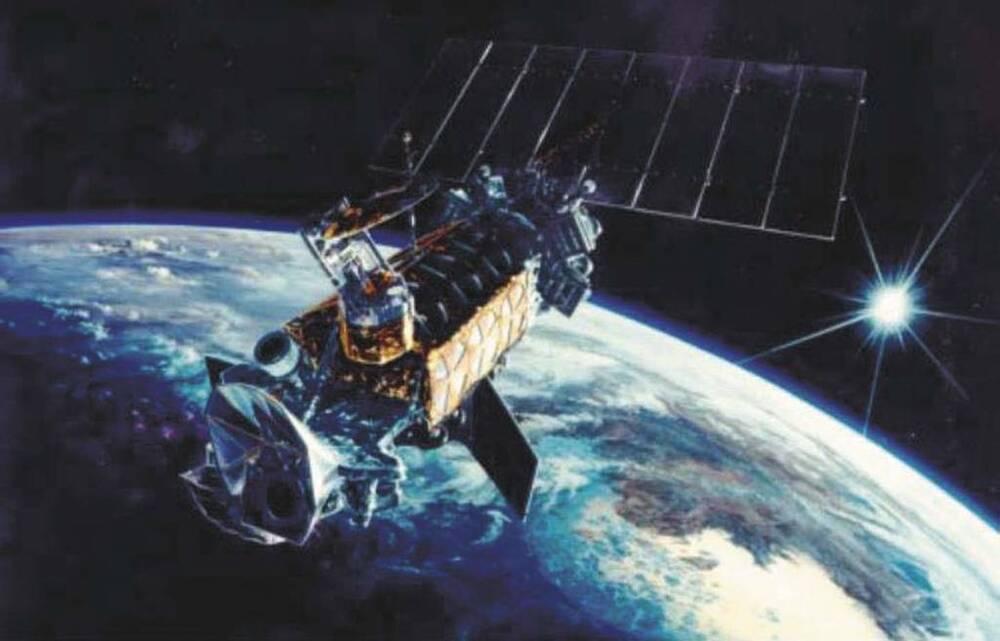
The new prototype is part of a program designed to replace the aging Defense Meteorological Satellite Program satellites on orbit.
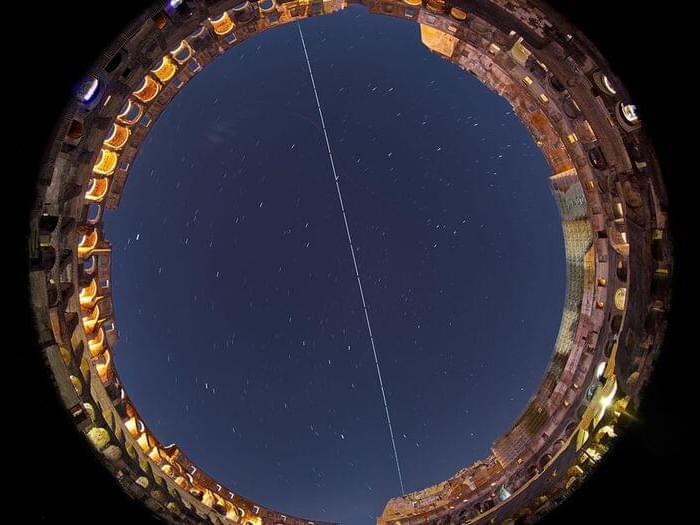



“Looking at the starry sky, with those thousand-year-old walls embracing the ancient constellations and the passing, modern ISS, was undoubtedly a once-in-a-lifetime experience,” Masi said in a statement on Thursday.
Masi also released an annotated version of the image showing constellations marked and labeled, from Pegasus to Ursa Minor.
The Colosseum is nearly 2,000 years old. The ISS has been in space for over 20 years. They are very different kinds of monuments, but they meld together beautifully in an image that speaks to the past and the present and how far humans have traveled.
A zoom into M87’s monster black hole, thanks to Hubble.
The supermassive black hole located at the heart of the M87 galaxy is home to one of the most impressive natural patterns in nature.

