STARFORGE, an initiative dedicated to modeling early star formation, has released stunning supercomputer simulations of young protostars.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Yeah, scientists just went there and came up with a faster way to create artificial DNA
DNA was personified in Jurassic Park, where the animated double helix that called himself Mr. DNA took you and a group of skeptical scientists through the oversimplified (and obviously fictional) steps to creating dino DNA — but there is some reality in this.
For all you dinosaur enthusiasts out there, synthesizing DNA can’t bring T.Rex and Brachiosaurus back from extinction. Though creating genes in a lab sounds like the original eureka moment of Jurassic Park, synthesizing human DNA has done everything from genetic sequencing and editing to detecting diseases like the current plague we are living through. There is just one step that has always been problematic.
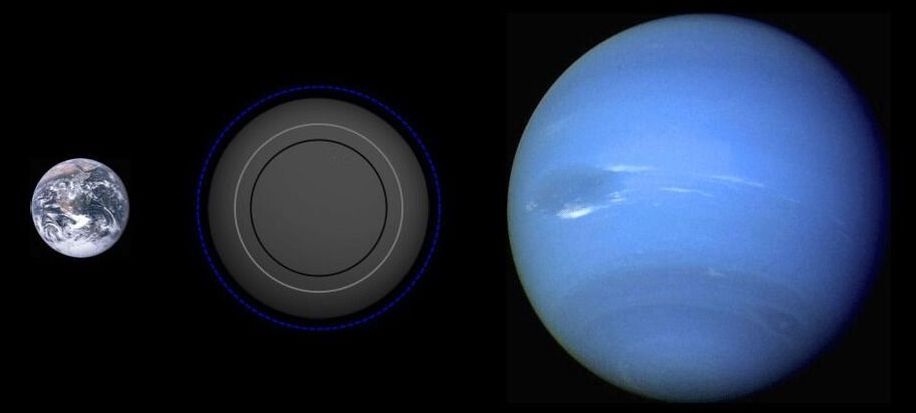
Larger Rocky Planets Might be Rare Because They Shrunk
Researchers at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Astrophysics published a paper last week that just might explain a mysterious gap in planet sizes beyond our solar system. Planets between 1.5 and 2 times Earth’s radius are strikingly rare. This new research suggests that the reason might be because planets slightly larger than this, called mini-Neptunes, lose their atmospheres over time, shrinking to become ‘super-Earths’ only slightly larger than our home planet. These changing planets only briefly have a radius the right size to fill the gap, quickly shrinking beyond it. The implication for planetary science is exciting, as it affirms that planets are not static objects, but evolving and dynamic worlds.
Exoplanet research is a very young field. As recently as 1992, no one had ever seen a planet beyond our solar system. Today, we’ve discovered more than 4700 of them, and that number is growing rapidly due to the efforts of dedicated planet-hunting space telescopes like Kepler (now defunct) and its successor, TESS. We’ve suddenly gained an enormous new sample size of planets to study, beyond the eight planets (sorry Pluto) that orbit around our sun.
Kepler, TESS, and other planet hunters have discovered brand new types of planets, like so-called ‘hot-Jupiters,’ large gas giants that orbit very close to their star. These were among the first exoplanets observed because their large size made them easy to find, and their small, fast orbital periods meant we could see them pass in front of their star more than once in a short period of time (some hot-Jupiters have a year that lasts only a few Earth days).

Scientists Just Made A Quantum Computing Breakthrough!!
Keep watching to look at three of the most fantastic quantum breakthroughs that bring liberation and freedom to the world of science today! Subscribe to Futurity for more videos.
#quantum #quantumcomputing #google.
As we advance as a species, there are a lot of things that once seemed impossible a century ago that are now a reality. It’s called evolving. For example, there was a time when most people believed the earth was flat. Then Eratosthenes came onto the scene and proved that the world is round.
At the time, it was groundbreaking. But today, quantum mechanics rules the roost. This school of physics deals with the physical realm on the scale of atoms and electrons; thus making many of the equations in classical mechanics useless. With that being said, let’s take a look at three of the most amazing quantum breakthroughs that are bringing liberation and freedom to the world of science today!
We kick things off with a team of Chinese scientists claiming to have constructed a quantum computer that has the ability to perform certain computations almost 100 trillion times faster than the world’s most advanced supercomputer.
