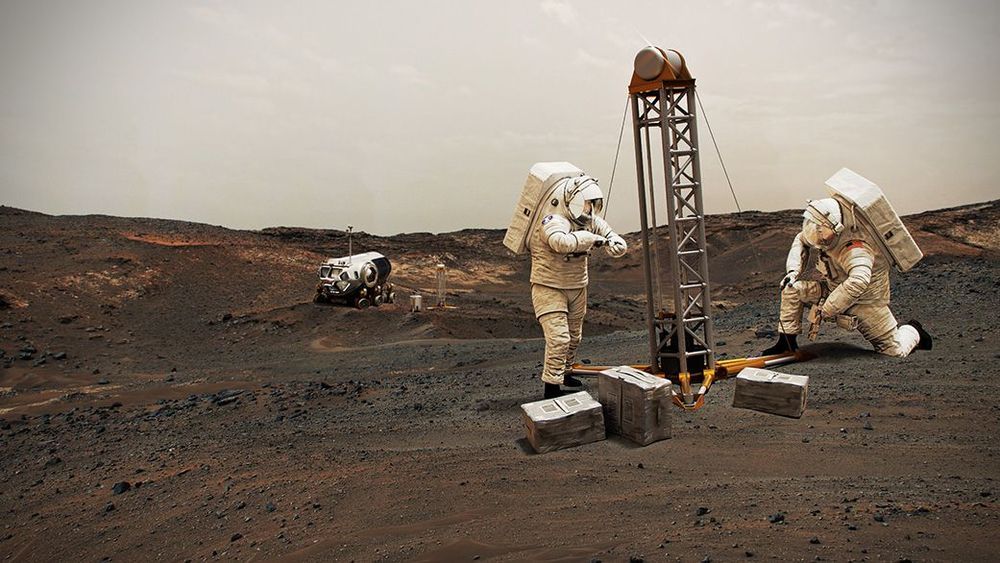
In a Q&A, spacesuit designer Amy Ross explains how five samples, including a piece of helmet visor, will be tested aboard the rover, which is targeting a July 30 launch.
NASA is preparing to send the first woman and next man to the Moon, part of a larger strategy to send the first astronauts to the surface of Mars. But before they get there, they’ll be faced with a critical question: What should they wear on Mars, where the thin atmosphere allows more radiation from the Sun and cosmic rays to reach the ground?
Amy Ross is looking for answers. An advanced spacesuit designer at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, she’s developing new suits for the Moon and Mars. So Ross is eagerly awaiting this summer’s launch of the Perseverance Mars rover, which will carry the first samples of spacesuit material ever sent to the Red Planet.