Page 9353
Nov 20, 2018
China one step closer satellite navigation system Beidou that could threaten dominance of GPS
Posted by Michael Lance in category: habitats
China moved a step closer to its dream of building a satellite navigation system that could challenge America’s GPS.
Aerospace firm plans a giant leap for Chinese satellite coverage with global network
Yang Changfeng, the chief designer of the system, said a basic Beidou-3 network would be in place by the end of the year to serve countries that have signed up for China’s Belt and Road Initiative – an ambitious transcontinental infrastructure initiative.
Nov 20, 2018
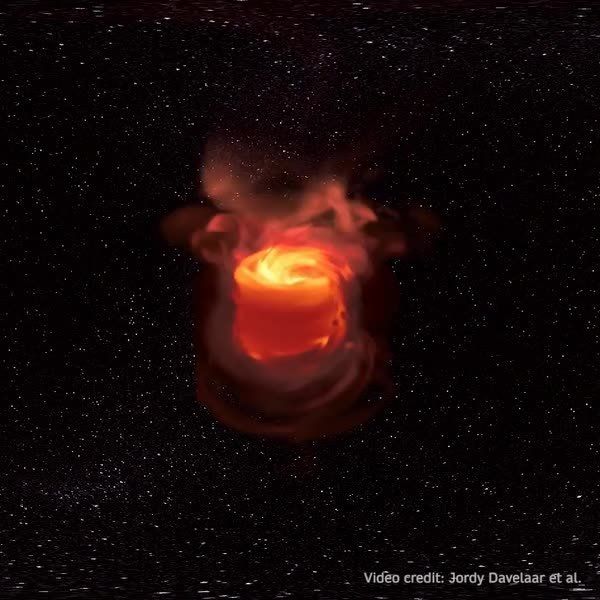
Observing Supermassive Black Holes in Virtual Reality
Posted by Michael Lance in categories: cosmology, virtual reality
Click on photo to start video.
Researchers have created a virtual reality simulation of a supermassive black hole. In a recent paper in “Computational Astrophysics and Cosmology” they present their latest visualization. The simulation is based on the black hole in the center of our own Galaxy; Sagittarius A* (Sgr A•. Read this SpringerOpen blog to learn more. https://bit.ly/2S2Xh8p
Can you craft a message to be understood by aliens?
The main goal of this activity is to educate the youth on Radio Astronomy techniques and Exoplanetary cutting-edge science, presenting the uniqueness of the Arecibo Observatory capability and raising the awareness of the possible risks involved on messaging unknown earthlings (through social medias) or extraterrestrial civilizations (through radio waves).
Diverse, inter-generation, multi-disciplinary and international teams of 10 students + 1 mentor (professor/scientist/teacher) will have to design the NEW Arecibo message. To unlock the call, register the teams and access the references and specifications for the project, the students will have first to learn about scientific method, AO activities, space sciences and peaceful uses of space issues for, then, be able to break coded messages, solve brain-puzzles and design their new Arecibo Message version.
Nov 19, 2018
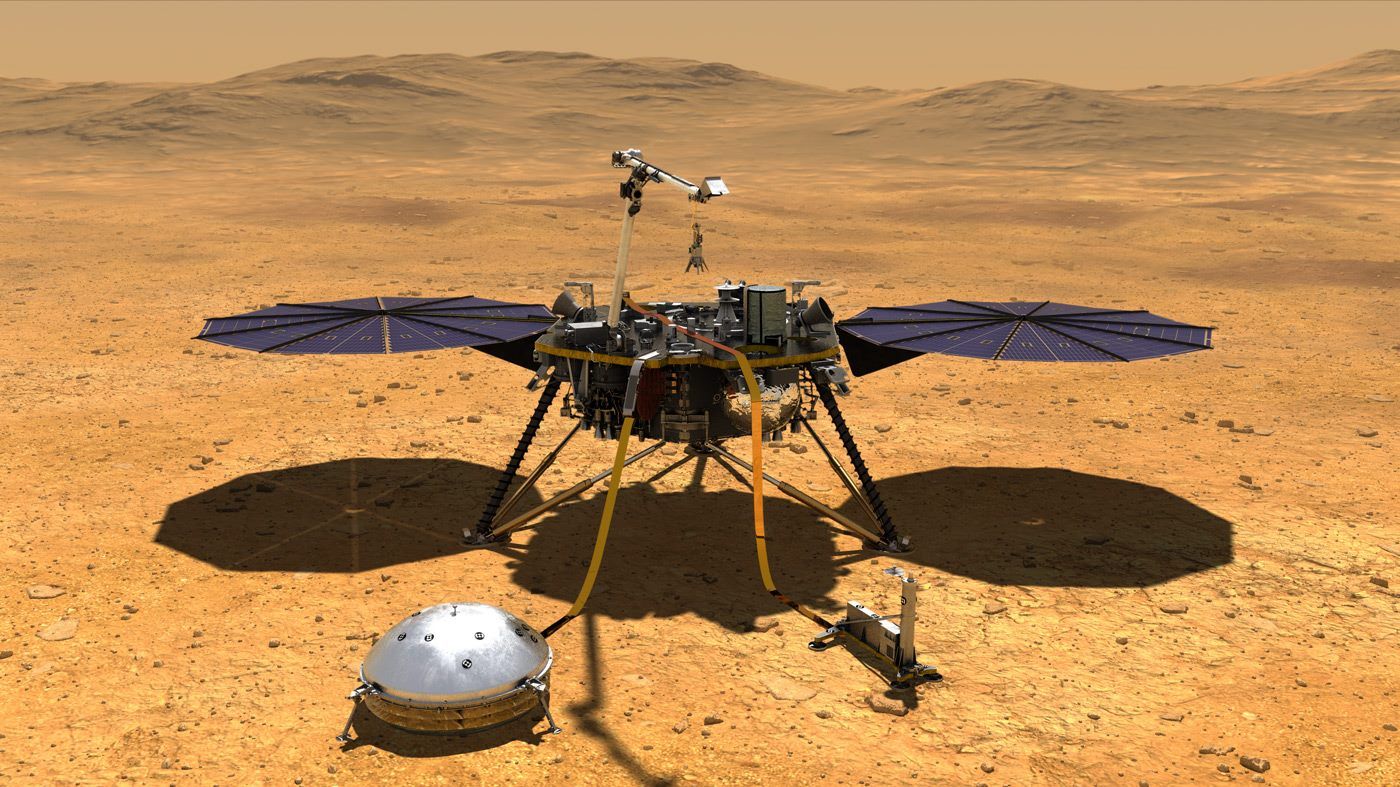
Our NASA InSight lander just needs some… — NASA — National Aeronautics and Space Administration
Posted by Michael Lance in category: space travel
Our NASA InSight lander just needs some peace and quiet to get its work done. After next week’s #MarsLanding, the spacecraft will study the entire Red Planet by… staying put. Learn how: https://go.nasa.gov/2FwIth3
Click on photo to start video.
