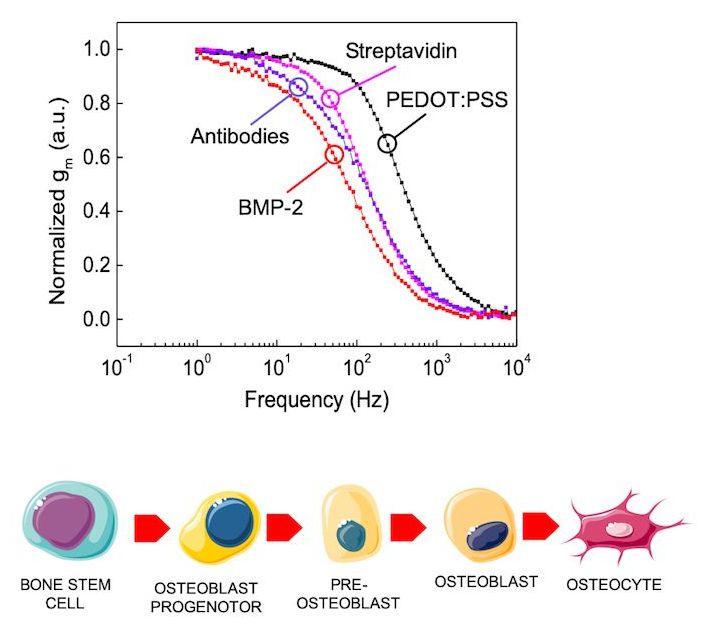
New technique detects real-time concentrations of an important cytokine molecule secreted as stem cells transform into bone.
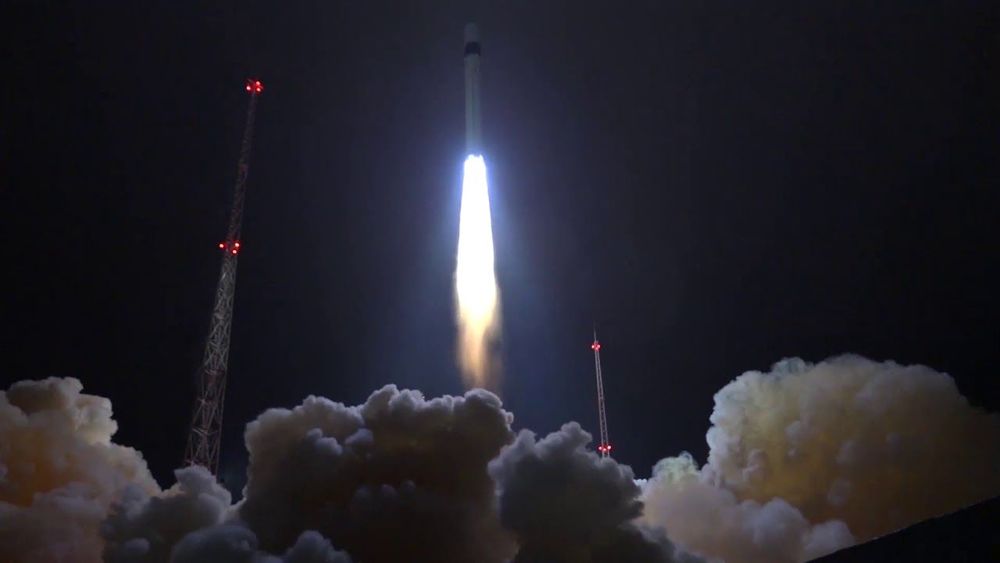
The final Rockot booster converted from an intercontinental ballistic missile launched into space Friday (Dec. 27) carrying a trio Russian satellites and a military payload into orbit.
The Rockot, a launch vehicle based on Russia’s RS-18 ballistic missile, launched three Gonets-M communications satellites into space from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome in northern Russia. The rocket also reportedly carried a military payload called Blits-M, a glass sphere designed to serve as a laser reflector, according to Russianspaceweb.com, which tracks the Russian space industry.
Syd Mead, creator of amazing vehicles and the universe of the movie “Blade Runner” died on December 30 at the age of 86.
