As AI and brain technology advance, scientists warn understanding of consciousness and awareness is lagging behind, raising ethical questions.


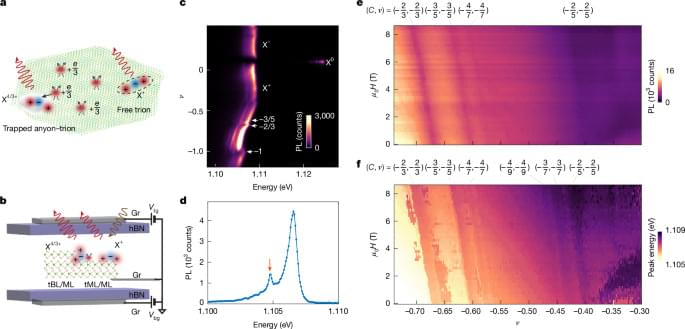
Physicists have uncovered surprising order inside one of the most puzzling states in modern materials science. It is a strange middle ground where electrons begin to behave differently, but full superconductivity has not yet taken hold.
Instead of falling into disorder, the system retains coordinated patterns right at the point where normal electrical behavior starts to break down. The finding suggests this transition is guided by an underlying structure, not randomness.
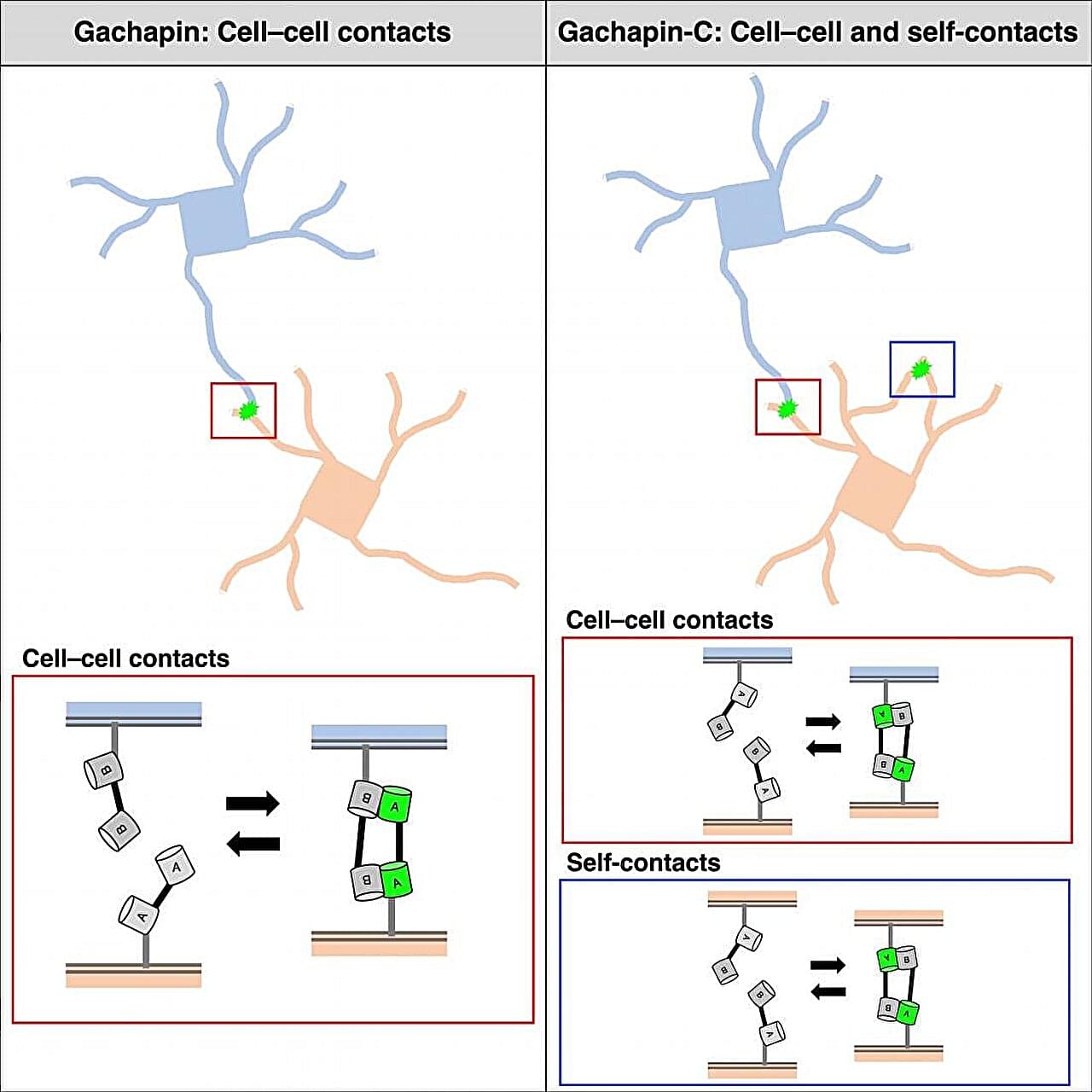
Living organisms are made up of hundreds of thousands of cells that cooperate to create the organs and systems that breathe, eat, move, and think. Now, researchers from Japan have developed a new way to track how and when cells touch each other to work together in these ways. In a study published in January in Cell Reports Methods, researchers from The University of Osaka reported the development of fluorescent markers for monitoring cell communication under a microscope.
Cells communicate with each other by making cell-to-cell contacts, and fluorescent markers are often used to visualize these contacts. The most commonly used marker for this purpose is green fluorescent protein (GFP). GFP can be divided into two halves that are expressed on different cells. When the cells touch, the two halves come together to form a complete GFP, letting off a fluorescent signal.
“Split GFP is useful for detecting the formation of stable connections between cells,” says lead author of the study Takashi Kanadome. “But because it takes time for the rejoined GFP to emit its signal and the association is irreversible, this approach cannot be used to detect dynamic cell–cell interactions in real-time.”
