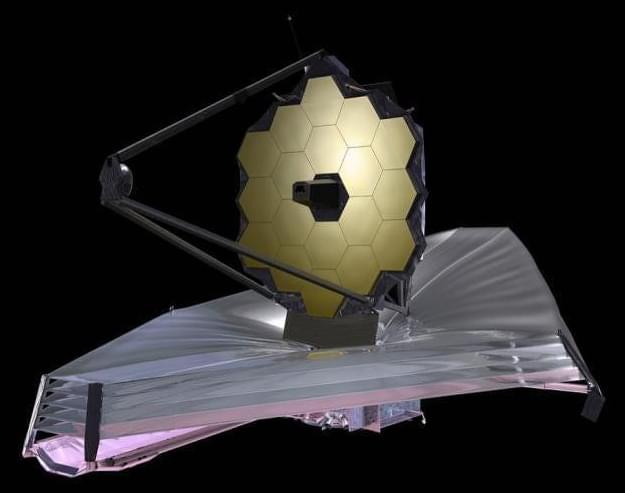
If December 22’s launch goes as planned then the engineers behind the $10 billion James Webb Space Telescope (JWST or “Webb” for short) are in for a nervous Christmas.
Forget that it was originally conceived in the 1990s and was first expected to launch in 2007. Forget also the initial rocket launch—usually viewed as the most nerve-wracking moment. This time it’s not the European Space Agency’s Ariane 5 rocket—due to lift Webb into space from the Guiana Space Center, Kourou, French Guiana on December 18, 2021—that’s giving engineers sleepless nights. It’s the 29 days of “space origami” they’ll have to endure after the launch as Webb unfolds from its collapse state into a “giant sunflower.”
You see, the technological marvel that is Webb is fully assembled, but folded into the 5.4 meter/17.7ft. fairing of the Ariane 5 for launch—the largest rocket fairing NASA could find. When it’s in-situ a whopping million miles/1.5 million kilometers from Earth at the second Lagrange point (L2) —almost certainly too far away for astronauts to fix if the worst happens—it will resemble a huge sunflower once unfurled.