This infrared tour of Jupiter’s north pole allows us to see deep inside the swirling clouds of the cyclones and anticyclones that permeate the planet’s polar regions. In the animation that uses data from our Juno spacecraft, the yellow areas are warmer (or deeper into Jupiter’s atmosphere) and the dark areas are colder (or higher up in Jupiter’s atmosphere). Take the virtual tour: https://go.nasa.gov/2Fwf7zm
Nov 19, 2018
At first glance, a bright blue crescent immediately jumps out of this image from our NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope
Posted by Michael Lance in categories: space, transportation
Is it a bird? A plane? No — it’s a galaxy. Take a closer look: https://go.nasa.gov/2FypUZL
Nov 19, 2018
Taurine transport gene sheds light on bad sleep
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: energy, neuroscience
Fruit flies and a common energy drink ingredient may help explain how the brain regulates sleep and how that regulation can go wrong.
Nov 19, 2018
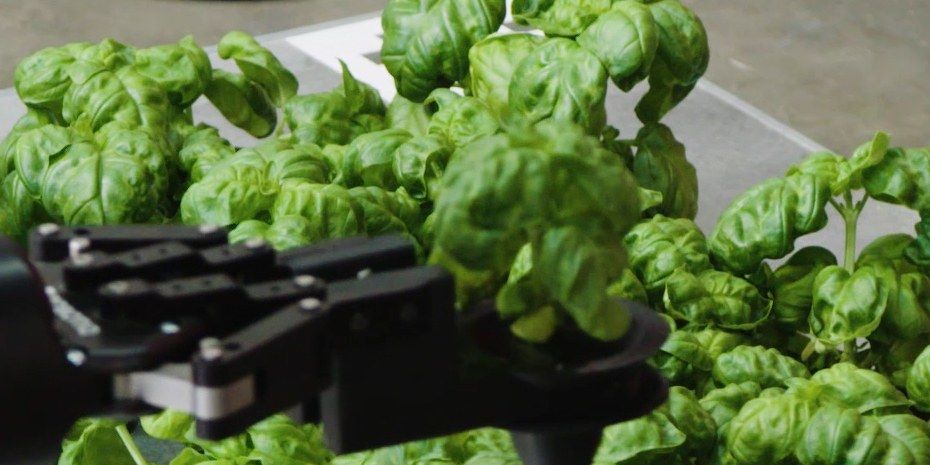
Are These Robots the Future of Farms?
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: food, robotics/AI, sustainability
Nov 19, 2018
Coming to terms with complexity: Eco-evolutionary dynamics under more than one selection pressure
Posted by Xavier Rosseel in categories: biotech/medical, evolution, genetics
We found that the evolution of anti-predatory defense in the prey species stabilized predator population size but that this was delayed in the presence of the abiotic stressor. This corresponded with a lack or delay in the evolution of resistance to the abiotic stressor. Therefore, the abiotic stressor had a big effect on the eco-evolutionary dynamics, weakening the evo-to-eco link. One might expect that this is caused by competition between (asexual) bacterial lineages possessing different adaptations, decreasing the rate and directionality of evolution under multiple selection pressures. Instead, the genomic investigation showed that different targets (genes or duplicated sites) were repeatedly mutated in the individual and combined treatments. The population genetics thus revealed complex mechanistic underpinnings for a seemingly sensible difference in dynamics. Perhaps a specific type of bacterial cell clumping or another adaptation is favored in the dual-stressor environment because of conferring a degree of resistance to both types of stressors? This could then direct the mutational path away from the optimal adaptations to the individual stressors.
It took us five years to disentangle the complex interplay between ecology and evolution in an experimental system consisting of bacteria, ciliates and antibiotics.