Jun 15, 2016
Physicists have mixed matter and light at room temperature for the first time
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: particle physics, quantum physics
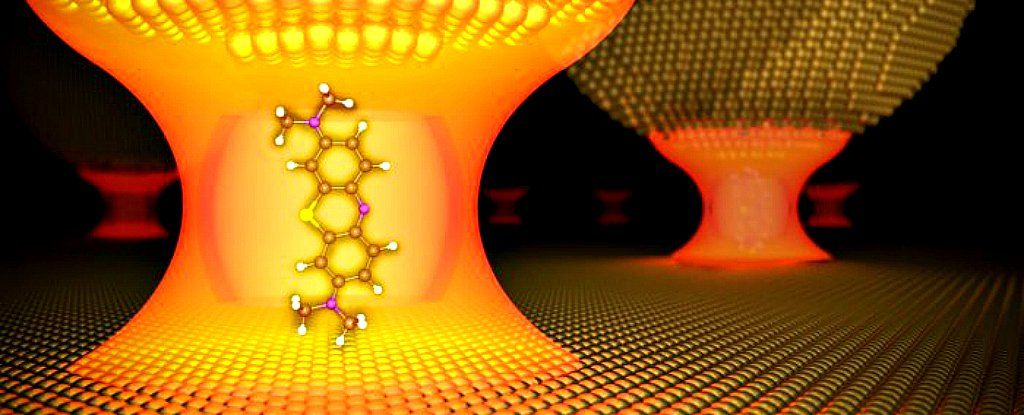
In a lovely demonstration of light’s quantum effects, physicists in the UK have just mixed a molecule with light at room temperature for the first time ever.
Light and matter are usually separate, with totally distinct properties, but now scientists have trapped a particle of light — called a photon — with a molecule in a tiny, golden cage of mirrors.
That’s a big deal, because it creates a whole new way to manipulate the physical and chemical properties of matter, and could change the way we process quantum information.
Continue reading “Physicists have mixed matter and light at room temperature for the first time” »