Peter Beck is charting his own course.
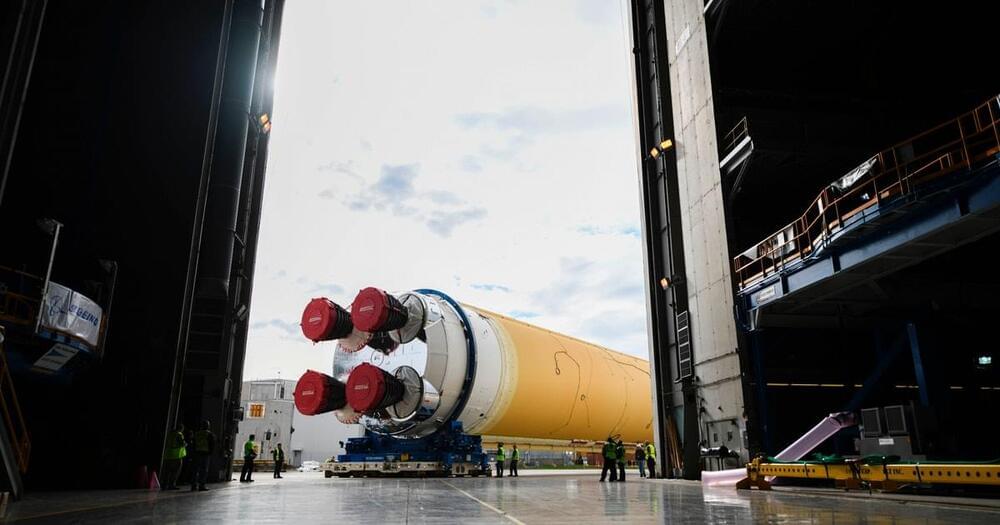
Rocket Lab CEO, Peter Beck, is charting his own course. The company’s lighter-than-ever, curved Neutron rocket ship is heading straight for Venus… one day.
Peter Beck is charting his own course.
Rocket Lab CEO, Peter Beck, is charting his own course. The company’s lighter-than-ever, curved Neutron rocket ship is heading straight for Venus… one day.


The design team was inspired by the orange gantry cranes at the freight terminal.
It’s no surprise that we love architecture and engineering marvels. In the past, we have brought you lists of architectural marvels that seem to defy the laws of science and the most interesting engineering designs around the world.
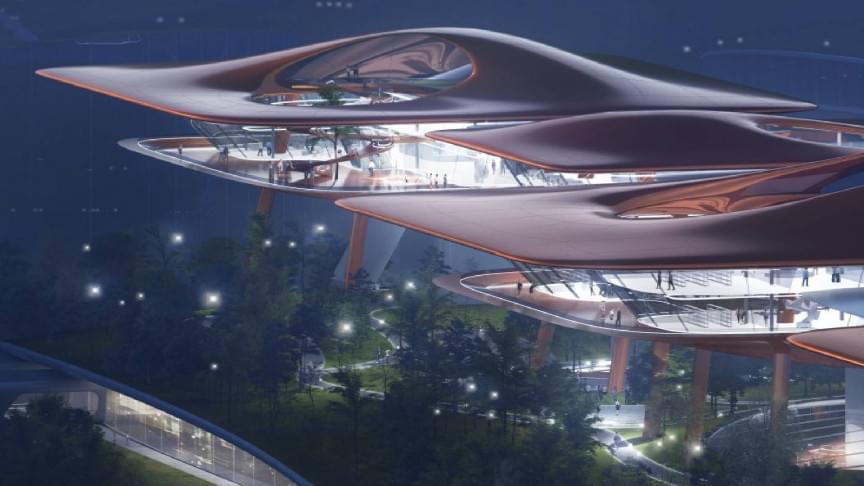
Now, we are bringing you an incredible creation from MAD Architects, led by Ma Yansong, in collaboration with the China Academy of Building Research (CASR). Together these organizations have won an international competition for the design of the Cuntan International Cruise Centre in Chongqing, China and its execution is a sight to behold.