The breakthrough sheds light on quantum computational advantage—which is also famously known as quantum supremacy. But it’s become a hotly-contested tech race between Chinese researchers and some of the largest US tech corporations such as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft.
Robotic ‘Third Eye’ Lets You Walk Safely While Looking At Your Phone
It may not look nice, but maybe it can help prevent accidents. 😃
It’s generally good to watch where you’re going while out walking around, but if you’re someone who just can’t resist a glance at your phone – or a full scrolling session – then this industrial design student’s third eye is for you.
Created as part of his Innovation Design Engineering degree at London’s Royal College of Art and Imperial College, student Minwook Paeng came up with the impressive piece of tech to help out all the ‘phono-sapiens’ out there.
With so much of our lives now wrapped up in our phones, Paeng’s ‘third eye’ offers a solution to issues that can present themselves as we walk around with our heads down, taking in everything on the screen.
Dr. Missy Cummings, Ph.D — Professor, Duke University — Director, Humans and Autonomy Laboratory
Engineering A Safer World For Humans With Self Driving Cars, Drones, and Robots — Dr. Missy Cummings PhD, Professor, Duke University, Director, Humans and Autonomy Laboratory, Duke Engineering.
Dr. Mary “Missy” Cummings, is a Professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, at the Pratt School of Engineering, at Duke University, the Duke Institute of Brain Sciences, and is the Director of the Humans and Autonomy Laboratory and Duke Robotics.
Dr. Cummings received her B.S. in Mathematics from the US Naval Academy in 1988, her M.S. in Space Systems Engineering from the Naval Postgraduate School in 1994, and her Ph.D. in Systems Engineering from the University of Virginia in 2004.
Dr… Cummings was one of the Navy’s first female fighter pilots earning the rank of lieutenant and serving as naval officer and military pilot from 1988–1999.
Dr. Cummings research interests include human-unmanned vehicle interaction, human-autonomous system collaboration, human-systems engineering, public policy implications of unmanned vehicles, and the ethical and social impact of technology.

Study reveals new details on what happened in the first microsecond of Big Bang
Researchers from University of Copenhagen have investigated what happened to a specific kind of plasma—the first matter ever to be present—during the first microsecond of Big Bang. Their findings provide a piece of the puzzle to the evolution of the universe, as we know it today.
About 14 billion years ago, our universe changed from being a lot hotter and denser to expanding radically—a process that scientists have named the Big Bang.
And even though we know that this fast expansion created particles, atoms, stars, galaxies and life as we know it today, the details of how it all happened are still unknown.
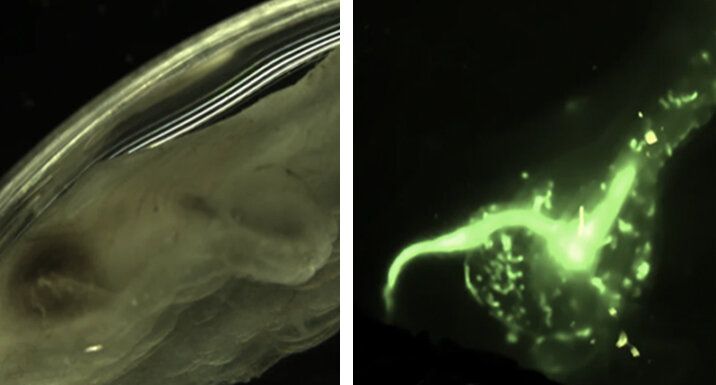
A new method to better study microscopic plastics in the ocean
If you’ve been to your local beach, you may have noticed the wind tossing around litter such as an empty potato chip bag or a plastic straw. These plastics often make their way into the ocean, affecting not only marine life and the environment but also threatening food safety and human health.
Eventually, many of these plastics break down into microscopic sizes, making it hard for scientists to quantify and measure them. Researchers call these incredibly small fragments nanoplastics and microplastics because they are not visible to the naked eye. Now, in a multiorganizational effort led by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre (JRC), researchers are turning to a lower part of the food chain to solve this problem.
The researchers have developed a novel method that uses a filter-feeding marine species to collect these tiny plastics from ocean water. The team published its findings as a proof-of-principle study in the scientific journal Microplastics and Nanoplastics.