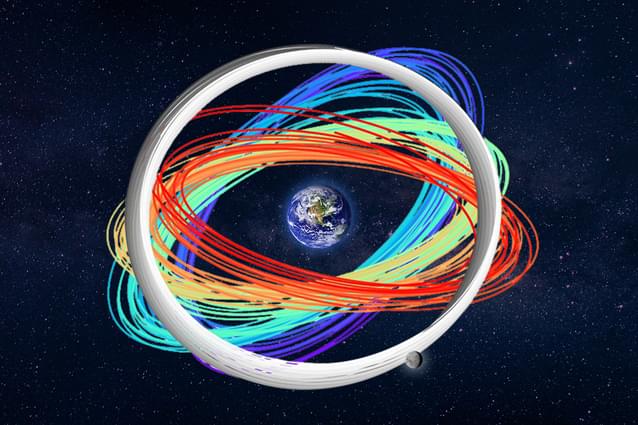

Satellites and spacecraft in the vast region between the earth and moon and just beyond — called cislunar space — are crucial for space exploration, scientific advancement and national security. But figuring out where exactly to put them into a stable orbit can be a huge, computationally expensive challenge.
In an open-access database and with publicly available code, researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have simulated and published one million orbits in cislunar space. The effort, enabled by supercomputing resources at the Laboratory, provides valuable data that can be used to plan missions, predict how small perturbations might change orbits and monitor space traffic.
To begin, the Space Situational Awareness Python package takes in a range of initial conditions for an orbit, like how elliptical and tilted the orbit is and how far it gets from the earth.
A landmark study suggests that this daily habit may reshape the way your mind activates.
Scientists say a real warp drive may no longer be pure science fiction, thanks to new breakthroughs in theoretical physics. Recent studies suggest space itself could be compressed and expanded, allowing faster-than-light travel without breaking known laws of physics. Unlike sci-fi engines, this concept wouldn’t move a ship through space — it would move space around the ship. Researchers are now exploring how energy, gravity, and exotic matter could make this possible. In this video, we explain how a warp drive could work and how close science really is.
