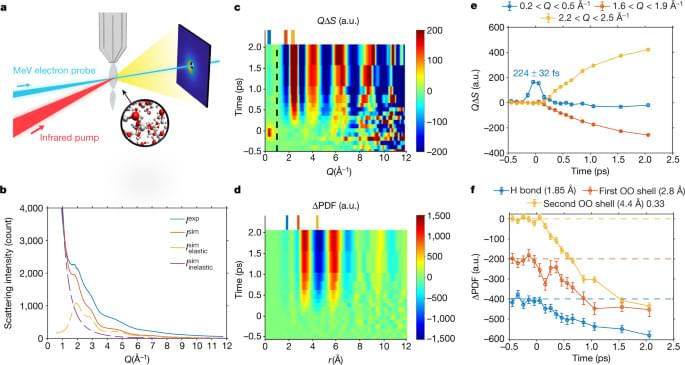
Liquid ultrafast electron scattering measures structural responses in liquid water with femtosecond temporal and atomic spatial resolution to reveal a transient hydrogen bond contraction then thermalization preceding relaxation of the OH stretch.
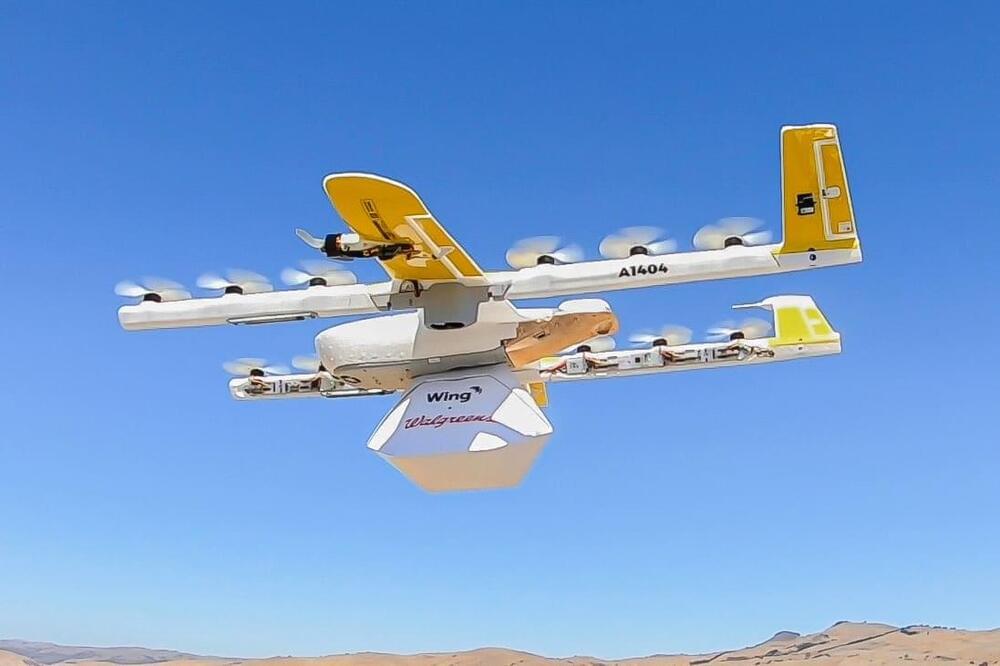



Alphabet’s Wing drone company allows users to order items such as food through a mobile app and is fast approaching 100,000 deliveries since its launch.
Alphabet’s drone company Wing delivered 10,000 cups of coffee, 1,700 snack packs and 1,200 roast chickens to customers in Logan, Australia, over the last year, the company said Wednesday in a blog post outlining its progress.
Wing was initially launched in 2019 in Australia, following a series of drone tests that began in 2014. The service, which was initially part of Alphabet’s experimental research division, allows users to order items such as food through a mobile app and is fast approaching 100,000 deliveries since its launch.
Wing hopes to one day deliver products to people all over the world without having to rely on drivers or delivery trucks like other companies. It’s the reason UPS, Uber and Amazon are also working on drone delivery.

Research indicates that flavonoids may protect against: high blood pressureTrusted Source heart attack and stroke type 2 diabetesTrusted Source certain types of cancer-medicalnewstoday.com
New research finds that people who consume foods high in flavonoids, such as berries, apples, and pears, have lower blood pressure than those who do not.
During an upcoming NASA mission, currently scheduled for an October lift-off, a spacecraft called Lucy will be the first to visit a fleet of primordial bodies trailing behind Jupiter. It will launch on the Atlas V 401 rocket.
The Lucy mission will be the first to explore the Trojan asteroids, a large group of asteroids that share Jupiter’s orbit around the Sun.

Okay, maybe not as big as the one in the picture.
Potatoes are my favorite vegetable; you can turn them into fries, bake them for an exquisite dish or mash them and eat them as a side dish. There are endless possibilities to cook a potato and what can be better than adding human fat gene in them to make them bigger and juicier?
Scientists have been experimenting with growing larger crops and it seems like they found the perfect solution; adding the human gene related to obesity and fat mass into the plants to yield super crops. The potato plants were inserted with a fat-regulating protein called FTO which changed the genetic code into producing extra proteins which resulted in large potatoes that were almost twice the size of regular ones grown from the same plant crop. “It [was] really a bold and bizarre idea. To be honest, we were probably expecting some catastrophic effects,” said Chuan He, a chemist at University of Chicago.

Circa 2020 o.o!
Researchers have created a miniature version of supernova shock waves in a lab here on Earth to solve a long-standing cosmic mystery.
When stars die and explode in supernovas, they create shock waves that emanate across the surrounding plasma. These powerful shock waves blast out cosmic rays, or highly energetic particles, out into the universe. The waves act almost like particle accelerators, pushing these particles out so fast that they approach the speed of light. However, scientists have yet to fully understand exactly how and why the shock waves accelerate these particles.
Magnetic excitations in multiferroic materials accompany electric polarization, known as electromagnons. The authors develop here a general framework to study electric polarization and nonlinear optical responses of noncentrosymmetric magnets based on spin models. They theoretically demonstrate the optical excitation of electromagnon-induced dc current generation (i.e., a photovoltaic effect) from the so-called shift current mechanism.