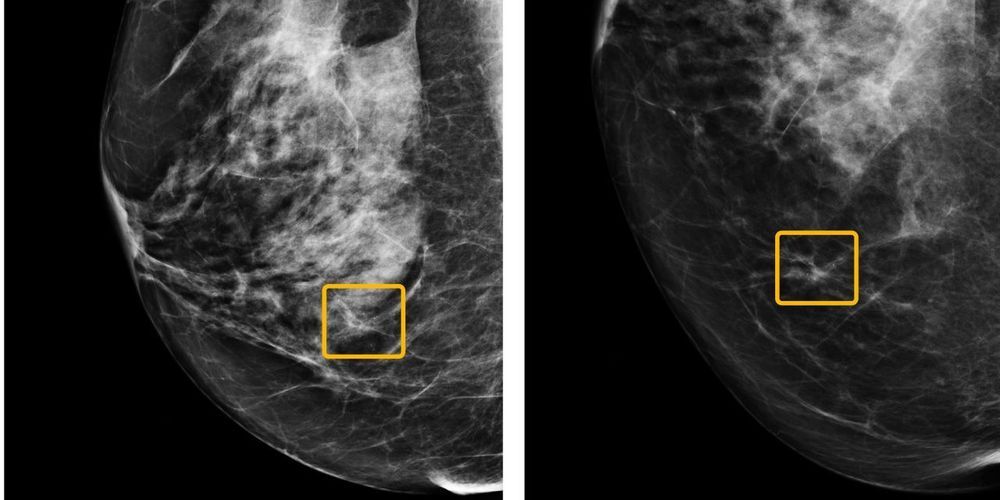
Google’s health research unit said it has developed an artificial-intelligence system that can match or outperform radiologists at detecting breast cancer, according to new research. But doctors still beat the machines in some cases.
The model, developed by an international team of researchers, caught cancers that were originally missed and reduced false-positive cancer flags for patients who didn’t actually have cancer, according to a paper published on Wednesday in the journal Nature. Data from thousands of mammograms from women in the U.K. and the U.S. was used to train the AI system.
But the algorithm isn’t yet ready for clinical use, the researchers said.
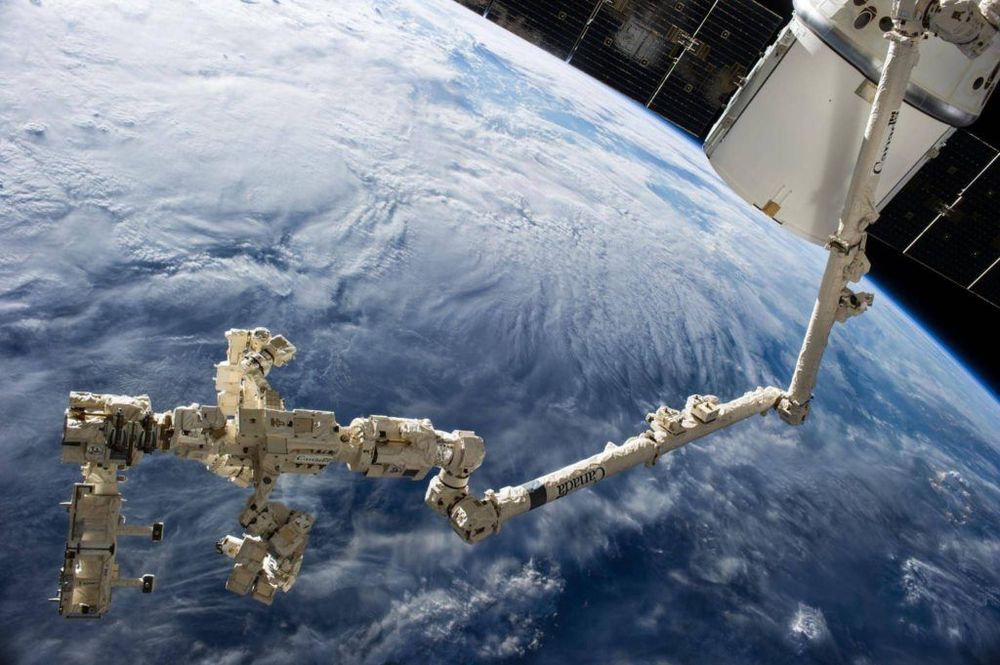
MDA created the Canadarm robotic manipulator. | Credit: MDA
In 2019, The Robot Report tracked 68 mergers and acquisitions for companies in the robotics industry, as of press time. This included 30 mergers and acquisitions through the first half of the year.
