While SolarWinds rightly drew attention earlier this year, Moscow’s Fancy Bear group has been on a password-guessing spree this whole time.


It appears your susceptibility to a virus, and also the intensity of the viral load that goes on to attack if your defences are breached, are inextricably linked to your sleep quality and circadian clock.
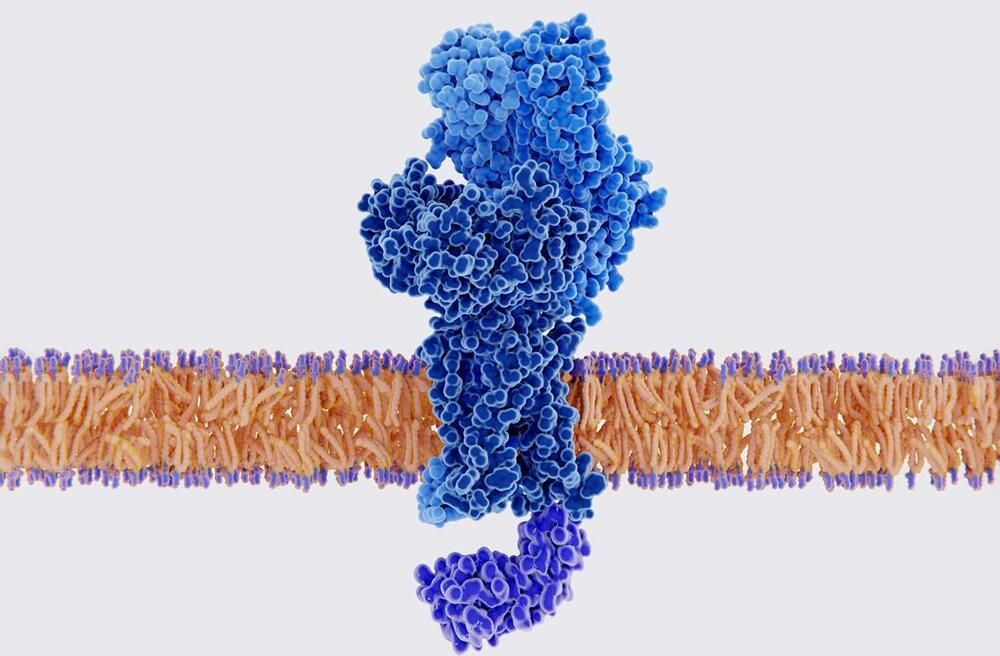
For the first time, an artificial molecular motor has been created that can ‘talk’ to living cells – by gently pulling their surface with enough physical force to elicit a biochemical response. The approach could help scientists decode the language that cells use to communicate with each other in tissues.
‘There is a mechanical language in the form of physical forces applied by the cells themselves, and we want to understand what information is communicated and what the consequences are,’ explains Aránzazu del Campo, who led the study at the Leibniz Institute for New Materials, Germany. ‘Ultimately, we want to be able to provide signals to cells and guide their function when they are not able to do that by themselves in disease cases.’
Usually, studying how cells communicate by sensing mechanical stimuli and producing biochemical responses requires prodding them with pipettes or the tip of an atomic force microscope. However, this doesn’t work at the more complex tissue level.
US$8.5 Billion In Funding — 150+ Projects
Dr. Maria Millan, MD, is the President and CEO of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM — https://www.cirm.ca.gov/), an organization that was created in 2004 when voters initially approved a state Proposition which allocated US$3 billion to fund this fascinating area of medicine, and which recently received an additional US$5.5 billion in renewed funding.
Dr. Millan is a physician-scientist who has devoted her career to treating and developing innovative solutions for children and adults with debilitating and life-threatening conditions.
After receiving her undergraduate degree from Duke University where she started her focus on immunology research, Dr. Millan obtained her MD degree and then went on to complete her surgical training and post-doctoral research at Harvard Medical School – Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
After a transplant surgery fellowship at Stanford University School of Medicine, Dr. Millan began her academic career with a pediatric and adult transplant surgery practice. In parallel, she continued her bench research at Stanford and became associate professor and director of the Pediatric Organ Transplant Program.




As smart watches are increasingly able to monitor the vital signs of health, including what’s going on when we sleep, a problem has emerged: Those wearable, wireless devices are often disconnected from our body overnight, being charged at the bedside.
“Quality of sleep and its patterns contain a lot of important information about patients’ health conditions,” says Sunghoon Ivan Lee, assistant professor in the University of Massachusetts Amherst College of Information and Computer Sciences and director of the Advanced Human Health Analytics Laboratory.
But that information can’t be tracked on smartwatches if the wearable devices are being charged as users sleep, which prior research has shown is frequently the case. Lee adds, “The main reason users discontinue the long-term use of wearable devices is because they have to frequently charge the on–device battery.”