What is this marvel of architecture? It’s a 66,000 216,535 square feet (square meter) cargo terminal located in Chongqing’s Liangjiang New Area within the Cuntan Port area that allows access to the Yangtze River.
Full Story:
The architecture looks like a city that seems to arrive from elsewhere and that could perhaps head somewhere else once again someday.
Artificial intelligence doesn’t hold a candle to the human capacity for harm.
Over the last few years, there has been a lot of talk about the threat of artificial general intelligence (AGI). An AGI is essentially an artificial superintelligence. It is a system that is able to understand — or learn — any intellectual task that a human can. Experts from seemingly every sector of society have spoken out about these kinds of AI systems, depicting them as Terminator-style robots that will run amok and cause massive death and destruction.
Elon Musk, the SpaceX and Tesla CEO, has frequently railed against the creation of AGI and cast such superintelligent systems in apocalyptic terms. At SXSW in 2018, he called digital superintelligences “the single biggest existential crisis that we face and the most pressing one,” and he said these systems will ultimately be more deadly than a nuclear holocaust. The late Stephen Hawking shared these fears, telling the BBC in 2014 that “the development of full artificial intelligence could spell the end of the human race.”
Full Story:
Fears of artificial intelligence run amok make for compelling apocalypse narratives, but the real dangers of artificial intelligence come more from humans than machines.

👽 Many experts, for years, believe that the scientific community no longer has a way to hide it. Life outside the earth exists. 🛸VIDEO 🛸
O’Connell reveals that life is capable of surviving in environments inhospitable to humans. For this reason, he believes that life can be found in a lake of sulfuric acid, inside barrels of nuclear waste, in water superheated to 122 degrees Celsius and even in Antarctica.
