Giant bacteria, Ca. Thiomargarita magnifica, have been found in Guadeloupe. They have organelles, DNA and measure one centimeter long.




A small trial of a new cancer drug has reportedly provided a result never before seen — the total remission of cancer in all of its participants.
According to a report in the New England Journal of Medicine, a dozen rectal cancer patients saw their tumors disappear completely after they received an experimental drug called dostarlimab.
“I believe this is the first time this has happened in the history of cancer,” Dr. Luis Alberto Diaz Jr., one of the trial leaders and a medical oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) Cancer Center, told The New York Times.

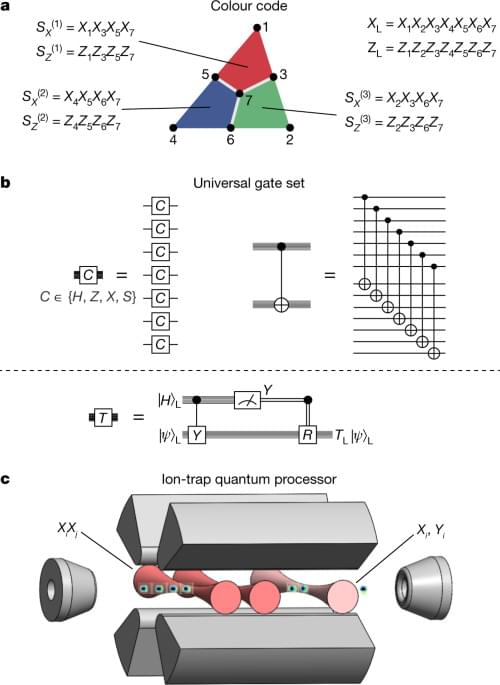


Summary: Findings reveal the molecular mechanism for acetylcholine in learning and memory.
Source: Fujita Health University.
Patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) have lower levels of the neuromodulator acetylcholine (ACh) in their brains. Donepezil, an AD drug, increases brain ACh levels and improves AD-associated learning deficits.
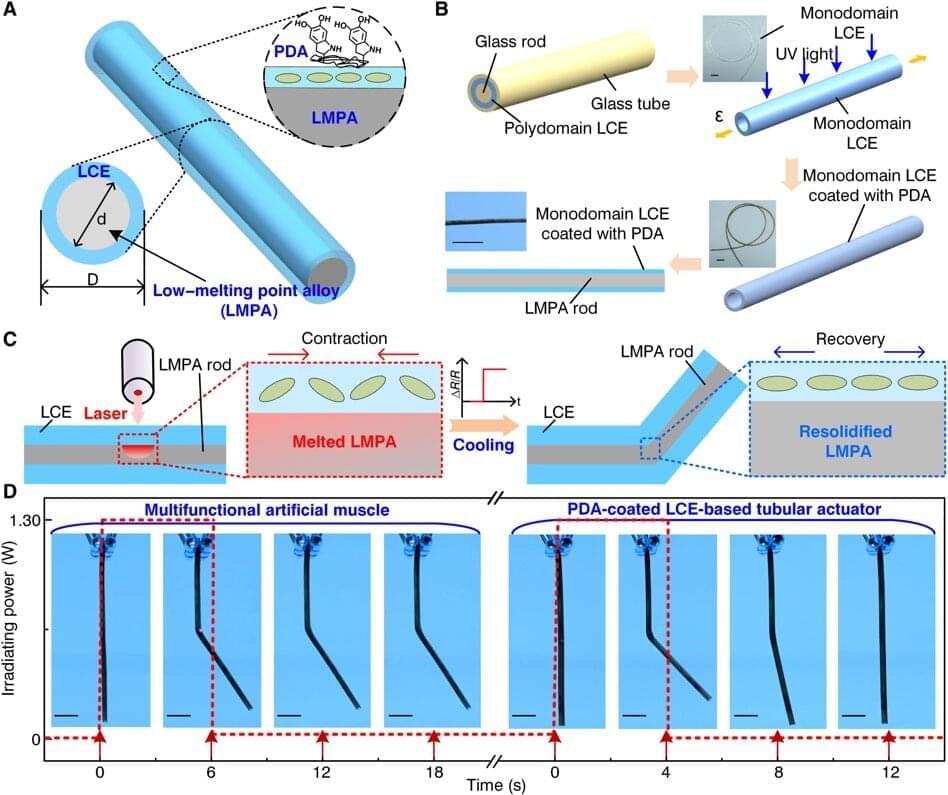
Materials scientists and bioengineers at the intersection of regenerative medicine and bioinspired materials seek to develop shape-programmable artificial muscles with self-sensing capabilities for applications in medicine. In a new report now published in Science Advances, Haoran Liu and a team of researchers in systems and communications engineering at the Frontier Institute of Science and Technology, Jiaotong University, China, were inspired by the coupled behavior of muscles, bones, and nerve systems of mammals and other living organisms to create a multifunctional artificial muscle in the lab. The construct contained polydopamine-coated liquid crystal elastomer (LCE) and low-melting point alloys (LMPA) in a concentric tube or rod. While the team adopted the outer liquid crystal-elastomer to mimic reversible contraction and recovery, they implemented the inner low-melting point alloy for deformation locking and to detect resistance mechanics, much like bone and nerve functions, respectively. The artificial muscle demonstrated a range of performances, including regulated bending and deformation to support heavy objects, and is a direct and effective approach to the design of biomimetic soft devices.
Soft robotics inspired by the skeleton–muscle–nerve system
Scientists aim to implement biocompatibility between soft robotic elements and human beings for assisted movement and high load-bearing capacity; however, such efforts are challenging. Most traditional robots are still in use in industrial, agricultural and aerospace settings for high-precision sensor-based, load-bearing applications. Several functional soft robots contrastingly depend on materials to improve the security of human-machine interactions. Soft robots are therefore complementary to hard robots and have tremendous potential for applications. Biomimetic constructs have also provided alternative inspiration to emulate the skeleton-muscle-nerve system to facilitate agile movement and quick reaction or thinking, with a unique body shape to fit tasks and perform diverse physiological functions. In this work, Liu et al were inspired by the fascinating idea of biomimicry to develop multifunctional artificial muscles for smart applications.
When something goes wrong in mitochondria, the tiny organelles that power cells, it can cause a bewildering variety of symptoms such as poor growth, fatigue and weakness, seizures, developmental and cognitive disabilities, and vision problems. The culprit could be a defect in any of the 1,300 or so proteins that make up mitochondria, but scientists have very little idea what many of those proteins do, making it difficult to identify the faulty protein and treat the condition.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the University of Wisconsin–Madison systematically analyzed dozens of mitochondrial proteins of unknown function and suggested functions for many of them. Using these data as a starting point, they identified the genetic causes of three mitochondrial diseases and proposed another 20 possibilities for further investigation. The findings, published May 25 in Nature, indicate that understanding how mitochondria’s hundreds of proteins work together to generate power and perform the organelles’ other functions could be a promising path to finding better ways to diagnose and treat such conditions.
“We have a parts list for mitochondria, but we don’t know what many of the parts do,” said co-senior author David J. Pagliarini, Ph.D., the Hugo F. and Ina C. Urbauer Professor and a BJC Investigator at Washington University. “It’s similar to if you had a problem with your car, and you brought it to a mechanic, and upon opening the hood they said, ‘We’ve never seen half of these parts before.’ They wouldn’t know how to fix it. This study is an attempt to define the functions of as many of those mitochondrial parts as we can so we have a better understanding of what happens when they don’t work and, ultimately, a better chance at devising therapeutics to rectify those problems.”