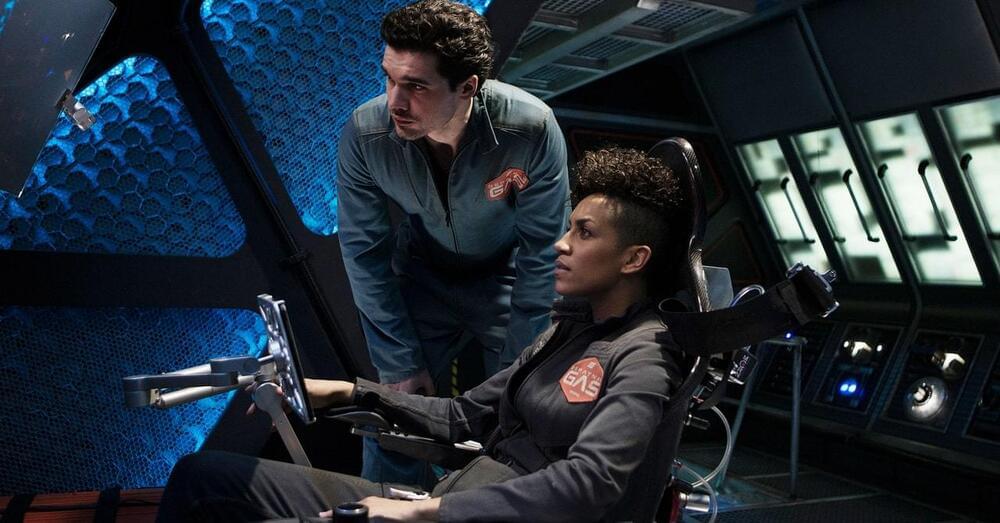
In a scene from season one, Jim Holden shows exquisite command of high school physics as he maneuvers himself onto a spaceship gangway.
As a fan of science fiction and science, I have to say that The Expanse has a bunch of great science. It’s not just the science in the show. The characters also seem to demonstrate an understanding of physics. One scene from the first season stands out in particular as a classic physics example.
I guess I should give a spoiler alert, but I’m not really giving away any major plot elements. But you have been warned.
OK, since you are still here let me describe the scene. Two main characters (Jim and Naomi) are running on a gangway connected to a spaceship. This gangway is inside a bigger ship that is accelerating (with the engines on) to produce artificial gravity. But wait! They are under fire. Some other dude wants to stop them from getting into the ship, so he fires his weapon. Eventually, someone shoots an important part of the bigger spaceship and its engines cut off. With no thrust, Jim and Naomi lose their artificial gravity and start floating off the gangway. They have magnetic boots, but the boots only work on the gangway. They are doomed.