Furthermore, he adds that Mars was once an ideal place for life. He believes that the presence of methane in its atmosphere is proof that extraterrestrial life existed there.
Obviously, this brings us closer to the theory that Mars, not only had life, but was able to adapt to survive in the climate caused by some nuclear disaster.
These words are the closest to a situation in which you do not want to mention. Also, what is wanted to be kept hidden: there could be life on Mars as on Earth.
That a recognized scientist ensures that we are at the gates of extraterrestrial contact is something incredible. In addition, he affirms it with a surprising bluntness.
That is why many experts, for years, believe that the scientific community no longer has a way to hide it. Life outside of Earth exists and we are about to contact it.
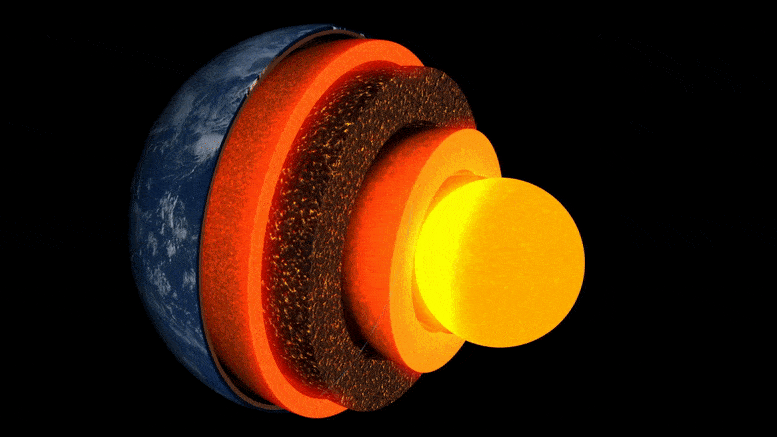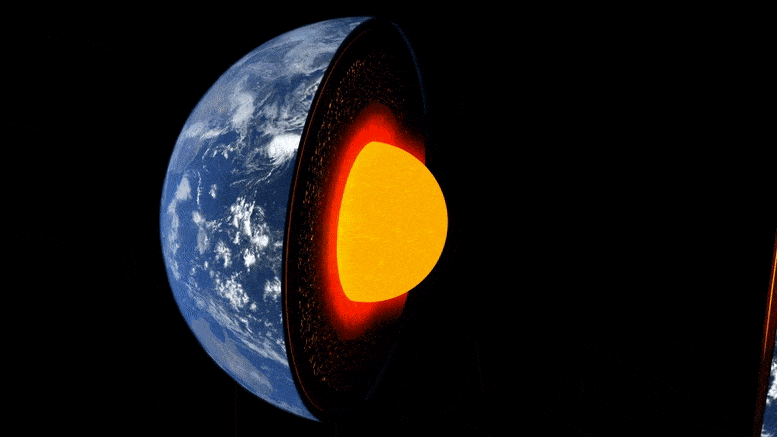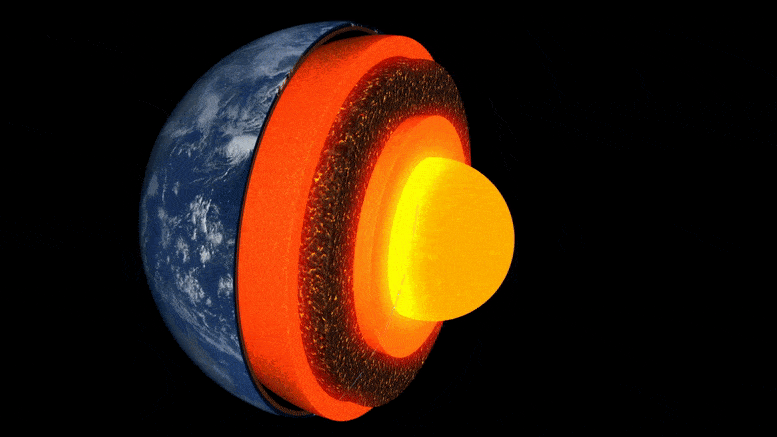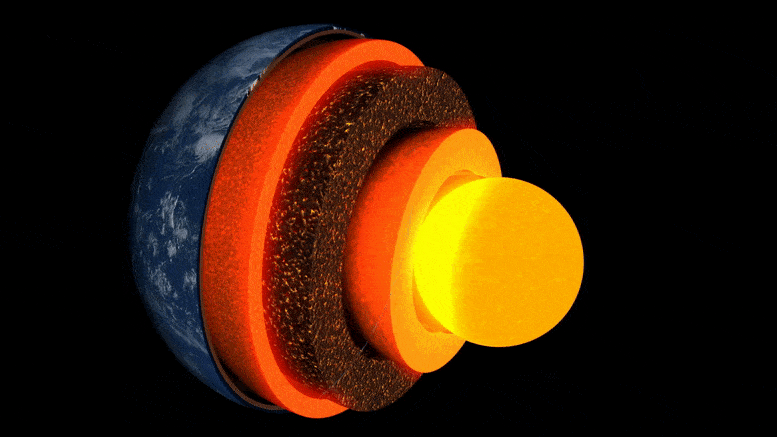
Researchers at ETH Zurich have demonstrated in the lab how well a mineral common at the boundary between the Earth’s core and mantle conducts heat. This leads them to suspect that the Earth’s heat may dissipate sooner than previously thought.
The evolution of our Earth is the story of its cooling: 4.5 billion years ago, extreme temperatures prevailed on the surface of the young Earth, and it was covered by a deep ocean of magma. Over millions of years, the planet’s surface cooled to form a brittle crust. However, the enormous thermal energy emanating from the Earth’s interior set dynamic processes in motion, such as mantle convection, plate tectonics, and volcanism.
Still unanswered, though, are the questions of how fast the Earth cooled and how long it might take for this ongoing cooling to bring the aforementioned heat-driven processes to a halt.
▶ Check out Brilliant with this link to receive a 20% discount! https://brilliant.org/NewMind.
