
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

AI on a photonic chip conducts image recognition at the speed of light
For the first time, researchers implemented a type of AI called a deep neural network into a photonic (light-based) device. In doing so, they’ve come closer to making a machine that processes what it “sees” like humans do, very quickly and efficiently.
For instance, the photonic deep neural network can classify a single image in less than 570 picoseconds, or nearly 2 billion images per second. To put things into perspective, the frame rate for fluid footage sits between 23 and 120 frames per second.
“Direct, clock-less processing of optical data eliminates analog-to-digital conversion and the requirement for a large memory module, allowing faster and more energy-efficient neural networks for the next generations of deep learning systems,” wrote the authors from the University of Pennsylvania.

Meteorite that landed in Cotswolds may solve mystery of Earth’s water
Water covers three-quarters of the Earth’s surface and was crucial for the emergence of life, but its origins have remained a subject of active debate among scientists.
Now, a 4.6bn-year-old rock that crashed on to a driveway in Gloucestershire last year has provided some of the most compelling evidence to date that water arrived on Earth from asteroids in the outer solar system.

Copyright and Artificial Intelligence: An Exceptional Tale
As the US government begins to consider some of the legal implications for copyright in connection with the development and deployment of artificial intelligence, it is important to first step back to ensure that we are properly guided by context and a proper understanding of our goals — grounded in an informed grasp of the relationship of copyright to the development of AI, and a fair observation of the state of legal developments around the world. Far too many observers have oversimplified how various countries have addressed the relationship between copyright and AI. The reality is that all who have done so have rejected the notion that copyright is not implicated, and have developed legal norms which carefully limit the scope of any exceptions with an eye towards facilitating licensing, even when they seek to expand the development of AI as a national economic imperative.
I have written about the approach taken by the EU in the updated Copyright Directive, and note here that despite claims about Japan’s legislation, even their provisions — as manifested in the 2018 amendments, are designed to avoid conflict with the legitimate interests of copyright owners. While I don’t necessarily agree with Japan’s approach, it is important to highlight that even its exceptions, as I understand them: recognize that text and data mining/machine learning does in fact implicate copyright; apply only to materials that have been lawfully acquired; require that the use of each work is “minor” relative to the TDM effort; and provide that license terms must be honored. While it remains unclear to me that Japan’s goal of respecting copyright as required by international law has been achieved, it is important to understand that claims that Japan has removed copyright as an issue that must be addressed in the development of AI are inaccurate.