In many cases, the companies involved did not disclose the terms of their deal. For example, self-driving car maker Waymo recently acquired U.K.-based startup Latent Logic, but it did not reveal the purchase price. So the list consists only of mergers and acquisitions for which we know the terms.
Elon Musk founded SpaceX in 2002 with the goal of populating outer space. But in the nearly 18 years since – and even as the rocket company continues to disrupt the global launch industry – the most complex life-form SpaceX has flown is a mouse.
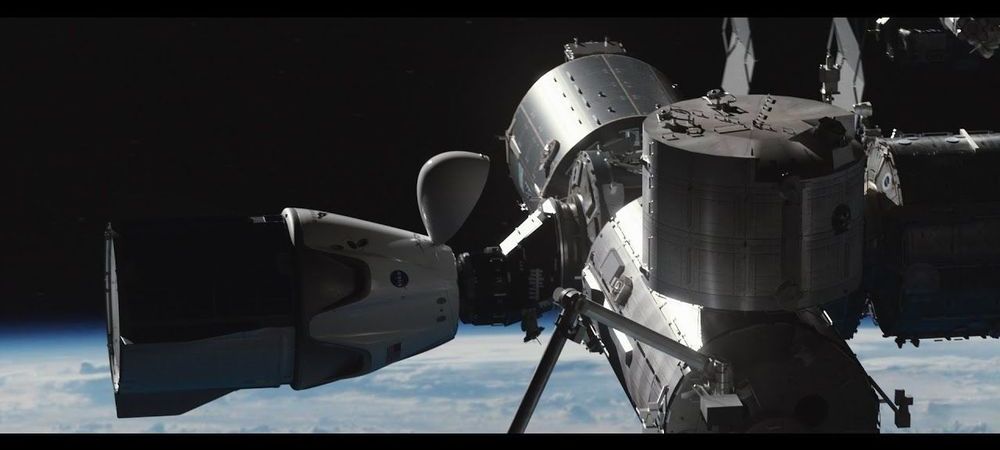
That should all change in early 2020, though, as SpaceX prepares to launch its first crewed mission aboard its new capsule-like spaceship, called Crew Dragon.
The NASA astronauts and spaceflight veterans Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley are set to board the Crew Dragon, rocket into orbit 250 miles above Earth, and dock with the football-field-size International Space Station.
Distances in the expanding Universe don’t work like you’d expect. Unless, that is, you learn to think like a cosmologist.
In a study published Jan. 1 in Nature, researchers from Google Health, and from universities in the U.S. and U.K., report on an AI model that reads mammograms with fewer false positives and false negatives than human experts. The algorithm, based on mammograms taken from more than 76,000 women in the U.K. and more than 15,000 in the U.S., reduced false positive rates by nearly 6% in the U.S., where women are screened every one to two years, and by 1.2% in the U.K., where women are screened every three years. The AI model also lowered false negatives by more than 9% in the U.S. and by nearly 3% in the U.K.
Working with medical experts, engineers at Google Health have created an AI model that lowers false positive and false negative rates for mammogram breast cancer screening.
Playing with fire can be dangerous and never more so than when confined in a space capsule floating 250 miles above the Earth. But in the past week astronauts onboard the International Space Station have intentionally lit a series of blazes in research designed to study the behaviour of flames in zero gravity.
The scientists behind the experiment, called Confined Combustion, say it will help improve fire safety on the ISS and on future lunar missions by helping predict how a blaze might progress in low gravity conditions.
Dr Paul Ferkul, of the Universities Space Research Association, who is working on the project, said: “That is the immediate and most practical goal since NASA can use the knowledge to improve material selection and fire safety strategies.”