THE SPIRIT OF INNOVATION
On November 16, 2021, an experimental aircraft called the ‘Spirit of Innovation’, designed by Rolls Royce, would record an average speed of just under 556 km/h or 345mph over a 3km span. The Spirit of Innovation is the world’s fastest, all electric aircraft. It superseded the previous record set by the Siemens eAircraft Extra 330 LE Aerobatic aircraft in 2017 by over 213 km/h or 132 mph, and it also climbed over 60 seconds faster to 3,000 meters or about 10,000 ft.
BUILDING THE AIRCRAFT
The Lycoming engine was replaced by three electric motors and the fuel tank by three battery packs. Combined, the battery packs, motors and control equipment were similar in weight to the existing power plant, however this fully electric system was now capable of outputting around 530hp continuously and almost 1000hp in bursts. By comparison, in a conventional aircraft, the overall weight is reduced as the fuel is used up. To compensate for this, the aircraft was converted to a single-seater to reduce weight further, though at the cost of moving the center of gravity slightly forward.
MOTOR
Designing the propulsion unit for the Spirit Of Innovation was also another major hurdle for the ACCEL team. Not only must the electric motor be compact and powerful, but also possess a high degree of reliability and the ability to tolerate failures, for aviation use. Because no single electric motor was commercially available that would meet these requirements, the team decided on a propulsion configuration composed of a stack of 3 YASA 750R axial flux electric motors coupled by a single shaft running through them. Using 3 of these motors in tandem not only met the power requirements of the ACCEL team but it also offered redundancy against motor failure.
While the entire triple motor system weighed just 111kg or about 244lbs, it was capable of generating around 750kw or 1000hp, though continuous total power was limited to around 210kw or about 280hp, due to thermal constraints.
COOLING
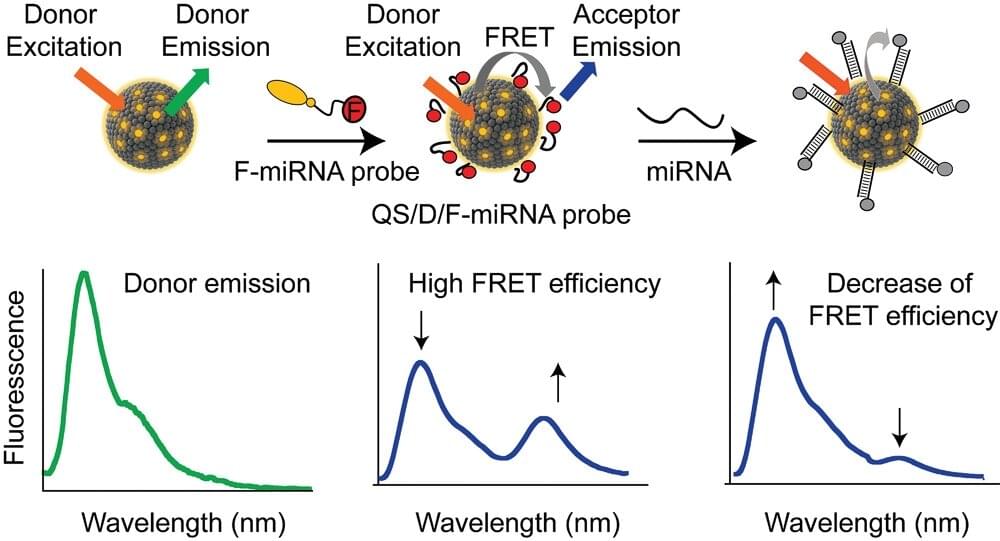
A new work by the Nanomol Group, belonging to the CIBER-BBN network, together with a team from the University of Rome Tor Vergata, presents new nanovesicles capable of crossing biological barriers such as cell membranes, while maintaining their sensing capacity, which makes them attractive probes for intracellular detection of biomarkers.
