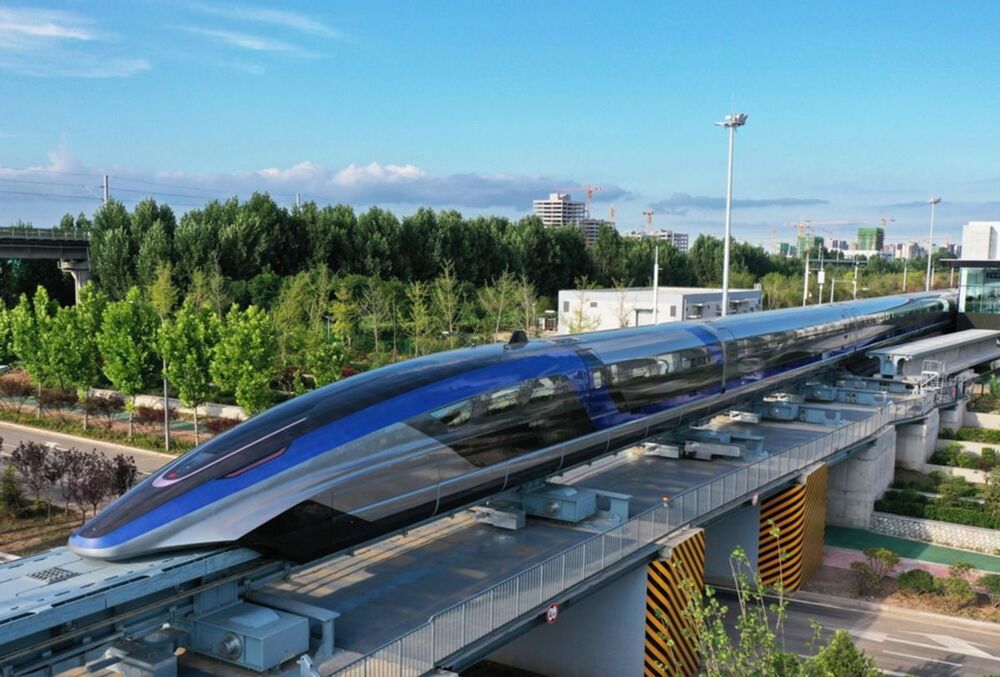
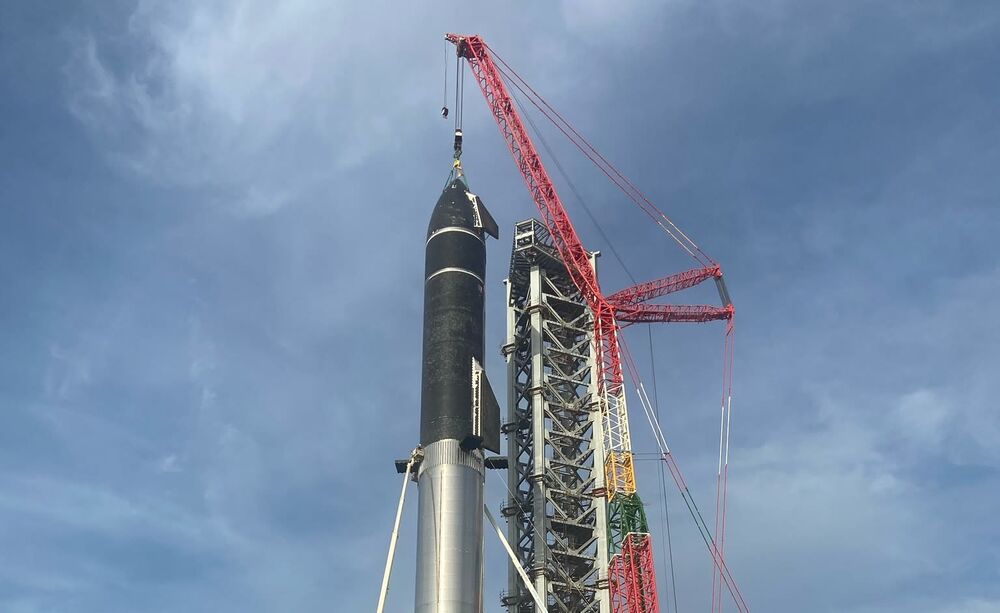
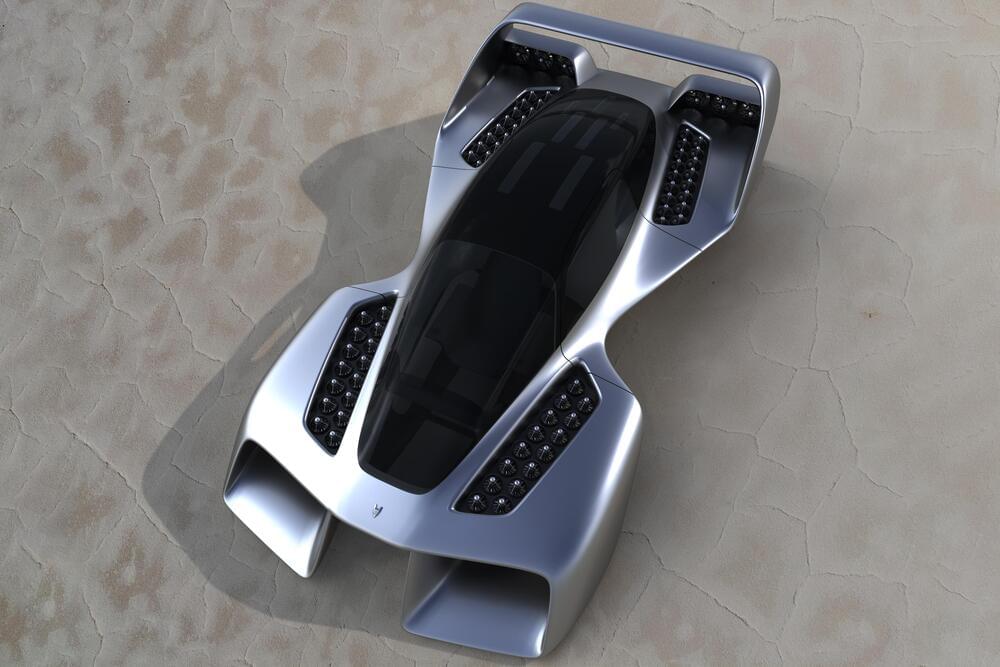
No, it’s not forbidden to innovate, quite the opposite, but it’s always risky to do something different from what people are used to. Risk is the middle name of the bold, the builders of the future. Those who constantly face resistance from skeptics. Those who fail eight times and get up nine.
(Credit: Adobe Stock)
Fernando Pessoa’s “First you find it strange. Then you can’t get enough of it.” contained intolerable toxicity levels for Salazar’s Estado Novo (Portugal). When the level of difference increases, censorship follows. You can’t censor censorship (or can you?) when, deep down, it’s a matter of fear of difference. Yes, it’s fear! Fear of accepting/facing the unknown. Fear of change.
What do I mean by this? Well, I may seem weird or strange with the ideas and actions I take in life, but within my weirdness, there is a kind of “Eye of Agamotto” (sometimes being a curse for me)… What I see is authentic and vivid. Sooner or later, that future I glimpse passes into this reality.