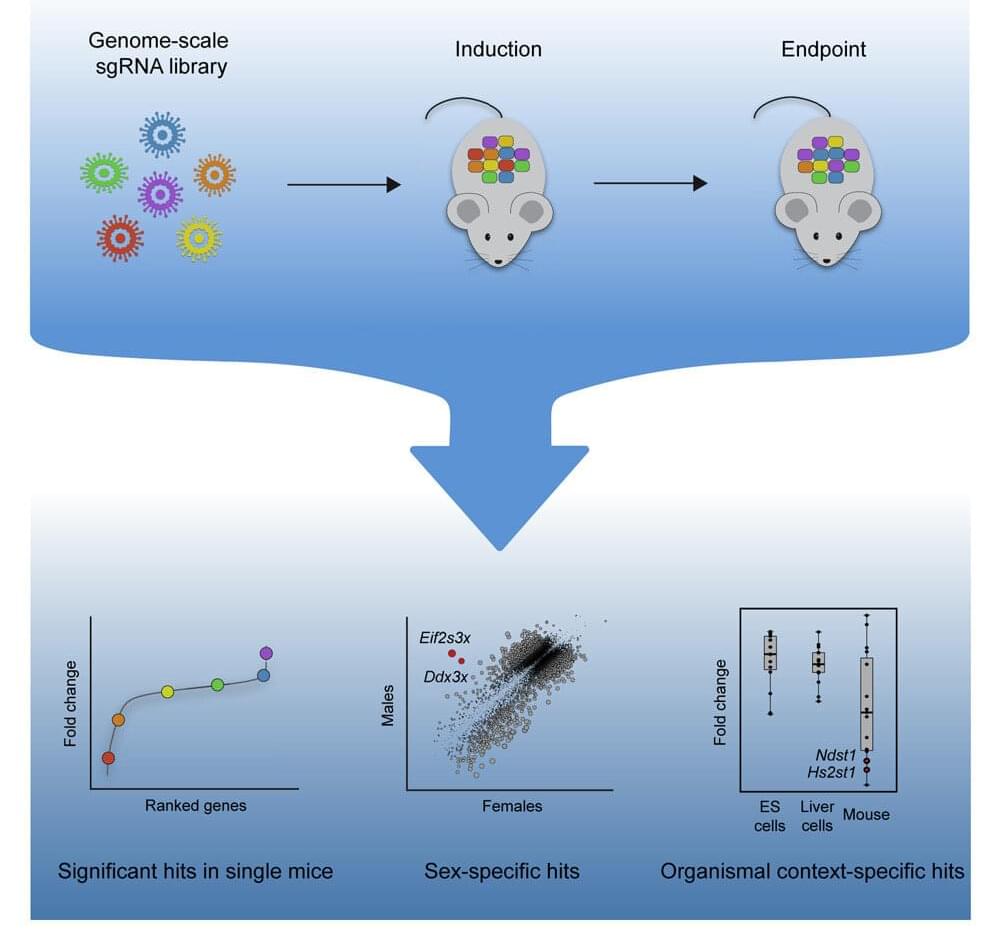
New technique for studying liver cells within an organism could shed light on the genes required for regeneration
The liver’s ability to regenerate itself is legendary. Even if more than 70% of the organ is removed, the remaining tissue can regrow an entire new liver.
Kristin Knouse, an MIT assistant professor of biology, wants to find out how the liver is able to achieve this kind of regeneration, in hopes of learning how to induce other organs to do the same thing. To that end, her lab has developed a new way to perform genome-wide studies of the liver in mice, using the gene-editing system CRISPR.
With this new technique, researchers can study how each of the genes in the mouse genome affects a particular disease or behavior. In a paper describing the technique, the researchers uncovered several genes important for liver cell survival and proliferation that had not been seen before in studies of cells grown in a lab dish.
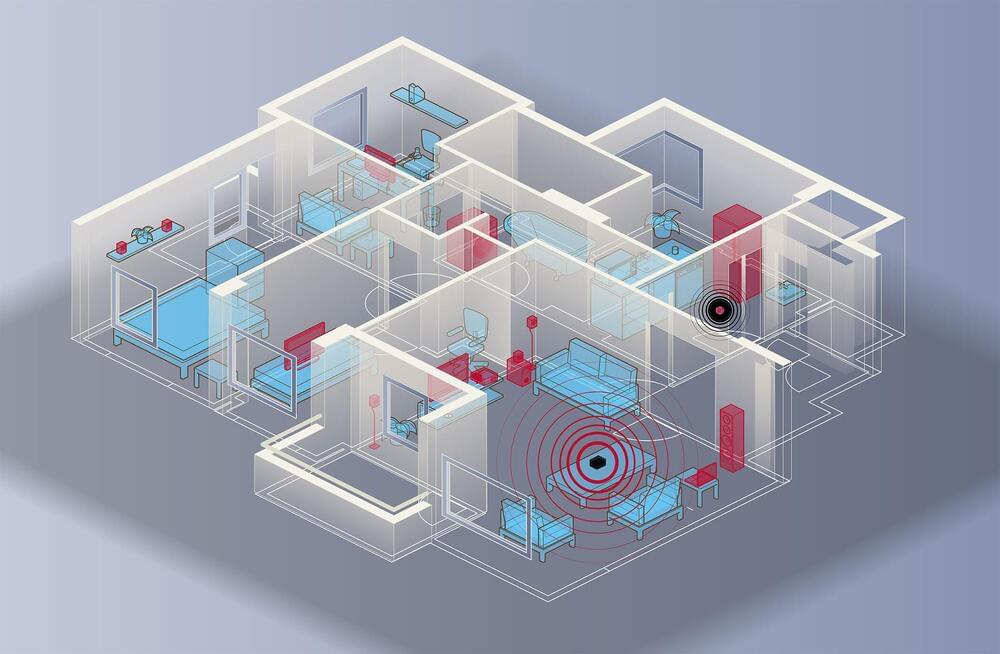
Smart home hubs leave users vulnerable to hackers
Machine learning programs mean even encrypted information can give cybercriminals insight into your daily habits.
Smart technology claims to make our lives easier. You can turn on your lights, lock your front door remotely and even adjust your thermostat with the click of a button.
But new research from the University of Georgia suggests that convenience potentially comes at a cost—your personal security.
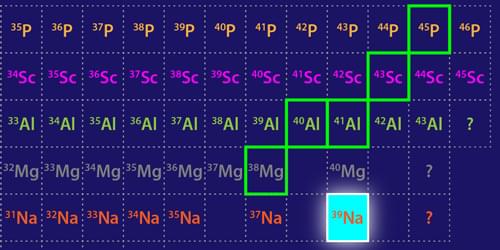
Probing the Limits of Nuclear Existence
Researchers have discovered the heaviest-known bound isotope of sodium and characterized other neutron-rich isotopes, offering important benchmarks for refining nuclear models.
The neutron dripline marks a boundary of nuclear existence—indicating isotopes of a given element with a maximum number of neutrons. Adding a neutron to a dripline isotope will cause the isotope to become unbound and release one or more of its neutrons. Mapping the dripline is a major goal of modern nuclear physics, as this boundary is a testing ground for nuclear models and has implications for our understanding of neutron stars and of the synthesis of elements in stellar explosions. Now studies by two groups extend our knowledge of the properties of nuclei close to the dripline [1, 2]. Working at the Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory (RIBF) in Japan, Deuk Soon Ahn of RIKEN and colleagues have discovered sodium-39 (39 Na), which likely marks the dripline location for the heaviest element to date (Fig. 1) [1].