In this short video, filmed at ASTRO 2021, Siemens Healthineers’ Gabriel Haras introduces the company’s portfolio of artificial intelligence (AI)-based products. Such technologies support the entire care pathway for cancer patients, from screening and diagnostics to treatment and follow-up, including innovations such as AI-based autocontouring and generation of synthetic CT from an MRI scan for radiotherapy planning.
Next, Varian’s Kevin O’Reilly comments on the combining of Varian and Siemens Healthineers into one united company. He notes that the integration of AI capabilities has increased Varian’s ability to innovate, and will help accelerate its intelligent cancer care strategy: accelerating the path to treatment, increasing global access to care, exploiting data-driven insight and improving personalization.
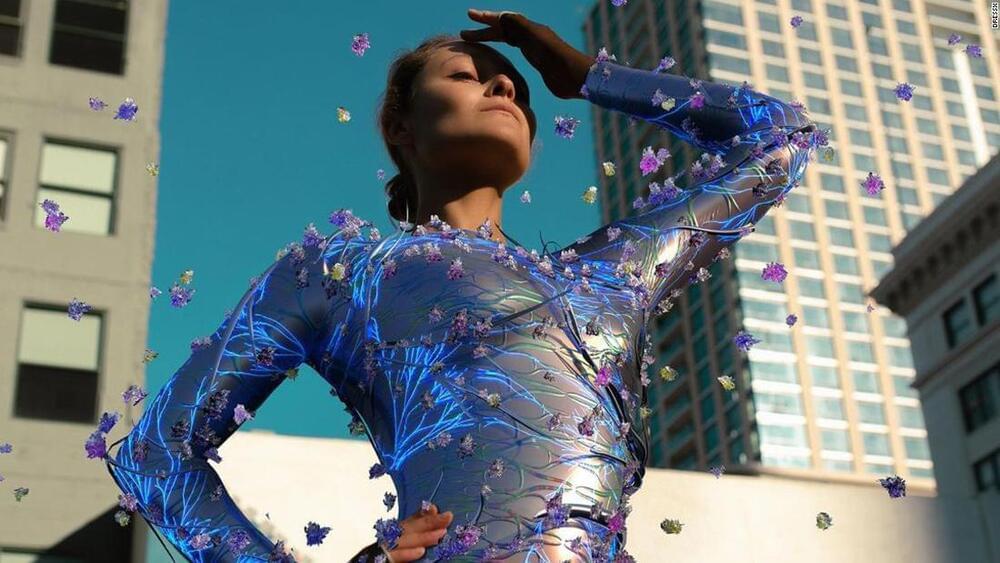

