experimental observation of branched flow of light.
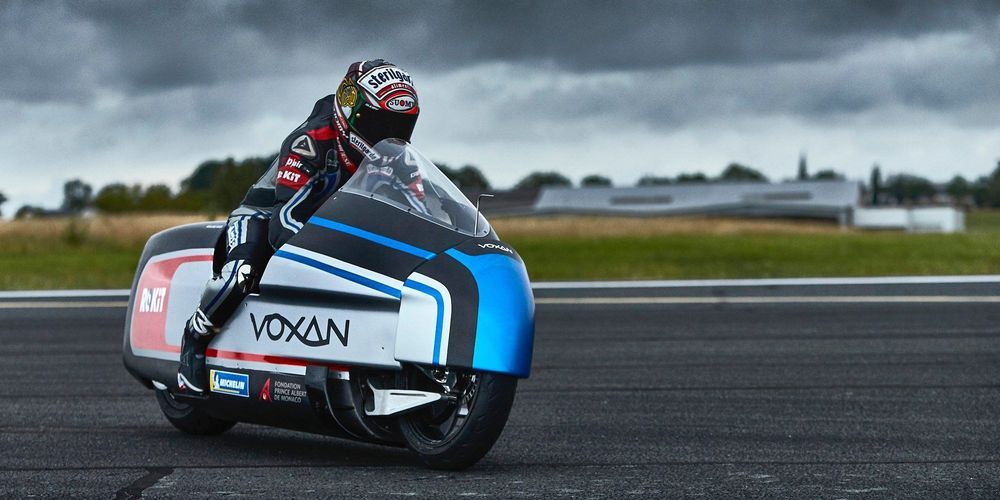

The dry ice-cooled electric motorcycle heading for the land speed world record
Originally intended to make the record attempt this month, plans for the (hopefully) record-breaking run have now been delayed until next year. There seems to be a lot of electric vehicle world record attempts being delayed lately.
But that’s no matter to the Voxan team, including six-time motorcycle racing world champion Max Biaggi, who plans to ride into the record books on the Salar de Uyuni salt flat in Bolivia in July 2021.
The delay may have prevented the team from making their record run this month, but it hasn’t stopped them from unveiling the impressive bike today.
F-15EX Fighters To Get General Electric Engines Under Urgent Purchase
The service still plans to hold an open competition to formally decide on what engine will power the bulk of the jets.
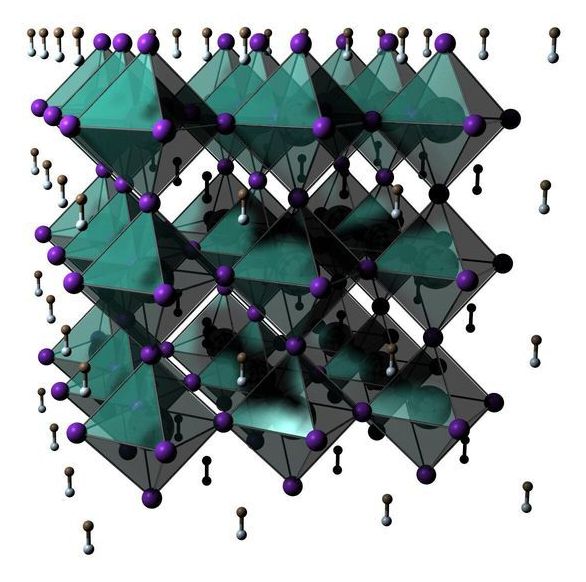
Crystal structure discovered almost 200 years ago could hold key to solar cell revolution
Solar energy researchers at Oregon State University are shining their scientific spotlight on materials with a crystal structure discovered nearly two centuries ago.
Not all materials with the structure, known as perovskites, are semiconductors. But perovskites based on a metal and a halogen are, and they hold tremendous potential as photovoltaic cells that could be much less expensive to make than the silicon-based cells that have owned the market since its inception in the 1950s.
Enough potential, researchers say, to perhaps someday carve significantly into fossil fuels’ share of the energy sector.
China completes new mega-airport
Construction is complete on Beijing’s new mega-airport. This is what it looks like.

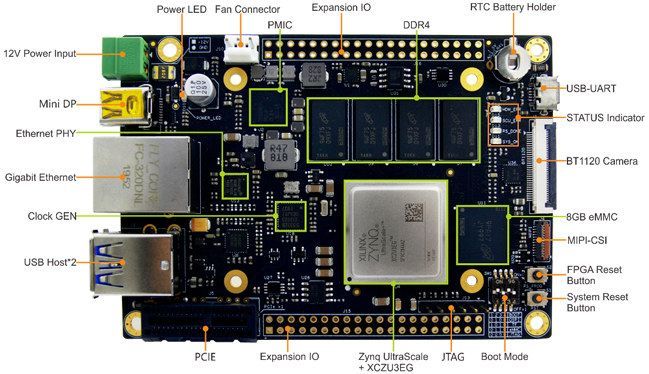
Zynq UltraScale+ Arm FPGA FZ3 Deep Learning Accelerator Card Supports Baidu Brain AI Tools
MYIR’s FZ3 card is a deep learning accelerator board powered by Xilinx Zynq UltraScale+ ZU3EG Arm FPGA MPSoC delivering up to 1.2TOPS for artificial intelligence products based on Baidu Brain AI open platform.
The FZ3 card also features 4GB RAM, 8GB eMMC flash, USB 2.0 & USB 3.0 ports, Gigabit Ethernet, DisplayPort (DP) output, PCIe interface, MIPI-CSI and more.
MYIR FZ3 card specifications: