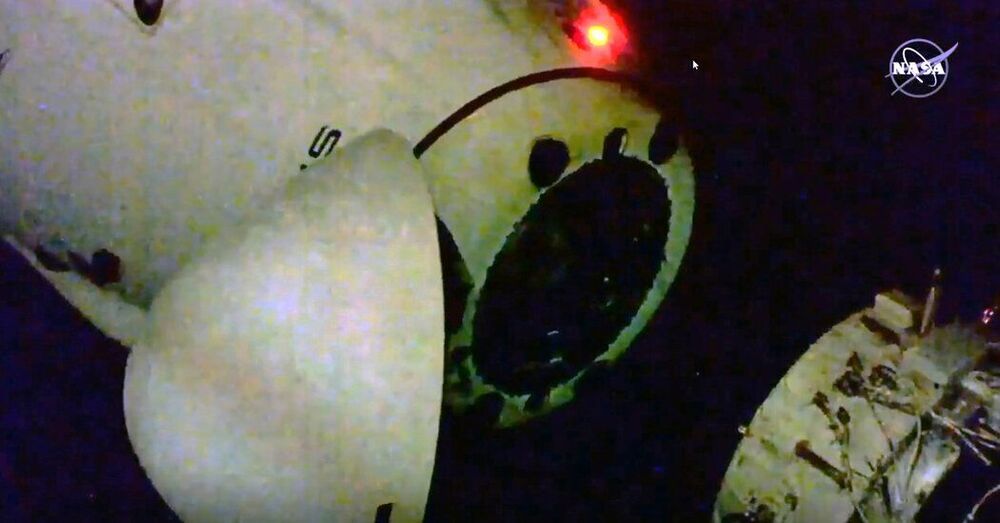
Crew-1, which launched to the space station in November, will head home in the capsule called Resilience.



Circa 2010
In a laboratory 10 miles east of downtown Los Angeles, a mechanical penis sputters to life. A technician starts a timer as a stream of water erupts from the apparatus’s brass tip, arcing into a urinal mounted exactly 12 inches away. James Krug smiles. His latest back-splatter experiment is under way.
Krug is an unusual entrepreneur. Twenty years ago, he was a rising star in the film and television business. He served as a vice president of the Disney Channel in the 1980s and ran a distribution company with members of the Disney family in the ’90s. But 11 years ago, Krug became convinced that the world did not need another TV show. What it needed was a better urinal.
Emmy award winning television commentator, radio personality, and newspaper columnist, juan williams, talking about inter-generational dynamics, ageism, and aging in america.
Progress, Potential, And Possibilities has the honor of being joined today by Emmy Award winning Television Commentator, Radio Personality, and Newspaper Columnist, Mr. Juan Williams.
Mr. Williams has been a Fox News Contributor since 1997 (including being a member of the nightly, current issue discussion show known as The Five), writes for several newspapers including The Washington Post, The New York Times, and The Wall Street Journal, and has been published in magazines such as The Atlantic Monthly and Time.
Mr. Williams was a senior news analyst for National Public Radio for 11 years and was at The Washington Post for 23 years, working as an editorial writer, op-ed columnist, White House correspondent and national correspondent.
Mr. Williams is an accomplished author with multiple books including Thurgood Marshall: American Revolutionary, Eyes on the Prize: America’s Civil Rights Years, and We the People: The Modern-Day Figures Who Have Reshaped and Affirmed the Founding Fathers’ Vision of America.
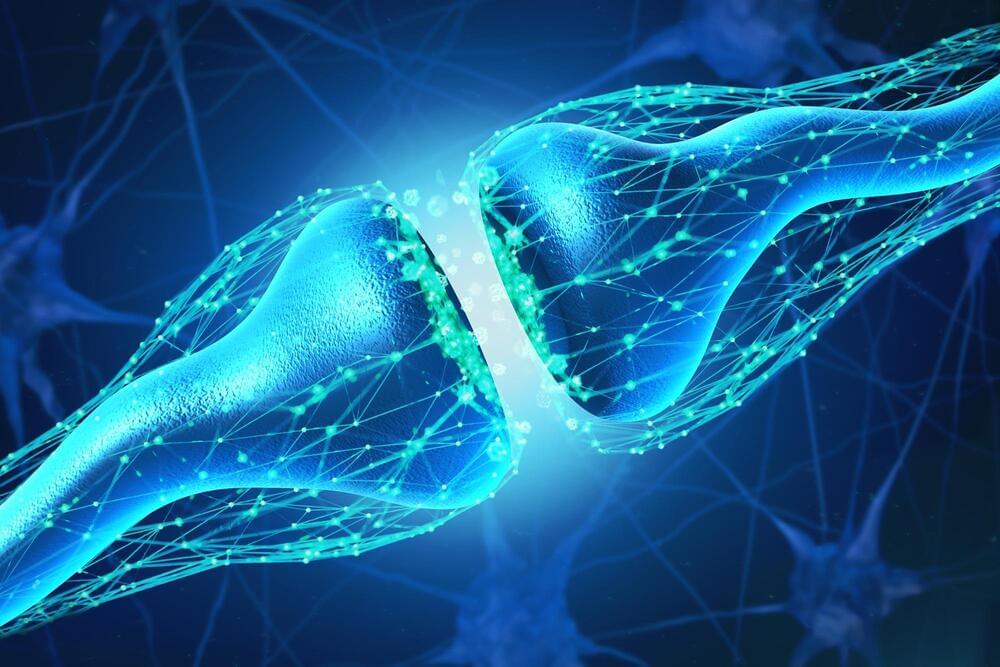



