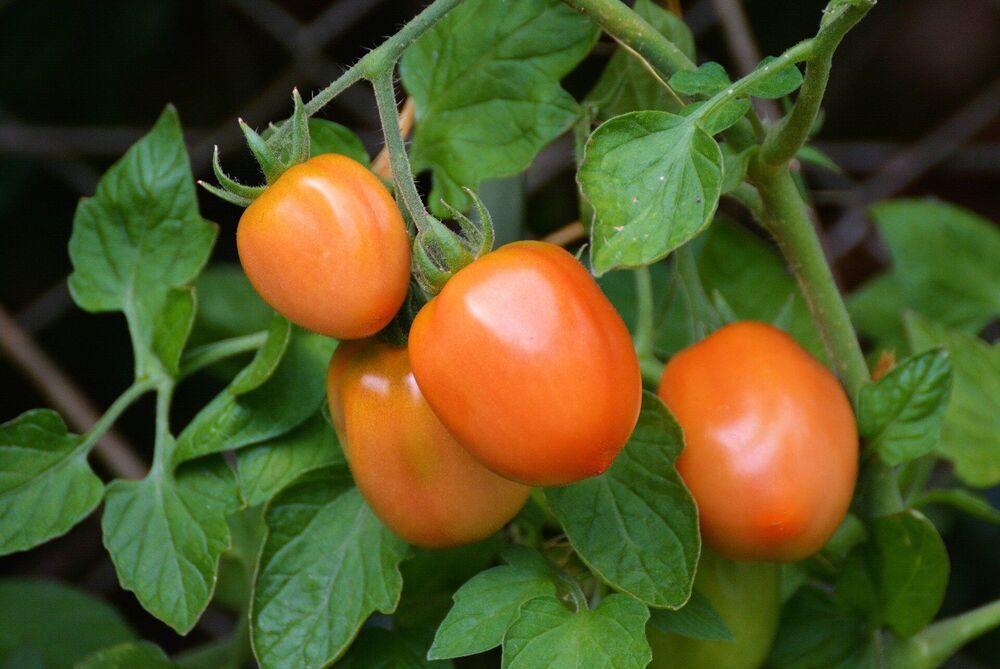
“Scientists found that a caterpillar called the tomato fruit worm not only chomps on tomatoes and their leaves, but also deposits enzyme-laden saliva on the plant, interfering with its ability to cry for help. If it all sounds a bit improbable, starting with the concept of plants crying for help, scientists also scoffed at that idea when it was first proposed a few decades ago. But it has been shown time and time again that when under attack, plants can emit chemical distress signals, causing their peers to mount some sort of defense. A classic example is the smell of a freshly mown lawn, which prompts the release of protective compounds in nearby blades of grass that have yet to be cut. In some cases, plant distress signals can even summon help from other species. That’s what happens with the tomato. When caterpillars nibble on the plant’s leaves, the leaf pores release volatile chemicals that are detected by a type of parasite: a wasp that lays eggs inside caterpillars. (Not to overwork the horror-movie analogy, but as with the hapless astronauts in the “Aliens” franchise, it doesn’t end well for the caterpillar.)”
While there’s a famous horror-movie spoof about killer tomatoes, no one seems to have made one about caterpillars—the insect pests that eat the juicy red fruits of summer.