Credit:
Star Wars: Episode VIII — The Last Jedi / Lucasfilm https://www.imdb.com/title/tt2527336/.… Trek Beyond / Paramount Pictures https://www.imdb.com/title/tt2660888/.… Lost in Space / New Line Cinema https://www.imdb.com/title/tt0120738/.… Parker Solar Probe touches the Sun: By NASA/Johns Hopkins APL/Ben Smith — https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/14036, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi… Parker Solar Probe: By NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio — Johns Hopkins University/APL/Betsy Congdon, Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory/Yanping Guo, Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory/John Wirzburger, NASA/Nicola Fox, NASA/Kelly Korreck, Johns Hopkins University/APL/Nour Raouafi, NASA/Joseph Westlake, eMITS/Joy Ng, eMITS/Beth Anthony, eMITS/Lacey Young, ADNET Systems, Inc./Aaron E. Lepsch — https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/14741, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi… Parker Solar Probe: By NASA/Johns Hopkins APL/Steve Gribben — http://parkersolarprobe.jhuapl.edu/Mu…, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index… Vertical Testbed Rocket: By NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center — https://www.nasa.gov/armstrong/, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi… […]cket_(AFRC-2017–11349-1_Masten-COBALT-UnTetheredFLT1).webm Interstellar / Paramount Pictures Stargate / Canal+ CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/.… Alcubierre: By AllenMcC., https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index… Miguel alcubierre: By Jpablo.romero, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index… Water wave analogue of Casimir effect: By Denysbondar, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi… Casimir plates: By Emok, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index… CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/.… Proxima Centauri b: By ESO/Konstantino Polizois/Nico Bartmann — http://www.eso.org/public/unitedkingd…, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi… WARP Reactor Concept Movie: By WarpingSpacetime, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi… Ag Micromirrors: By Simpik, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi… Animation is created by Bright Side.
Star Trek Beyond / Paramount Pictures https://www.imdb.com/title/tt2660888/.…
Lost in Space / New Line Cinema https://www.imdb.com/title/tt0120738/.…
Parker Solar Probe touches the Sun: By NASA/Johns Hopkins APL/Ben Smith — https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/14036, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
Parker Solar Probe: By NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio — Johns Hopkins University/APL/Betsy Congdon, Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory/Yanping Guo, Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory/John Wirzburger, NASA/Nicola Fox, NASA/Kelly Korreck, Johns Hopkins University/APL/Nour Raouafi, NASA/Joseph Westlake, eMITS/Joy Ng, eMITS/Beth Anthony, eMITS/Lacey Young, ADNET Systems, Inc./Aaron E. Lepsch — https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/14741, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
Parker Solar Probe: By NASA/Johns Hopkins APL/Steve Gribben — http://parkersolarprobe.jhuapl.edu/Mu…, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index…
Vertical Testbed Rocket: By NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center — https://www.nasa.gov/armstrong/, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi… […]cket_(AFRC-2017–11349-1_Masten-COBALT-UnTetheredFLT1).webm.
Interstellar / Paramount Pictures.
Stargate / Canal+
CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/.…
Alcubierre: By AllenMcC., https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index…
Miguel alcubierre: By Jpablo.romero, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index…
Water wave analogue of Casimir effect: By Denysbondar, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
Casimir plates: By Emok, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index…
CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/.…
Proxima Centauri b: By ESO/Konstantino Polizois/Nico Bartmann — http://www.eso.org/public/unitedkingd…, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
WARP Reactor Concept Movie: By WarpingSpacetime, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
Ag Micromirrors: By Simpik, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
Animation is created by Bright Side.
Are we living inside a computer simulation? The evidence is more compelling than you think.
In this deep exploration of the Simulation Hypothesis, we examine the scientific and philosophical arguments that suggest our reality might be code. From Nick Bostrom’s groundbreaking trilemma to quantum mechanics acting like a computer program, from the fine-tuned constants of physics to Elon Musk’s probabilistic arguments—we follow the evidence wherever it leads. Whether we’re simulated or not, the question reveals profound truths about consciousness, reality, and what it means to be human.
CHAPTERS:
0:00 — The Uncomfortable Question.
4:47 — Nick Bostrom’s Trilemma: The Logical Trap.
9:34 — The Ancestor Simulation Scenario.