Researchers have developed a brain-like computing device that is capable of learning by association.
Similar to how famed physiologist Ivan Pavlov conditioned dogs to associate a bell with food, researchers at Northwestern University and the University of Hong Kong successfully conditioned their circuit to associate light with pressure.
The research will be published today (April 30, 2021) in the journal Nature Communications.
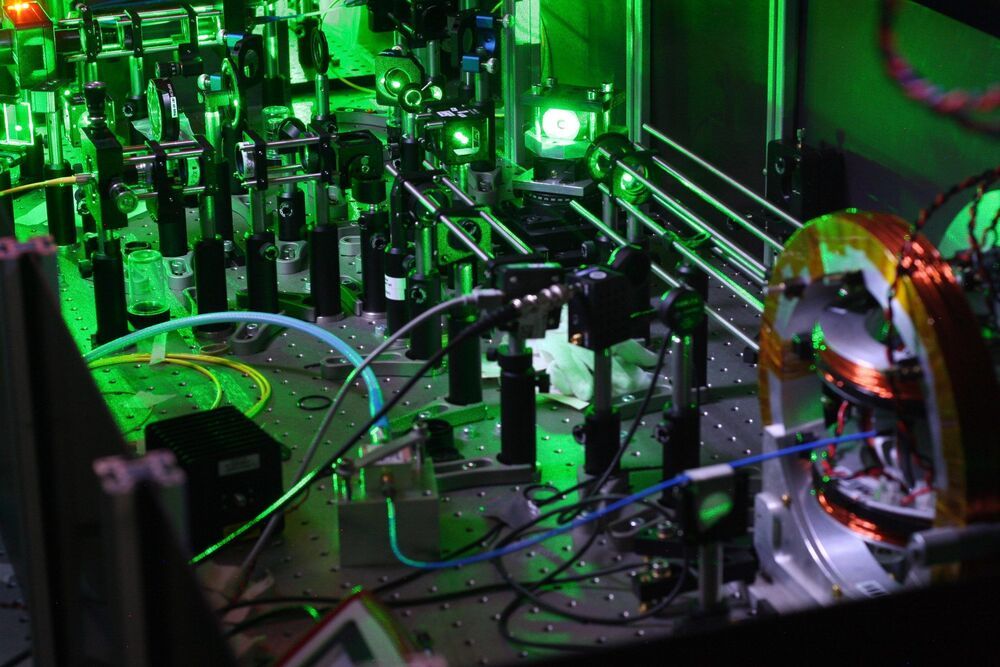


Protocol to reverse engineer Hamiltonian models advances automation of quantum devices.
Scientists from the University of Bristol ’s Quantum Engineering Technology Labs (QETLabs) have developed an algorithm that provides valuable insights into the physics underlying quantum systems — paving the way for significant advances in quantum computation and sensing, and potentially turning a new page in scientific investigation.
In physics, systems of particles and their evolution are described by mathematical models, requiring the successful interplay of theoretical arguments and experimental verification. Even more complex is the description of systems of particles interacting with each other at the quantum mechanical level, which is often done using a Hamiltonian model. The process of formulating Hamiltonian models from observations is made even harder by the nature of quantum states, which collapse when attempts are made to inspect them.

Oshkosh can make 100% battery-electric delivery trucks for the U.S. Postal Service, likely dashing Workhorse’s hopes of reigniting the competition.
Oshkosh Truck Corp. (NYSE: OSK) can make 100% battery-electric delivery trucks for the U.S. Postal Service, undercutting an assertion by Workhorse Group (NASDAQ: WKHS) that its being passed over for the contract dooms the mail service to remaining a source of planet-warming greenhouse gas emissions.
Not so, Oshkosh President and CEO John Pfeifer told analysts on the company’s fiscal second-quarter earnings call Wednesday.
“We can do 100% electric vehicles from Day One,” Pfeiffer said. “If the U.S. Postal Service came to us tomorrow and said, ‘We’ve got the funding to do 100% electric from 2023,’ we can do it.”