The authors of a review conclude that probiotics may improve cognitive function or lessen cognitive decline in adults but not children.


Blockchain Technology on Mars.
Can a Mars economy be established on top of Blockchain Technologies?
In this youtube we’ll review the basic principles of Blockchain Technologies, and how they can be applied on another planet.
Mars is an isolated planet, with travel time of ~ 6 month and communication time of 5 – 20 minutes to Earth. Sometimes, when the Sun is between Earth and Mars communication can’t be established without a relay station, which may slow communication even further.
The initial settlements on Mars will have a small number of people when compared to Earth. So, Mars can’t effort to have a financial and legal system similar to Earth. Those system must be cheaper, faster and more efficient to operate.
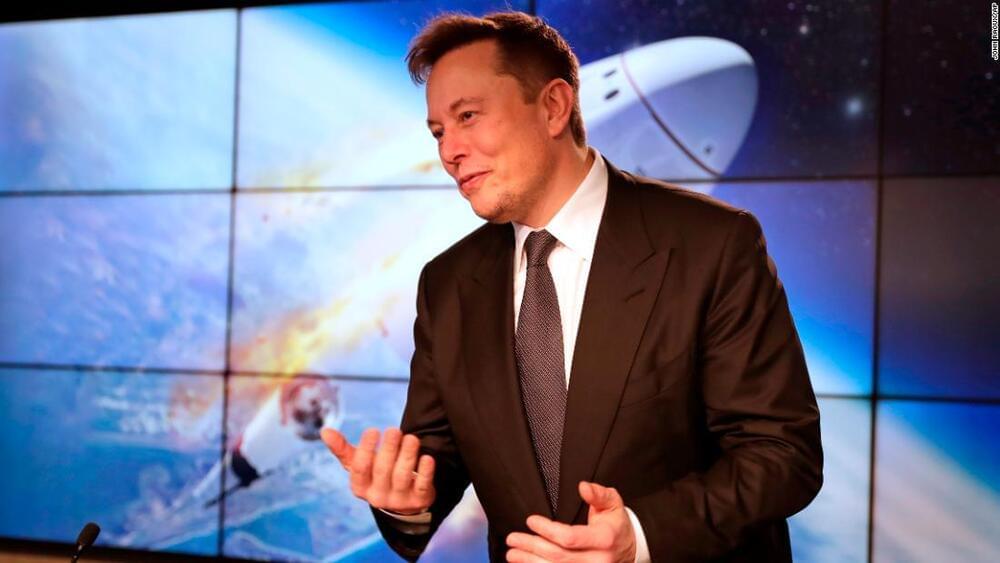



It looks like Elon is putting more of his money into SpaceX. This makes sense as he has tons of money and SpaceX seems to have more growth potential than Tesla because his Starlink and Starship will both be very hard for other companies to compete against. (Just the amount of capital it would take to make competing products is staggering.)
I’m not saying that Tesla won’t be worth $10 trillion one day, I’m just saying SpaceX has more growth potential. Elon seems to agree.
What’s Elon Musk doing with the billions he’s collected in the past two months from selling shares in Tesla?
It seems possible, maybe even likely, that he’s put at least some of the money into SpaceX, the other company of which he is CEO and primary shareholder.
Most of the proceeds from his $16.4 billion in Tesla stock sales since November 8 will go to pay an estimated $11 billion federal tax bill, leaving him with more than $5 billion to do whatever he sees fit.


According to The Atlantic, The New York Times publishes more than 150 articles a day and more than 250 on Sundays. The Wall Street Journal publishes about 240 stories every day. Other websites, like Buzzfeed, publish more than 6,000 stories every month.