“The development of probes capable of sensing the biological environment and signaling the presence of a specific target molecule is a challenge with relevance in a variety of biomedical applications, from drug delivery to diagnostic tools,” says Mariana Köber, ICMAB researcher and corresponding author of the study, together with Nora Ventosa, from ICMAB, and Alessandro Porchetta, from the University of Rome Tor Vergata.
This work, which has been published in Advanced Functional Materials, presents the design of fluorescent nanovesicles functionalized with biomimetic DNA capable of translating their binding to a target molecule into an optical output, through a change in Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and fluorescent emission.
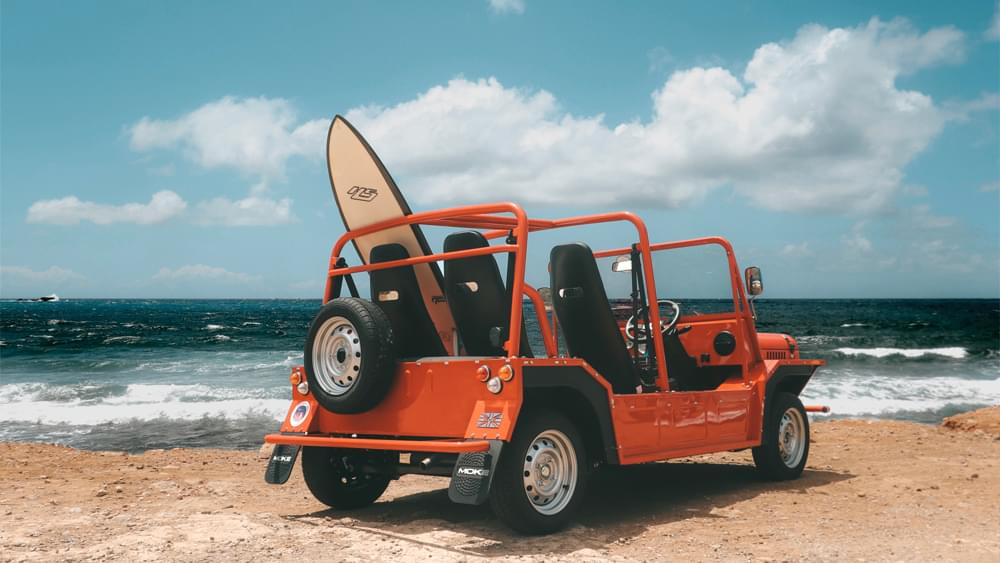

Moke International makes the car in Britain before final assembly in France. The revised chassis has been re-engineered to accommodate four passengers, and look for an all-electric version to be released in the summer. Priced from around $30,000, the Moke can be customized with a choice of 13 colors, including eye-popping Flamingo Pink and Florida Orange. My tester also wears gleaming chrome trim and badging on the hood.
Other stylistic touches include leather hood straps and a retro radio, which is actually able to be heard above the wind noise, at least at speeds below 45 mph. And on a wet day, with weather equipment in place, the windscreen can be heated for improved visibility. In all, this upgraded version is not far off from Sir Alec’s initial car—basic in the extreme and as quintessentially British as fish and chips or a warm pint of beer.

Accordingly, it is reportedly telling customers how to bypass its “genuine” ink bullshit. (translation)
We value you as a customer and a constant user of Canon products. Due to the persistent global shortage of semiconductor components, Canon is currently facing challenges in sourcing certain electronic components that are used in our consumables for our multifunction printers (MFP). These components lead e.g. B. Features such as the detection of the remaining toner level. In order to ensure a continuous and reliable supply of consumables, we have decided to deliver consumables without semiconductor components until normal supply is restored. There is no negative impact on print quality when using consumables without electronic components, but certain additional functions, such as e. B. the detection of the toner level may be impaired.
The instructions appear to be straightforward—for the models I checked all you have to do is ignore onerous error messages—so it seems incorrect to claim Canon blocks the use of third-party cartridges. HP’s ink DRM is clearly more despised —they not only block non-DRM ink, but the ink is region locked and they expect you to pay for and maintain a subscription to it.