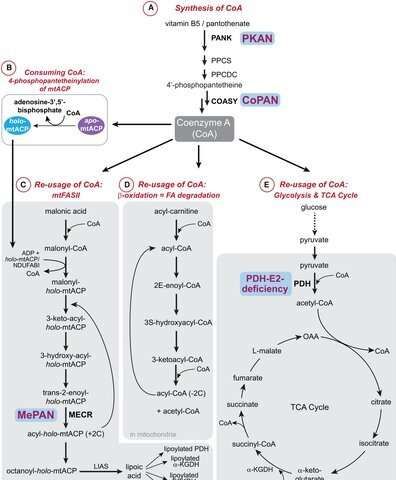
It shouldn’t be any secret that mitochondria can make their own fatty acids. The enzymes mitochondria use to do it were discovered decades ago. Unfortunately, only a few individuals among the biologically literate masses have come to appreciate this critical fact about mitochondrial behavior. Perhaps the bigger issue is why mitochondria would go to all the trouble when cells can already make all the fatty acids they need.
Wikipedia itself remains largely in the dark when it comes to mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis. It does contain several exhaustive entries for enzymatic players in the main cellular fatty acid processes, but it is hard pressed even to mention that mitochondria can do it, too. For years, the small cadre of devotees who studied it referred to it as FASII, for fatty acid synthesis type II. This was because it looked just like the pathways of the same name used by bacteria, from which mitochondria are derived. Eukaryotes, on the other hand, employ FAS type I (FASI) in the cytoplasm.
The main difference seems to be that the FASI enzymes have partially merged into large multifunctional conglomerates that carry out whole sequences of reactions together. Presumably, this makes for greater efficiency because the many enzymes and substrates needn’t slowly diffuse to find each other within a large cytoplasmic reaction space. In the fullness of time, something curious happened to the field: A trickle of more recent papers began using a new name for FASII as done by mitochondria: It was now mtFAS.