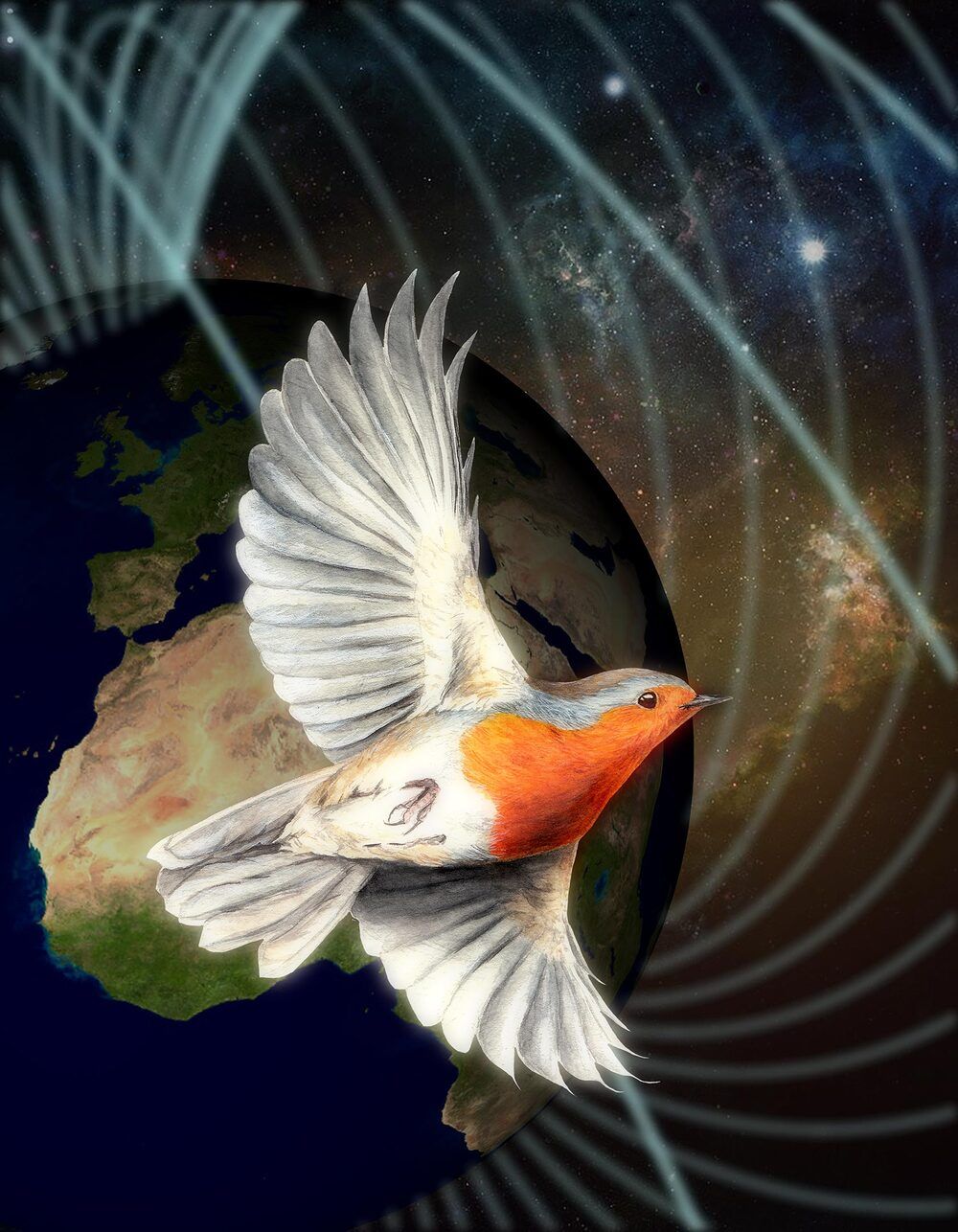
Humans perceive the world around them with five senses — vision, hearing, taste, smell and touch. Many other animals are also able to sense the Earth’s magnetic field. For some time, a collaboration of biologists, chemists and physicists centred at the Universities of Oldenburg (Germany) and Oxford (UK) have been gathering evidence suggesting that the magnetic sense of migratory birds such as European robins is based on a specific light-sensitive protein in the eye. In the current edition of the journal Nature, this team demonstrate that the protein cryptochrome 4, found in birds’ retinas, is sensitive to magnetic fields and could well be the long-sought magnetic sensor.
First author Jingjing Xu, a doctoral student in Henrik Mouritsen’s research group in Oldenburg, took a decisive step toward this success. After extracting the genetic code for the potentially magnetically sensitive cryptochrome 4 in night-migratory European robins, she was able, for the first time, to produce this photoactive molecule in large quantities using bacterial cell cultures. Christiane Timmel’s and Stuart Mackenzie’s groups in Oxford then used a wide range of magnetic resonance and novel optical spectroscopy techniques to study the protein and demonstrate its pronounced sensitivity to magnetic fields.
The team also deciphered the mechanism by which this sensitivity arises — another important advance. “Electrons that can move within the molecule after blue-light activation play a crucial role,” explains Mouritsen. Proteins like cryptochrome consist of chains of amino acids: robin cryptochrome 4 has 527 of them. Oxford’s Peter Hore and Oldenburg physicist Ilia Solov’yov performed quantum mechanical calculations supporting the idea that four of the 527 — known as tryptophans — are essential for the magnetic properties of the molecule. According to their calculations, electrons hop from one tryptophan to the next generating so-called radical pairs which are magnetically sensitive. To prove this experimentally, the team from Oldenburg produced slightly modified versions of the robin cryptochrome, in which each of the tryptophans in turn was replaced by a different amino acid to block the movement of electrons.