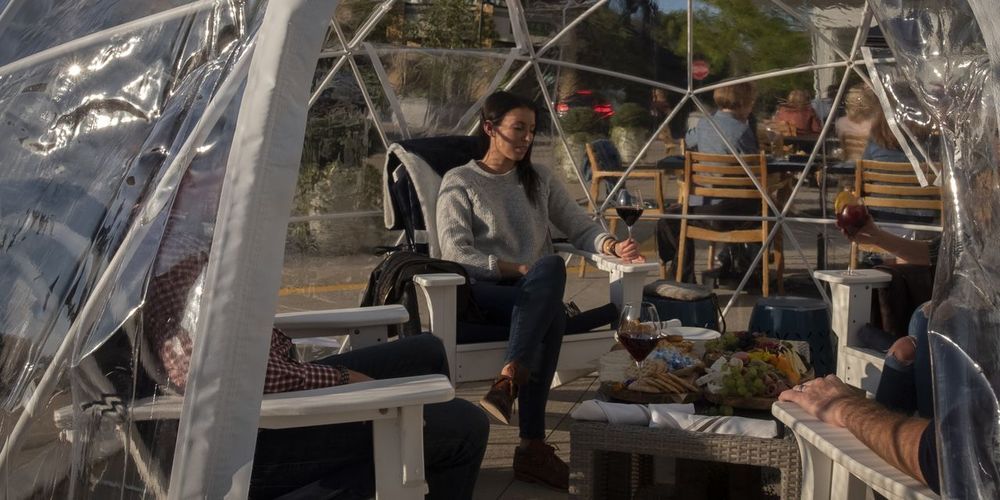
Restaurant owners say they have grown accustomed this year to constantly reinventing themselves to survive. Getting around Mother Nature as the U.S. heads toward winter may be their biggest challenge yet.
Sales from outdoor dining, reduced indoor dining, delivery, and takeout haven’t equaled what most restaurants expected to earn this year before the pandemic upended public life, some owners say. Adding heaters and other fixtures to draw diners to outdoor tables as the weather cools adds to the costs of sustaining a modest revenue stream.
But determined restaurant operators say they have no other choice. They say running at a loss while they have funds to do so—in the hope that the threat of the virus abates—is better than the challenges they would face after closing temporarily, such as finding reliable staff.