Digital fashion marketplaces have recently opened, including DressX, hoping that shoppers will be keen to start a virtual wardrobe. Credit: DressX
Outfitting our digital personas is nothing new, from making pixelated Dollz in the early 2000s to shopping these days for new wardrobe additions in Animal Crossing. The video game industry has more recently laid the groundwork for digital fashion, with outfits or “skins,” in games like Overwatch and Fortnite generating billions in revenue.
Some major fashion players have already begun capitalizing on the gaming market — in 2019, Louis Vuitton designed skins for League of Legends, and Nike and Ralph Lauren have this year offered avatar accessories through the virtual world-building platform Roblox. Outside of gaming environments, NFTs — or non-fungible tokens, which use blockchain technology to verify ownership of digital assets — have allowed digital fashion to be monetized more broadly as well. (This fall, Dolce & Gabbana’s NFT collection sold out for 1,885.719 ETH, at the time equivalent to $6 million).
2021 saw massive growth in the demand for edge computing — driven by the pandemic, the need for more efficient business processes, as well as key advances in the Internet of Things, 5G and AI.
In a study published by IBM in May, for example, 94 percent of surveyed executives said their organizations will implement edge computing in the next five years.
From smart hospitals and cities to cashierless shops to self-driving cars, edge AI — the combination of edge computing and AI — is needed more than ever.
Kindly see my latest FORBES article on technology predictions for the next decade:
Thanks and have a great weekend! Chuck Brooks.
We are approaching 2022 and rather than ponder the immediate future, I want to explore what may beckon in the ecosystem of disruptive technologies a decade from now. We are in the initial stages of an era of rapid and technological change that will witness regeneration of body parts, new cures for diseases, augmented reality, artificial intelligence, human/computer interface, autonomous vehicles, advanced robotics, flying cars, quantum computing, and connected smart cities. Exciting times may be ahead.
By 2032, it will be logical to assume that the world will be amid a digital and physical transformation beyond our expectations. It is no exaggeration to say we are on the cusp of scientific and technological advancements that will change how we live and interact.
What should we expect in the coming decade as we begin 2022? While there are many potential paradigms changing technological influences that will impact the future, let us explore three specific categories of future transformation: cognitive computing, health and medicine, and autonomous everything.

A new study claims machine learning is starting to look a lot like human cognition.
In 2019, The MIT Press Reader published a pair of interviews with Noam Chomsky and Steven Pinker, two of the world’s foremost linguistic and cognitive scientists. The conversations, like the men themselves, vary in their framing and treatment of key issues surrounding their areas of expertise. When asked about machine learning and its contributions to cognitive science, however, their opinions gather under the banner of skepticism and something approaching disappointment.
“In just about every relevant respect it is hard to see how [machine learning] makes any kind of contribution to science,” Chomsky laments, “specifically to cognitive science, whatever value it may have for constructing useful devices or for exploring the properties of the computational processes being employed.”
While Pinker adopts a slightly softer tone, he echoes Chomsky’s lack of enthusiasm for how AI has advanced our understanding of the brain:
“Cognitive science itself became overshadowed by neuroscience in the 1990s and artificial intelligence in this decade, but I think those fields will need to overcome their theoretical barrenness and be reintegrated with the study of cognition — mindless neurophysiology and machine learning have each hit walls when it comes to illuminating intelligence.”
Full Story:
Albert Einstein and Stephen Hawking – the most famous physicists of the twentieth century — both spent decades trying to find a single law that could explain how the world works on the scale of the atom and on the scale of galaxies. In short, the Standard Model describes the physics of the very small. General relativity describes the physics of the very large. The problem? The two theories tell different stories about the fundamental nature of reality. Einstein described the problem nearly a century ago in his 1923 Nobel lecture 0, telling the audience that a physicist who searches for, “an integrated theory cannot rest content with the assumption that there exist two distinct fields totally independent of each other by their nature.” Even while on his deathbed, Einstein worked on a way to unite all the laws of physics under one unifying theory.

5G will probably not hurt you, but having these products anywhere around definitely will.
5G is rapidly overtaking other wireless technology networks and may very soon become the standard for cell phone coverage. But there has been a lot of backlash with protesters stating the technology might be harmful to human health.
This has resulted in a rise of anti-5G products that claim to protect against the supposedly harmful radiation. A lot of these products have been discovered to be scams and now a new report from BBC reveals they may actually be dangerous.
The Dutch authority for nuclear safety and radiation protection (ANVS) issued a warning about ten products it found to be radioactive, and anti 5G necklaces were found to be one of them. The ANVS warned that these products could cause harm with long-term wear.
“Don’t wear it anymore, put it away safely and wait for the return instructions,” the ANVS said in a statement.
“The sellers in the Netherlands known to the ANVS have been told that the sale is prohibited and must be stopped immediately and that they must inform their customers about this.”
For the most part, scientists claim that 5G is actually safe. The World Health Organization has stated that 5G mobile networks are not that different from existing 3G and 4G signals making them completely harmless.