
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


AI’s Impact On Biotechnology
Biotechnology is a curious marriage of two seemingly disparate worlds. On one end, we have living organisms—wild, unpredictable celestial creations that can probably never be understood or appreciated enough, while on the other is technology—a cold, artificial entity that exists to bring convenience, structure and mathematical certainty in human lives. The contrast works well in combination, though, with biotechnology being an indispensable part of both healthcare and medicine. In addition to those two, there are several other applications in which biotechnology plays a central role—deep-sea exploration, protein synthesis, food quality regulation and preventing environmental degradation. The increasing involvement of AI in biotechnology is one of the main reasons for its growing scope of applications.
So, how exactly does AI impact biotechnology? For starters, AI fits in neatly with the dichotomous nature of biotechnology. After all, the technology contains a duality of its own—machine-like efficiency combined with the quaintly animalistic unpredictability in the way it works. In general terms, businesses and experts involved in biotechnology use AI to improve the quality of research and for improving compliance with regulatory standards.
More specifically, AI improves data capturing, analysis and pattern recognition in the following biotechnology-based applications:

Engineers Have Created a Gecko-Inspired Hand That Can Hold an Egg
Now, Stanford engineers have created a new robotic hand, designed with finger pads that can grip like a gecko in order to be able to grip at just the right strength, according to the publication in Science Robotics.
“Anthropomorphic robotic manipulators have high grasp mobility and task flexibility but struggle to match the practical strength of parallel jaw grippers. Gecko-inspired adhesives are a promising technology to span that gap in performance, but three key principles must be maintained for their efficient usage: high contact area, shear load sharing, and evenly distributed normal stress,” write the authors in their study. “This work presents an anthropomorphic end effector that combines those adhesive principles with the mobility and stiffness of a multiphalange, multifinger design.”
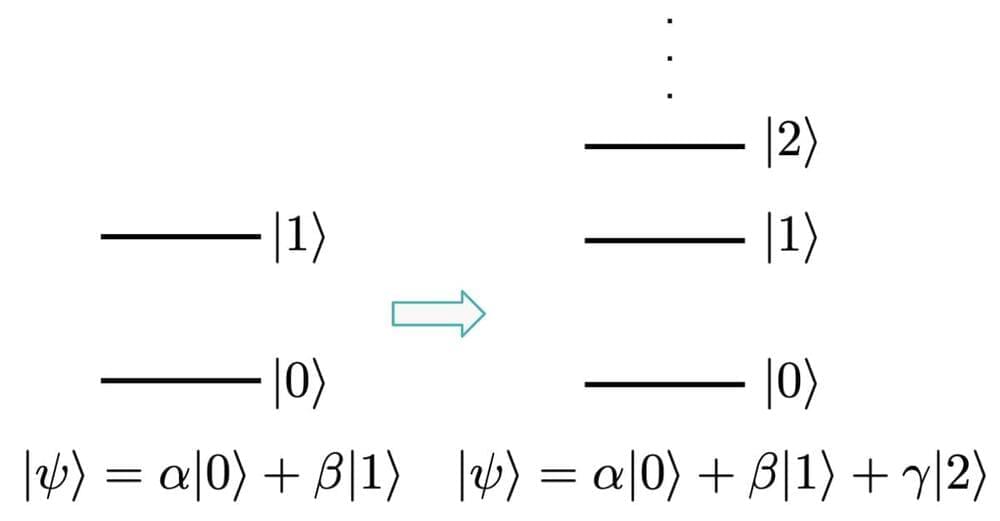
Beyond Qubits: Unlocking the Third State in Quantum Processors
By Alex Hill, Senior Quantum Systems Engineer
Qubits are the basic building block of a quantum processor, and are so named because they represent a continuum of complex superpositions of two basic quantum states. The power of qubits comes in part from their ability to encode significantly more information than a classical bit — an infinite set of states between 0 and 1. In mathematical terms, quantum gates that manipulate the state of individual qubits are unitary operators drawn from SU.
Rigetti’s superconducting quantum processors are based on the transmon design [1]. Each physical qubit is an anharmonic oscillator, meaning that the energy gaps between subsequent qubit energy states decrease as the qubit climbs higher up the state ladder. We typically only address the first two states, 0 and 1 (in the literature, sometimes referred to as g(round) and e(xcited)); however, the design of our qubits supports even higher states. The simple structure of the transmon energy levels gives superconducting qubits the unique ability to address many of these states in a single circuit.

US concerns grow over potential Russian cyber targeting of Ukraine amid troop buildup
The increase in tensions between the United States and Russia due to Moscow amassing troops on the border with Ukraine is raising concerns Russia may not only put boots on the ground but also turn to hacking operations to put pressure on the U.S. and Ukraine.
Those concerns are underlined by massive hacking efforts by Russia against Ukraine over the past few years and the ransomware attacks linked to Russian hackers against critical U.S. organizations.
“This is a Russian calling card,” Mark Montgomery, senior director of the Center on Cyber and Technology Innovation at the Foundation for Defense of Democracies, told The Hill Wednesday. “I do worry that they will use their cyber and disinformation tools to try to undermine the stability of the Ukrainian economic security and national security.”


Suspected Chinese hackers breach more US defense and tech firms
A suspected Chinese hacking campaign has breached four more US defense and technology companies in the last month, and hundreds more US organizations are running the type of vulnerable software that the attackers have exploited, according to research shared with CNN.
The apparent espionage activity, which the National Security Agency helped investigate when it emerged in recent months, is more extensive than previously known and has seen the hackers steal passwords from targeted organizations with a goal of intercepting sensitive communications.
The cybersecurity researchers in November publicly confirmed just one victimized US organization, CNN reported then, but they now say the number is at least five and could continue to grow.


NASA’s Webb Space Telescope Confirmed for December 24 Launch
The James Webb Space Telescope is confirmed for the target launch date of December 24, at 7:20 a.m. EST.
Late on December 17, teams at the launch site successfully completed encapsulation of the observatory inside the Ariane 5 rocket that will launch it to space. Webb’s final launch readiness review will be held on Tuesday, December 21 and, if successful, roll-out is planned for Wednesday, December 22.